Abstract
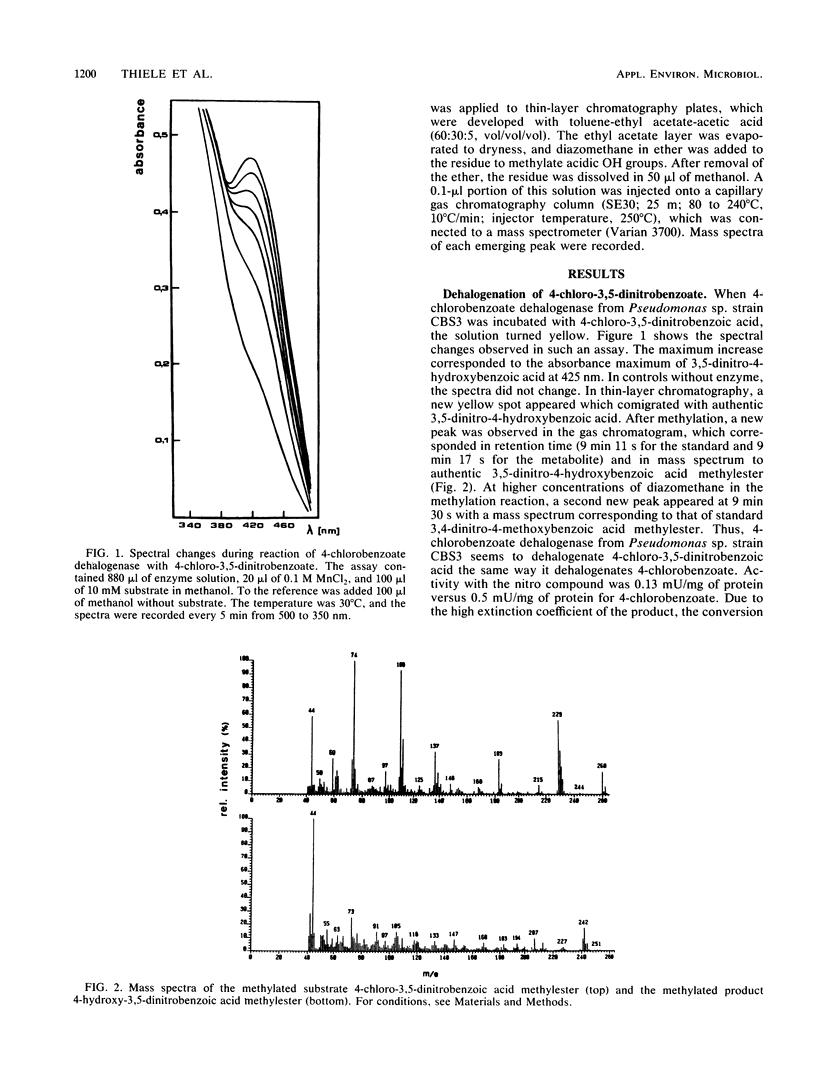
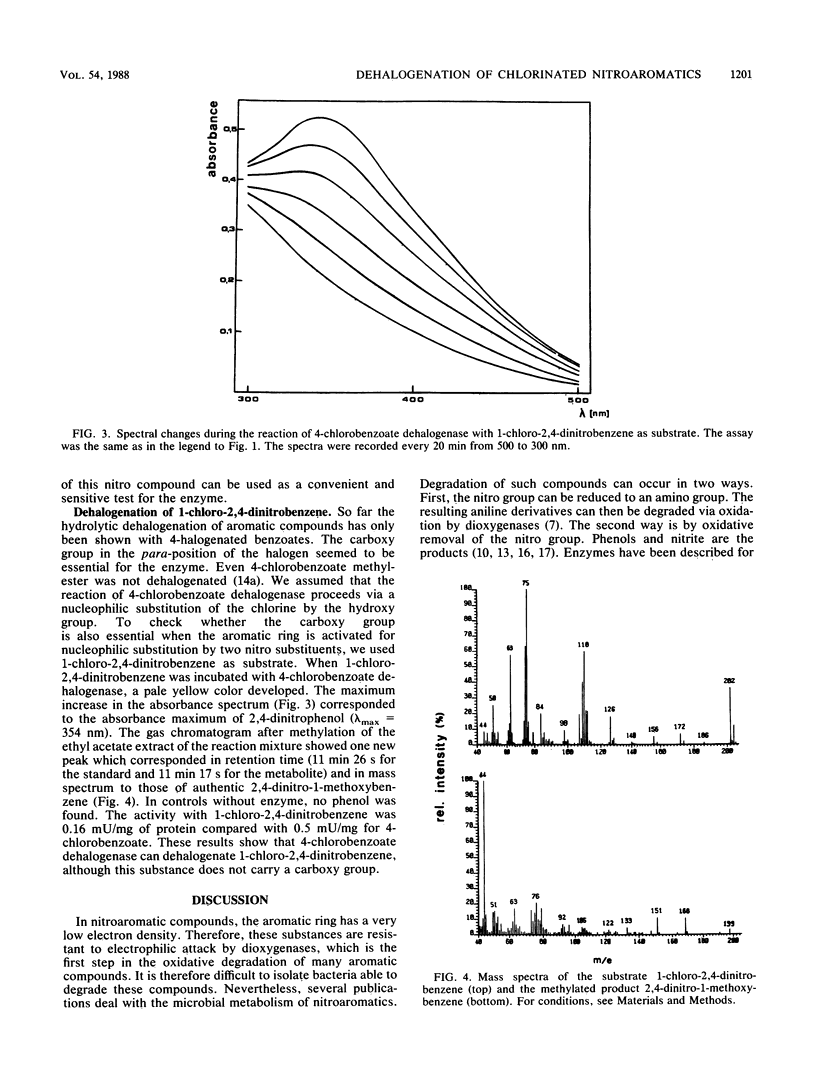
4-Chlorobenzoate dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 converted 4-chloro-3,5-dinitrobenzoate to 3,5-dinitro-4-hydroxybenzoate and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene to 2,4-dinitrophenol. The activities were 0.13 mU/mg of protein for 4-chloro-3,5-dinitrobenzoate and 0.16 mU/mg of protein for 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene compared with 0.5 mU/mg of protein for 4-chlorobenzoate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atri F. R. Chlorierte Kohlenwasserstoffe in der Umwelt IV. Chlorbenzol, 1,2,4-Trichlorbenzol, Chlornitrobenzole, Chloraniline, 2-Chlorethanol, 1,3-Dichlorpropanol (2), Epichlorhydrin. Schriftenr Ver Wasser Boden Lufthyg. 1986;70:1–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn C., Lenke H., Knackmuss H. J. Nitrosubstituted aromatic compounds as nitrogen source for bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):208–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.208-210.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingens F., Eberhardt H., Oltmanns O. Mikrobieller Abbau des Chloramphenicols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):345–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Feeherry F. E., Levinson H. S. Microbial transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and other nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):949–958. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.949-958.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Thiele J., Klages U., Lingens F. Incorporation of [18O]water into 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the reaction of 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase from pseudomonas spec. CBS 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90933-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner G., Nguyen P. T. Mechanisms of the reductive denitration of pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) and the reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene (HCB). Xenobiotica. 1984 Sep;14(9):705–710. doi: 10.3109/00498258409151468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Wyss O., Gibson D. T. Enzymatic oxidation of p-nitrophenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):634–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhakar-Barik, Siddaramappa R., Sethunathan N. Metabolism of nitrophenols by bacteria isolated from parathion-amended flooded soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1976;42(4):461–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00410177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Kocher H. P., Timmis K. N. Influence of para-substituents on the oxidative metabolism of o-nitrophenols by Pseudomonas putida B2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):334–339. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.334-339.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


