Abstract
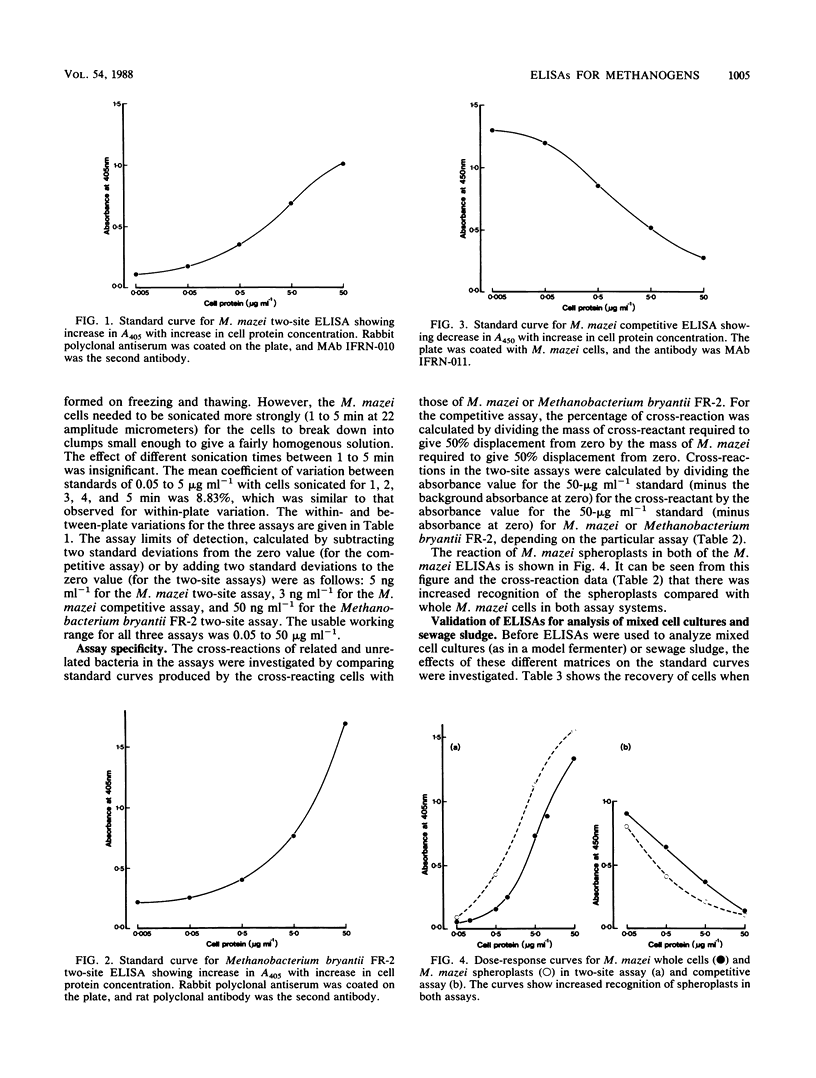
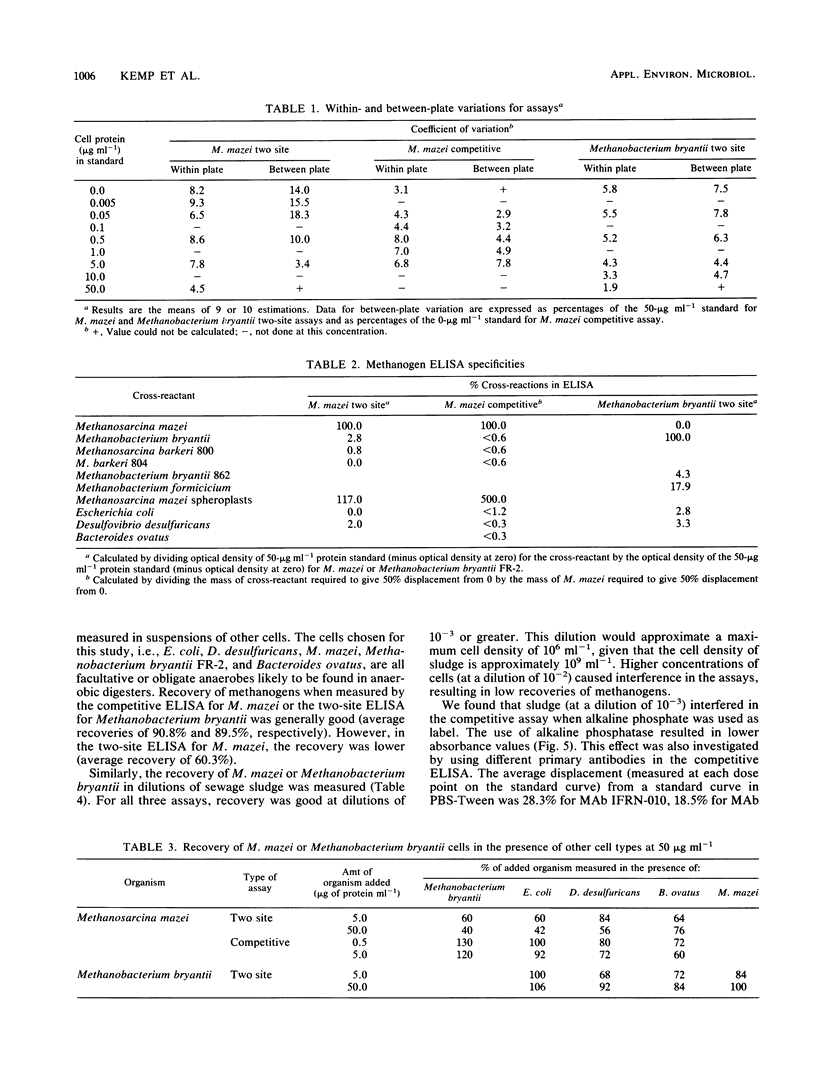
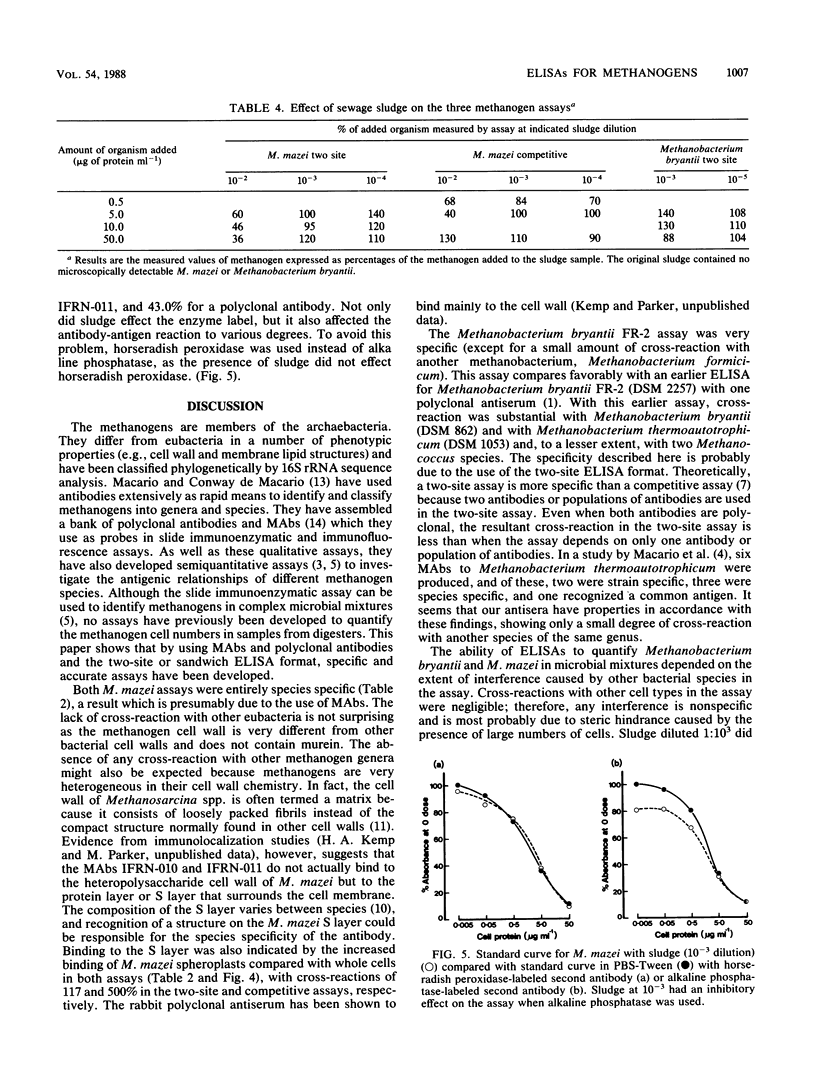
Three microtitration plate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) have been developed: a competitive ELISA and a two-site (or indirect sandwich) ELISA for Methanosarcina mazei S6 and a two-site ELISA for Methanobacterium bryantii FR-2. The assays were sensitive, with limits of cell protein detection of 3 ng ml−1, 5 ng ml−1, and 50 ng ml−1, respectively, and showed good precision. The M. mazei assays used monoclonal antibodies and were entirely species specific, showing no cross-reaction with methanogens of other genera or with other species of the same genus. The Methanobacterium bryantii assay, which used two polyclonal antisera, showed only a slight cross-reaction with one other Methanobacterium species but no cross-reaction with methanogens of other genera. The use of the ELISAs for quantitative analysis of mixed cultures and of sewage sludge samples was investigated. Sludge diluted at 1:103 or more caused no significant interference in any of the three ELISAs. Various cultures of bacteria, methanogens, and nonmethanogens at a protein concentration of 50 μg ml−1 showed no significant interference in the M. mazei competitive assay and the Methanobacterium bryantii two-site assay, although they did cause falsely low results in the M. mazei two-site assay.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer D. B. Detection and quantitation of methanogens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):797–801. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.797-801.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Biggerstaff M., Greenall C., Kemeny D. M. ELISA detection of human IgG subclass antibodies to Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 27;87(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90348-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway de Macario E., Macario A. J., Jovell R. J. Slide immunoenzymatic assay (SIA) in hybridoma technology. Methods Enzymol. 1986;121:509–525. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)21051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway de Macario E., Macario A. J., Magariños M. C., König H., Kandler O. Dissecting the antigenic mosaic of the Archaebacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum by monoclonal antibodies of defined molecular specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6346–6350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway de Macario E., Macario A. J., Wolin M. J. Specific antisera and immunological procedures for characterization of methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):320–328. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.320-328.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz R. F., Sebacher D. I., White D. C. Biomass measurement of methane forming bacteria in environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods. 1983;1:53–61. doi: 10.1016/0167-7012(83)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


