Abstract
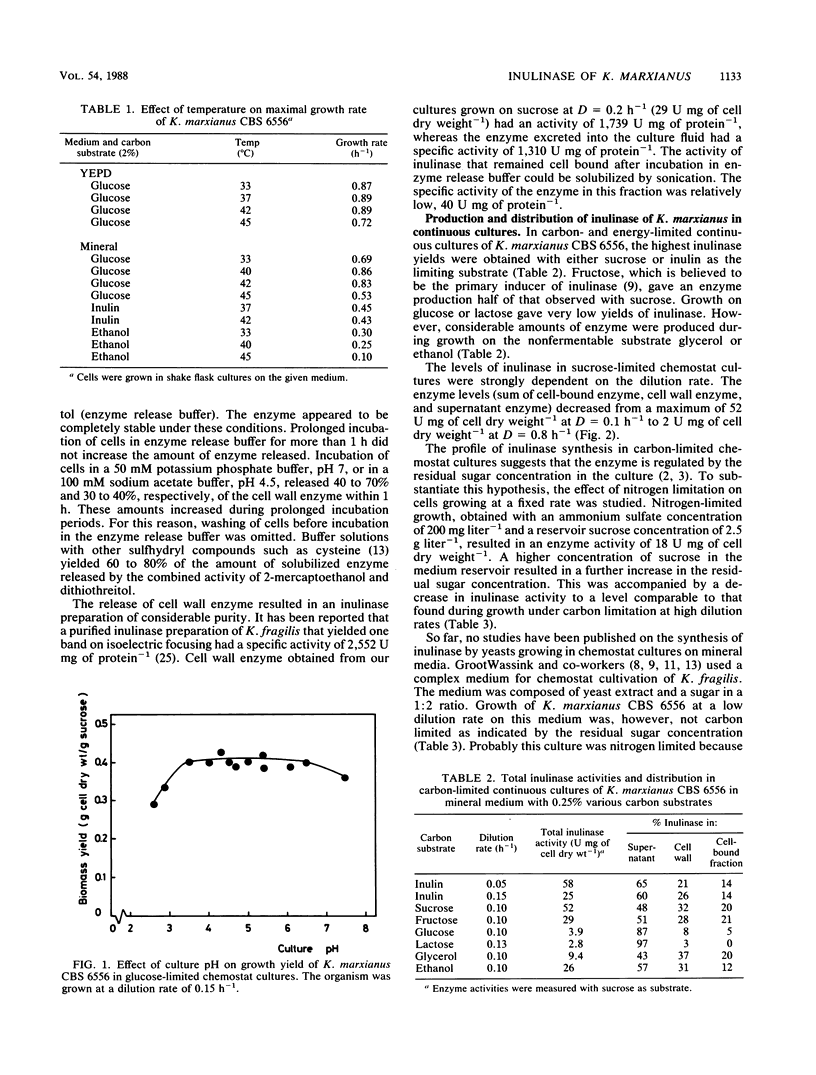
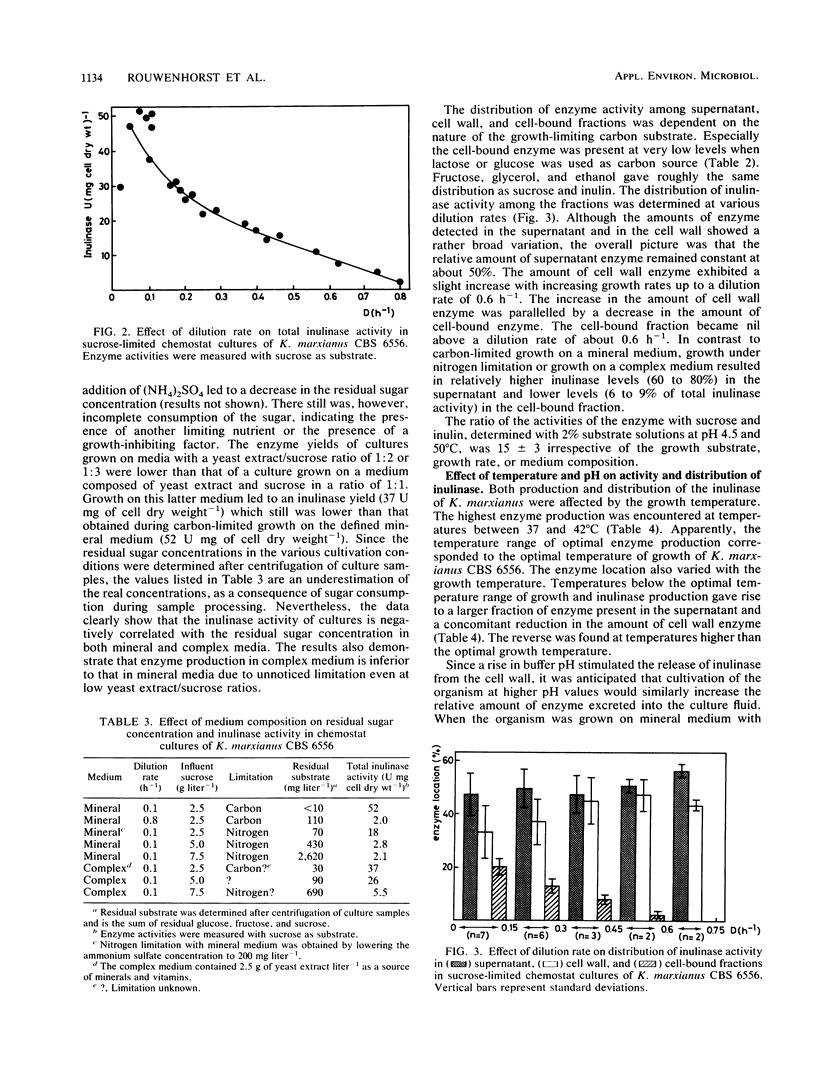
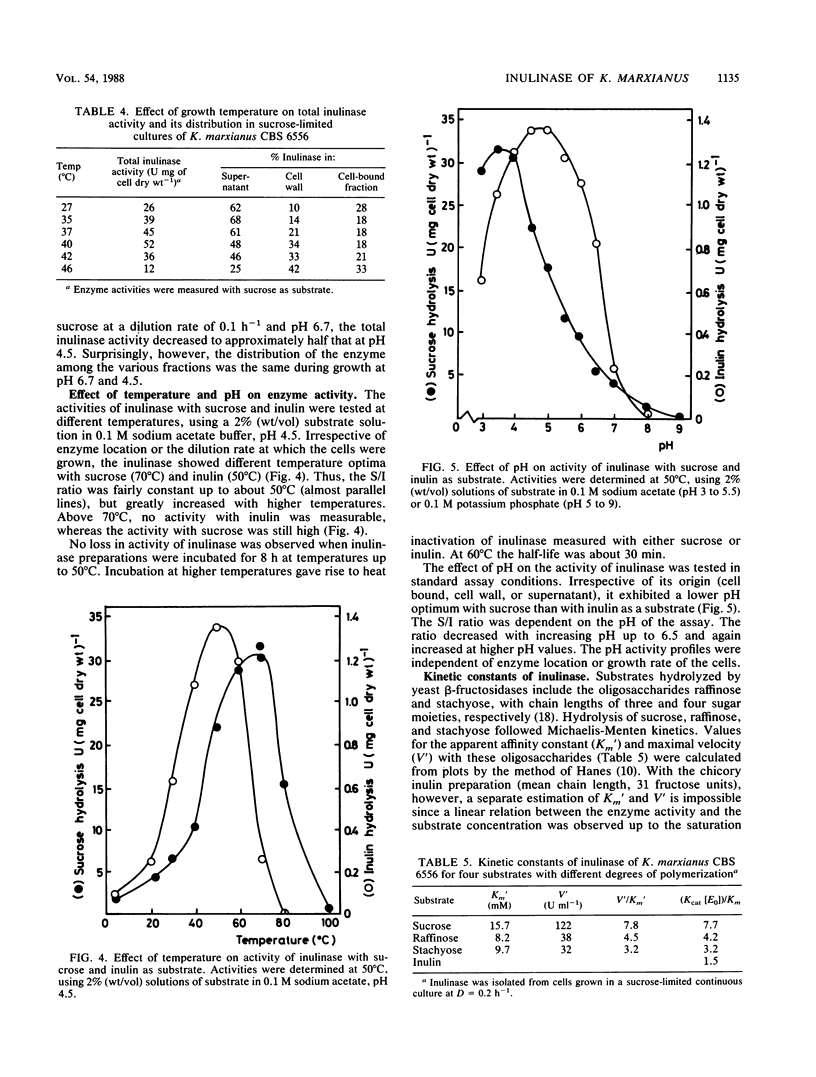
From a screening of several Kluyveromyces strains, the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS 6556 was selected for a study of the parameters relevant to the commercial production of inulinase (EC 3.2.1.7). This yeast exhibited superior properties with respect to growth at elevated temperatures (40 to 45°C), substrate specificity, and inulinase production. In sucrose-limited chemostat cultures growing on mineral medium, the amount of enzyme decreased from 52 U mg of cell dry weight−1 at D = 0.1 h−1 to 2 U mg of cell dry weight−1 at D = 0.8 h−1. Experiments with nitrogen-limited cultures further confirmed that synthesis of the enzyme is negatively controlled by the residual sugar concentration in the culture. High enzyme activities were observed during growth on nonsugar substrates, indicating that synthesis of the enzyme is a result of a derepression/repression mechanism. A substantial part of the inulinase produced by K. marxianus was associated with the cell wall. The enzyme could be released from the cell wall via a simple chemical treatment of cells. Results are presented on the effect of cultivation conditions on the distribution of the enzyme. Inulinase was active with sucrose, raffinose, stachyose, and inulin as substrates and exhibited an S/I ratio (relative activities with sucrose and inulin) of 15 under standard assay conditions. The enzyme activity decreased with increasing chain length of the substrate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beluche I., Guiraud J. P., Galzy P. Inulinase activity of Debaromyces cantarellii. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1980;25(1):32–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02876395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Villanueva J. R., Sentandreu R. The mechanism of catabolite inhibition of invertase by glucose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon P. C., Esmon B. E., Schauer I. E., Taylor A., Schekman R. Structure, assembly, and secretion of octameric invertase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4387–4394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A., de Bruijn J. M., Niedeveld C. J. Bacteria and yeasts as possible candidates for the production of inulinases and levanases. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1985;51(3):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF02439942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes C. S. Studies on plant amylases: The effect of starch concentration upon the velocity of hydrolysis by the amylase of germinated barley. Biochem J. 1932;26(5):1406–1421. doi: 10.1042/bj0261406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidby D. K., Davies R. Thiol induced release of invertase from cell walls of Saccharomyces fragilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 24;201(2):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mormeneo S., Sentandreu R. Molecular events associated with glucose repression of invertase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1986;52(1):15–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00402683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER H. E., PHAFF H. J. The pattern of action of inulinase from Saccharomyces fragilis on inulin. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2438–2441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tammi M., Ballou L., Taylor A., Ballou C. E. Effect of glycosylation on yeast invertase oligomer stability. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4395–4401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme E. J., Derycke D. G. Microbial inulinases: fermentation process, properties, and applications. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1983;29:139–176. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman W. E., Day D. F. Purification and properties of the beta-fructofuranosidase from Kluyveromyces fragilis. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80927-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman W. E., Day D. F. The cell wall-associated inulinase of Kluyveromyces fragilis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1984;50(4):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00394648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


