Abstract
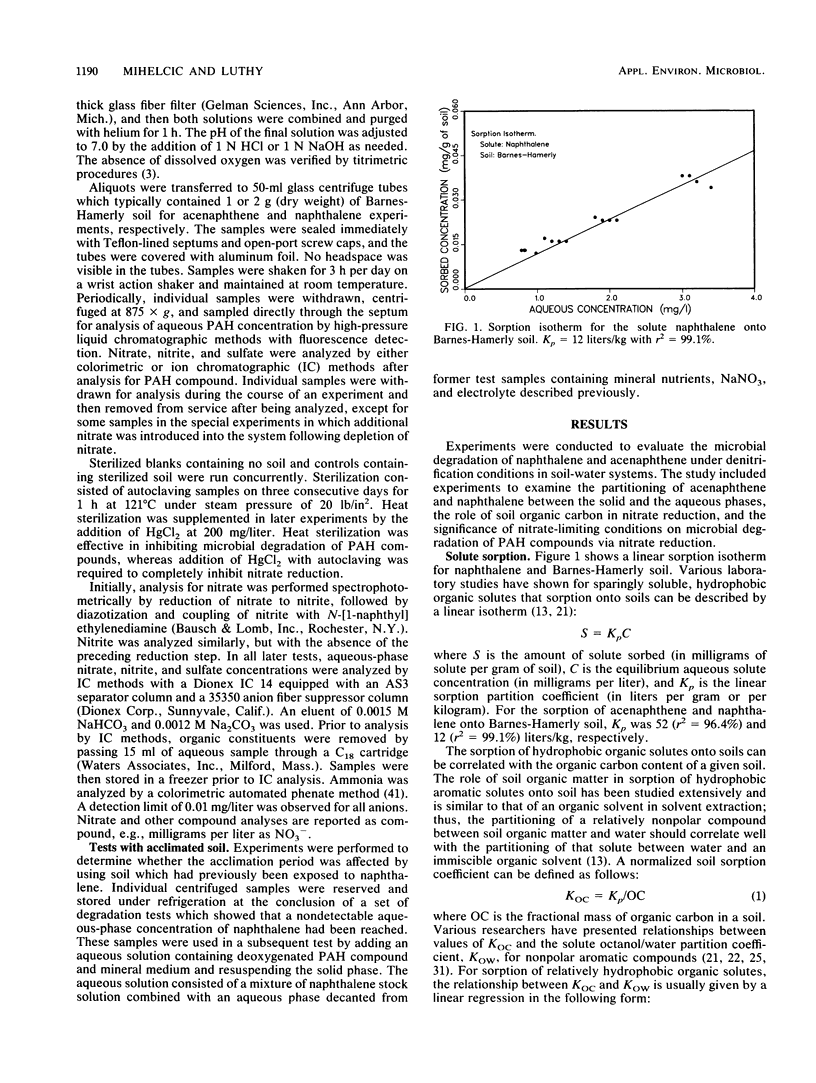
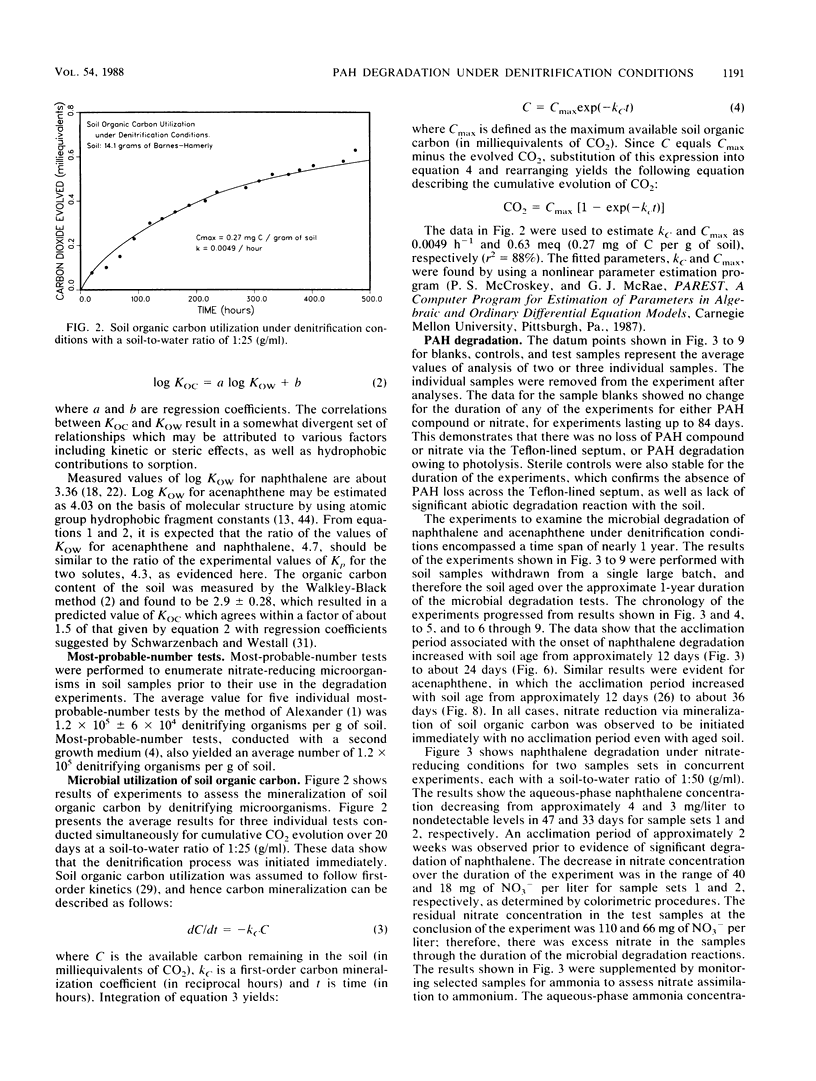
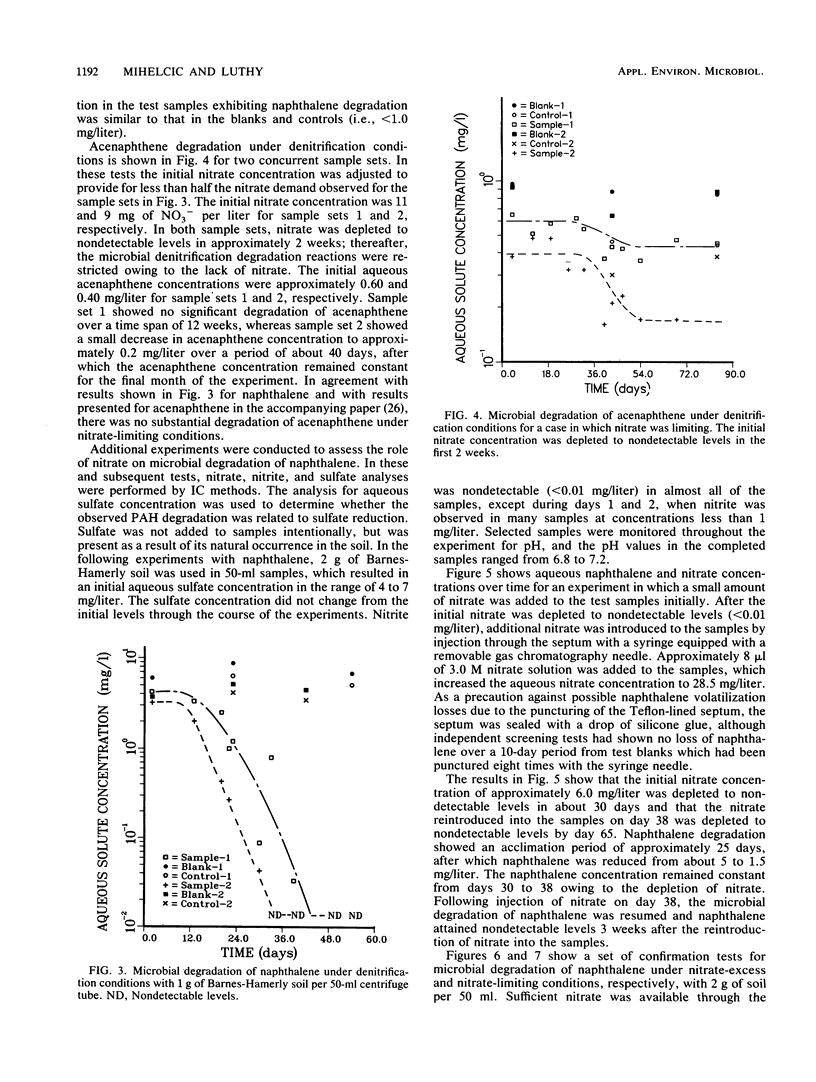
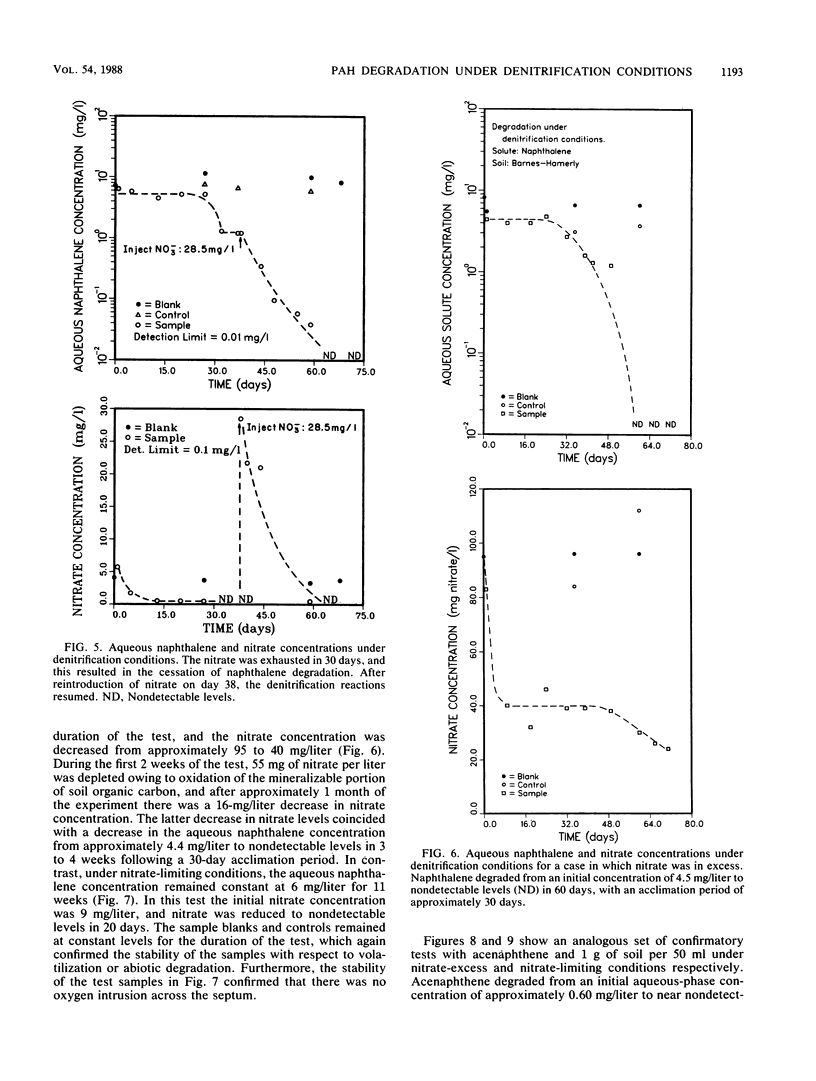
This study examined the microbial degradation of acenaphthene and naphthalene under denitrification conditions at soil-to-water ratios of 1:25 and 1:50 with soil containing approximately 10(5) denitrifying organisms per g of soil. Under nitrate-excess conditions, both acenaphthene and naphthalene were degraded from initial aqueous-phase concentrations of about 1 and several mg/liter respectively, to nondetectable levels (less than 0.01 mg/liter) in less than 9 weeks. Acclimation periods of 12 to 36 days were observed prior to the onset of microbial degradation in tests with soil not previously exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) compounds, whereas acclimation periods were absent in tests with soil reserved from prior PAH degradation tests. It was judged that the apparent acclimation period resulted from the time required for a small population of organisms capable of PAH degradation to attain sufficient densities to exhibit detectable PAH reduction, rather than being a result of enzyme induction, mutation, or use of preferential substrate. About 0.9% of the naturally occurring soil organic carbon could be mineralized under denitrification conditions, and this accounted for the greater proportion of the nitrate depletion. Mineralization of the labile fraction of the soil organic carbon via microbial denitrification occurred without an observed acclimation period and was rapid compared with PAH degradation. Under nitrate-limiting conditions the PAH compounds were stable owing to the depletion of nitrate via the more rapid process of soil organic carbon mineralization. Soil sorption tests showed at the initiation of a test that the total mass of PAH compound was divided in comparable proportions between solute in the aqueous phase and solute sorbed on the solid phase. The microbial degradation of the PAH compound depends on the interrelationships between (i) the desorption kinetics and the reversibility of desorption of sorbed compound from the soil, (ii) the concentration of PAH-degrading microorganisms, and (iii) the competing reaction for nitrate utilization via mineralization of the labile fraction of naturally occurring soil organic carbon.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas R. M. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Mar;45(1):180–209. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.1.180-209.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossert I. D., Young L. Y. Anaerobic oxidation of p-cresol by a denitrifying bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1117–1122. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1117-1122.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer E. J., McCarty P. L. Transformations of halogenated organic compounds under denitrification conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1295–1299. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1295-1299.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Biochemistry of the bacterial catabolism of aromatic compounds in anaerobic environments. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):17–22. doi: 10.1038/270017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbes S. E., Schwall L. R. Microbial transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in pristine and petroleum-contaminated sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):306–316. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.306-316.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike I., Hattori A. Denitrification and ammonia formation in anaerobic coastal sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):278–282. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.278-282.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihelcic J. R., Luthy R. G. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds under various redox conditions in soil-water systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1182–1187. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1182-1187.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. Enzymic adaptation in bacteria: its biochemical and genetic basis. Essays Biochem. 1968;4:105–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp R. J., Pfaender F. K. Influence of easily degradable naturally occurring carbon substrates on biodegradation of monosubstituted phenols by aquatic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):394–401. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.394-401.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleat R., Robinson J. P. The bacteriology of anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;57(3):381–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Capacity for denitrification and reduction of nitrate to ammonia in a coastal marine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):301–305. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.301-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. F., Campbell W. L., Chinoy I. Anaerobic degradation of the benzene nucleus by a facultatively anaerobic microorganism. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.430-437.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins B. A., Jones S. H., Alexander M. Explanations for the acclimation period preceding the mineralization of organic chemicals in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):791–796. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.791-796.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Kuhn E. P., Schwarzenbach R. P. Rapid microbial mineralization of toluene and 1,3-dimethylbenzene in the absence of molecular oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):944–947. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.944-947.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


