Abstract
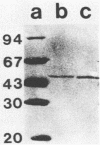
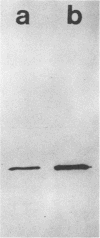
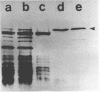
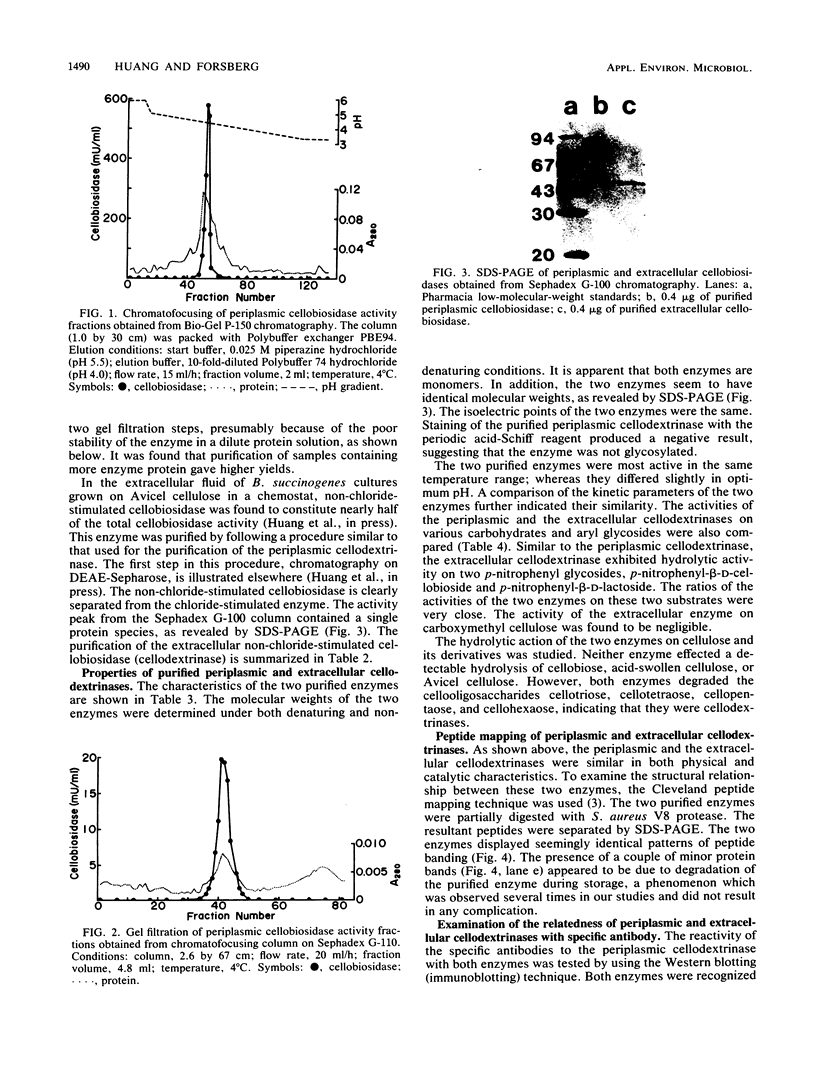
Both the periplasmic and the extracellular cellodextrinases from Bacteroides succinogenes S85 grown on Avicel microcrystalline cellulose were purified to homogeneity by column chromatography and characterized. Over 70% of the total cellobiosidase activity displayed by cells was accounted for by these enzymes. The periplasmic and extracellular cellodextrinases had identical molecular weights (50,000), as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and identical isoelectric points (4.9). In addition, the two enzymes were similar in catalytic properties, with Km and Vmax values of approximately 0.24 mM and 21 μmol/min per mg of protein, respectively. Examination of the two enzymes by using peptide mapping and immunoblotting techniques provided additional evidence indicating their identical nature. Immunoblotting of the extracellular culture fluid with affinity-purified antibody to the periplasmic cellodextrinase revealed one band with a molecular weight corresponding to that of the periplasmic cellodextrinase. The stability of the purified periplasmic cellodextrinase in aqueous solution was markedly enhanced by increased protein content. This enzyme showed a low affinity for crystalline cellulose.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Beveridge T. J., Hellstrom A. Cellulase and Xylanase Release from Bacteroides succinogenes and Its Importance in the Rumen Environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):886–896. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.886-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J., MacAlister T. J., Rothfield L. I. Role of murein lipoprotein in morphogenesis of the bacterial division septum: phenotypic similarity of lkyD and lpo mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1467–1471. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1467-1471.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. M., Doerner K. C., White B. A. Purification and characterization of an exo-beta-1,4-glucanase from Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4581–4588. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4581-4588.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Yasuda S. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a mutant of E. coli lacking a murein-lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1417–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Forsberg C. W. Isolation of a Cellodextrinase from Bacteroides succinogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1034–1041. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1034-1041.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaroni J. C., Portalier R. C. Genetic and biochemical characterization of periplasmic-leaky mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1351–1358. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1351-1358.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Gottfried S., Rothfield L. Leakage of periplasmic enzymes by mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of "periplasmic leaky" mutants. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):520–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.520-525.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHale A., Coughlan M. P. Synergistic hydrolysis of cellulose by components of the extracellular cellulase system of Talaromyces emersonii. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80971-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya K., Shimizu M., Taya M., Shimizu S. Purification and properties of cellobiosidase from Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):407–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.407-409.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Analysis of cytoskeletal structures using blot-purified monospecific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:467–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]