Abstract
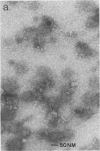
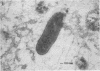
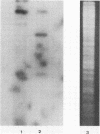
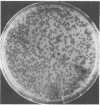
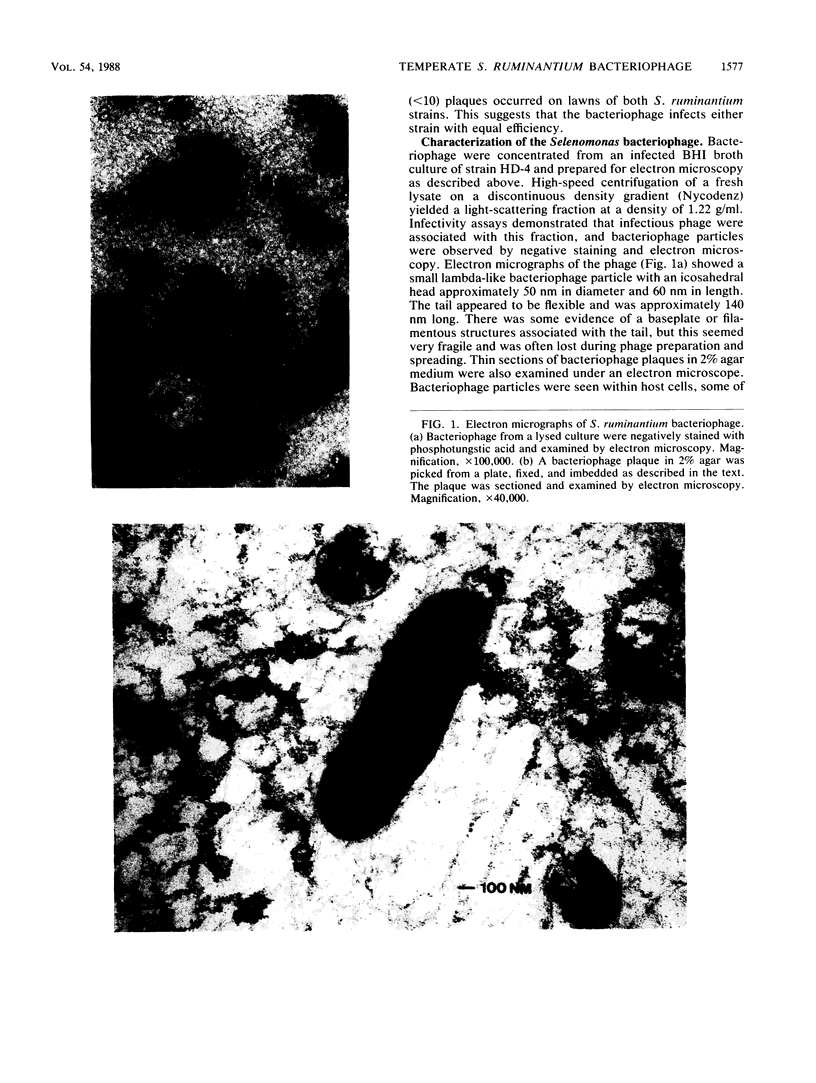
A temperate bacteriophage was obtained from an isolate of the ruminal anaerobe Selenomonas ruminantium. Clear plaques that became turbid on further incubation occurred on a lawn of host bacteria. Cells picked from a turbid plaque produced healthy liquid cultures, but these often lysed on storage. Mid-log-phase liquid cultures incubated with the bacteriophage lysed and released infectious particles with a titer of up to 3 X 10(7) PFU/ml. A laboratory strain of S. ruminantium, HD-4, was also sensitive to this bacteriophage, which had an icosohedral head (diameter, 50 nm) and a flexible tail (length, 140 nm). The bacteriophage contained 30 kilobases of linear, double-stranded DNA, and a detailed restriction map was constructed. The lysogenic nature of infection was demonstrated by hybridization of bacteriophage DNA to specific restriction fragments of infected host genomic DNA and by identification of a bacteriophage genomic domain which may participate in integration of the bacteriophage DNA. Infection of S. ruminantium in vitro was demonstrated by two different methods of cell transformation with purified bacteriophage DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Transformation of Streptococcus lactis Protoplasts by Plasmid DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1213–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1213-1215.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orpin C. G., Munn E. A. The occurrence of bacteriophages in the rumen and their influence on rumen bacterial populations. Experientia. 1974 Sep 15;30(9):1018–1020. doi: 10.1007/BF01938983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J. Polyethylene glycol-facilitated transformation of Bacteroides fragilis with plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):466–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.466-469.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]