Abstract
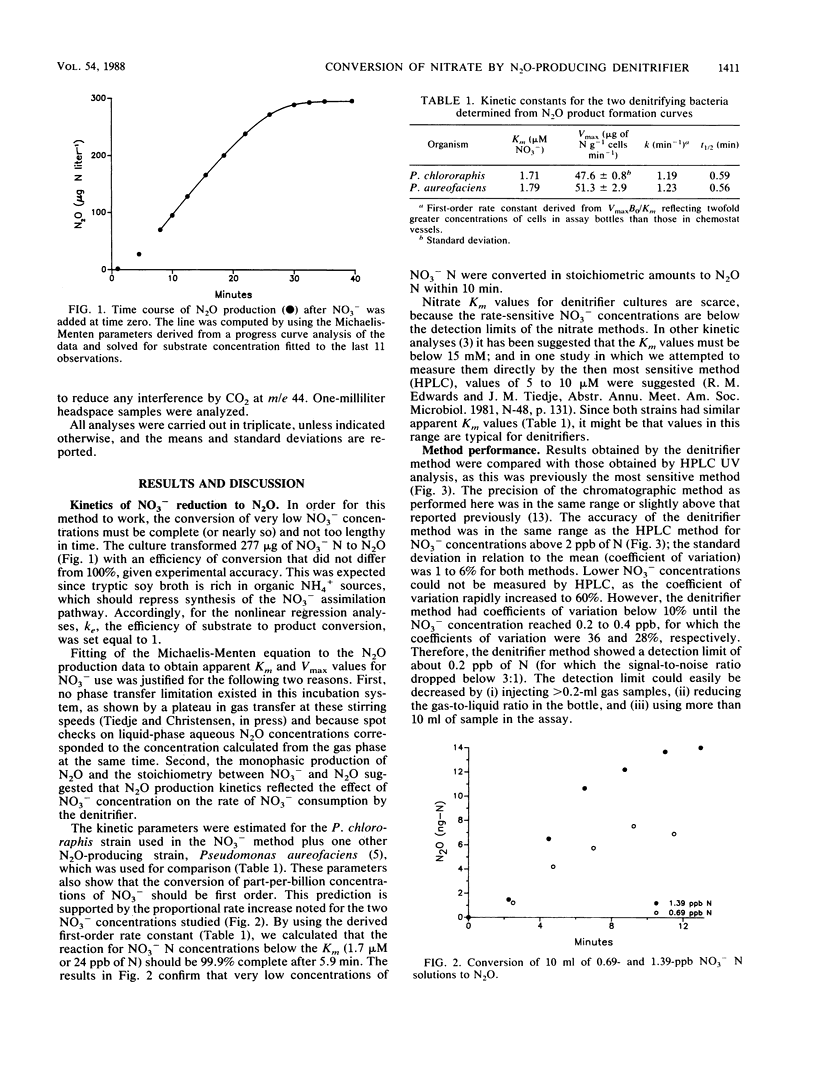
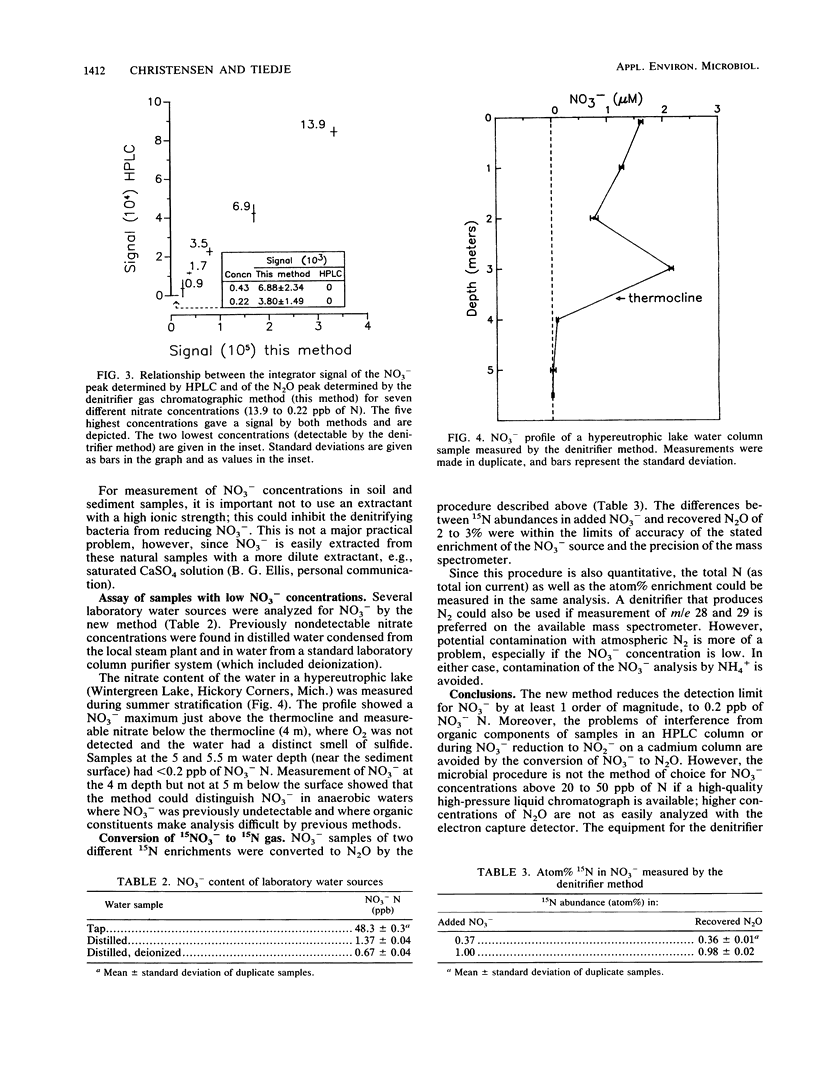
A more sensitive analytical method for NO3− was developed based on the conversion of NO3− to N2O by a denitrifier that could not reduce N2O further. The improved detectability resulted from the high sensitivity of the 63Ni electron capture gas chromatographic detector for N2O and the purification of the nitrogen afforded by the transformation of the N to a gaseous product with a low atmospheric background. The selected denitrifier quantitatively converted NO3− to N2O within 10 min. The optimum measurement range was from 0.5 to 50 ppb (50 μg/liter) of NO3− N, and the detection limit was 0.2 ppb of N. The values measured by the denitrifier method compared well with those measured by the high-pressure liquid chromatographic UV method above 2 ppb of N, which is the detection limit of the latter method. It should be possible to analyze all types of samples for nitrate, except those with inhibiting substances, by this method. To illustrate the use of the denitrifier method, NO3− concentrations of <2 ppb of NO3− N were measured in distilled and deionized purified water samples and in anaerobic lake water samples, but were not detected at the surface of the sediment. The denitrifier method was also used to measure the atom% of 15N in NO3−. This method avoids the incomplete reduction and contamination of the NO3− -N by the NH4+ and N2 pools which can occur by the conventional method of 15NO3− analysis. N2O-producing denitrifier strains were also used to measure the apparent Km values for NO3− use by these organisms. Analysis of N2O production by use of a progress curve yielded Km values of 1.7 and 1.8 μM NO3− for the two denitrifier strains studied.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aerssens E., Tiedje J. M., Averill B. A. Isotope labeling studies on the mechanism of N-N bond formation in denitrification. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9652–9656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M. R., Tiedje J. M. Kinetic explanation for accumulation of nitrite, nitric oxide, and nitrous oxide during bacterial denitrification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1074–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1074-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone M. K., Firestone R. B., Tiedje J. M. Nitric oxide as an intermediate in denitrification: evidence from nitrogen-13 isotope exchange. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):10–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90575-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt S. K., Simkins S., Alexander M. Models for the kinetics of biodegradation of organic compounds not supporting growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):323–331. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.323-331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. R., Huffaker R. C. Determination of nitrate and nitrite by high-pressure liquid chromatography: comparison with other methods for nitrate determination. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):110–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk R. J., Pearson C. J., Jackson W. A. Reduction of plant tissue nitrate to nitric oxide for mass spectrometric 15N analysis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Aug;97(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


