Abstract
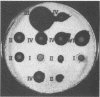
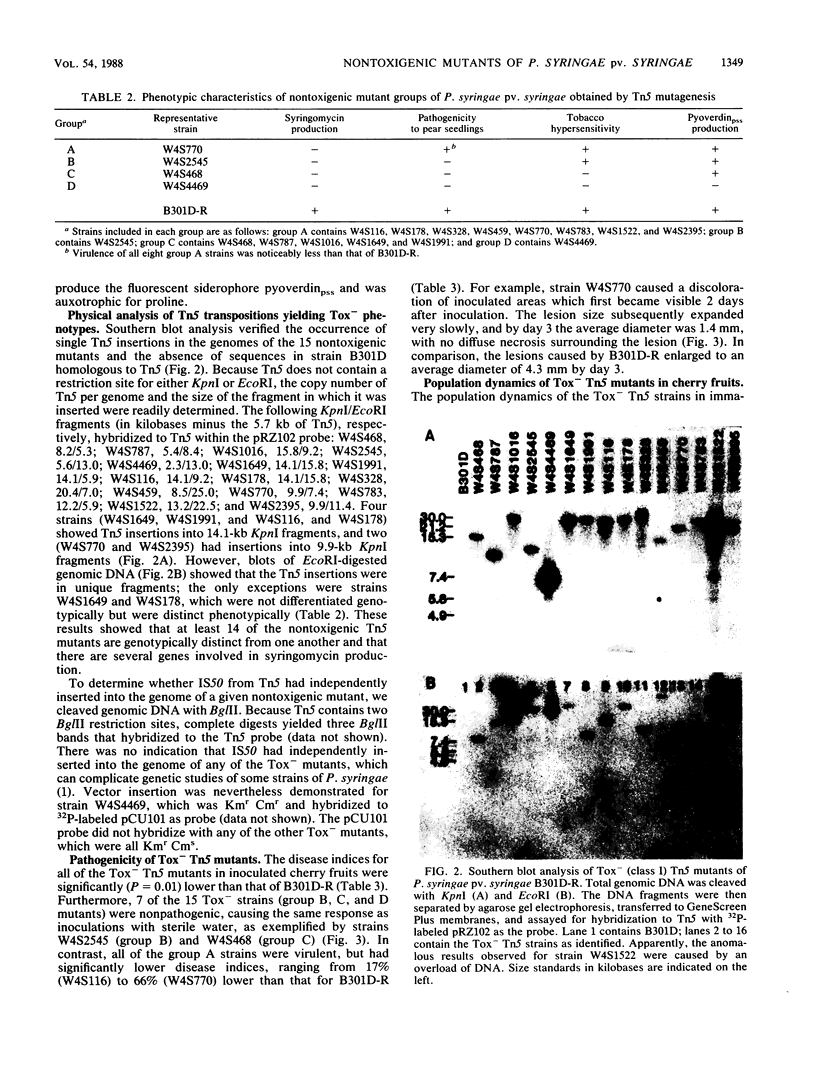
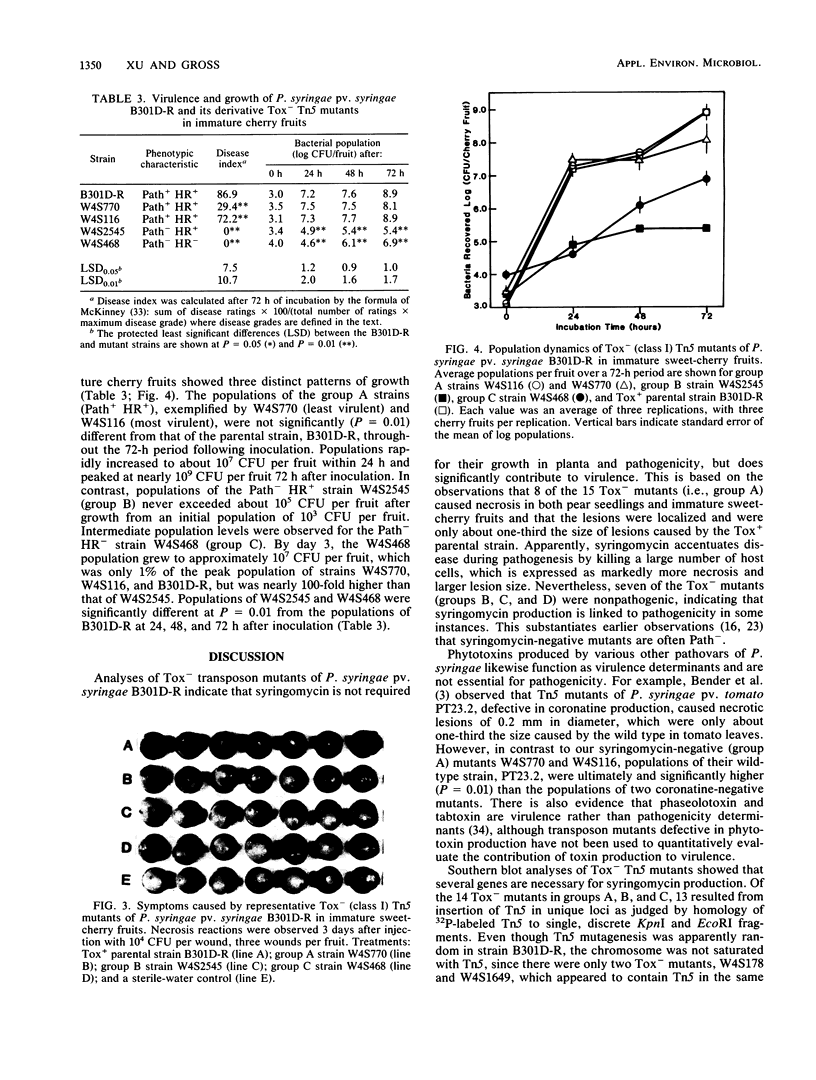
Syringomycin is a necrosis-inducing phytotoxin produced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. To determine whether syringomycin production is a determinant in virulence or pathogenicity, we isolated nontoxigenic (Tox−) Tn5-containing mutants and then quantitatively evaluated them for the ability to multiply and cause disease in immature sweet-cherry fruits. Transposon Tn5 was delivered to Tox+ strain B301D-R by using the suicide vector, pGS9, and the resultant kanamycin-resistant (Kmr) colonies were screened for changes in syringomycin production by testing for antibiosis against Geotrichum candidum. Southern blot analysis of KpnI-and EcoRI-digested DNA showed that 15 (0.3%) Tox− mutants were isolated which had Tn5 inserted into 1 of 14 distinct loci. Phenotypic characterization of the Tox− mutants identified three major groups, which were differentiated by pathogenicity and ability to cause a tobacco hypersensitive reaction (HR). The eight strains in group A were pathogenic (Path+) in cherry fruit assays, but the disease index was 17 to 66% lower (significant at P = 0.01) than for the parental Tox+ strain, B301D-R. The population dynamics of group A strains W4S770 and W4S116 in cherry fruits were, however, indistinguishable from that of strain B301D-R. The remaining seven Tox− strains were nonpathogenic; group B strain W4S2545 (Path− HR+) and group C strain W4S468 (Path− HR−) developed significantly lower populations (105 to 107 CFU per cherry fruit) 3 days after inoculation than strain B301D-R did (nearly 109 CFU per fruit). The data indicate that syringomycin is not essential for pathogenicity, but contributes significantly to virulence.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidwai A. P., Zhang L., Bachmann R. C., Takemoto J. Y. Mechanism of Action of Pseudomonas syringae Phytotoxin, Syringomycin : Stimulation of Red Beet Plasma Membrane ATPase Activity. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):39–43. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchholz W. G., Thomashow M. F. Host range encoded by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor-inducing plasmid pTiAg63 can be expanded by modification of its T-DNA oncogene complement. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.327-332.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody Y. S., Gross D. C. Characterization of Pyoverdin(pss), the Fluorescent Siderophore Produced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):928–934. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.928-934.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppels D. A. Generation and Characterization of Tn5 Insertion Mutations in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):323–327. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.323-327.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. C., Cody Y. S., Proebsting E. L., Radamaker G. K., Spotts R. A. Distribution, population dynamics, and characteristics of ice nucleation-active bacteria in deciduous fruit tree orchards. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1370–1379. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1370-1379.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. C. Regulation of syringomycin synthesis in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae and defined conditions for its production. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;58(2):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinkauf H., von Döhren H. Biosynthesis of peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:259–289. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren P. B., Peet R. C., Panopoulos N. J. Gene cluster of Pseudomonas syringae pv. "phaseolicola" controls pathogenicity of bean plants and hypersensitivity of nonhost plants. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):512–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.512-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. K., Chatterjee A. K. Isolation and characterization of Tn5 insertion mutants of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae altered in the production of the peptide phytotoxin syringotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.14-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obukowicz M., Shaw P. D. Construction of tn3-containing plasmids from plant-pathogenic pseudomonads and an examination of their biological properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):468–473. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.468-473.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peet R. C., Lindgren P. B., Willis D. K., Panopoulos N. J. Identification and cloning of genes involved in phaseolotoxin production by Pseudomonas syringae pv. "phaseolicola". J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1096–1105. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1096-1105.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Iyer V. N. Suicide plasmid vehicles for insertion mutagenesis in Rhizobium meliloti and related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1292–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1292-1300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Iyer V. N. Transposon Tn5 specifies streptomycin resistance in Rhizobium spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):580–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.580-589.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Measurement of DNA length by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Dec;100(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., An G., Flores C., Nester E. W. A Tn3 lacZ transposon for the random generation of beta-galactosidase gene fusions: application to the analysis of gene expression in Agrobacterium. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):891–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Nutter R., Montoya A. L., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Integration and organization of Ti plasmid sequences in crown gall tumors. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K. Synthetic and complex media for the rapid detection of fluorescence of phytopathogenic pseudomonads: effect of the carbon source. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1523–1524. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1523-1524.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]