Abstract
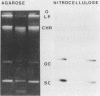
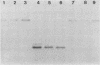
After an outbreak of salmonellosis in humans caused by Salmonella typhimurium bacteriophage type 135, 62 isolates from human, animal, and water sources were retained for further analysis. Most of the isolates (92%) could be placed in one of five plasmid pattern groups, with a majority containing a common 60-kilobase plasmid and a smaller 3.8-kilobase-pair plasmid. This small plasmid, pIMVS1, was labeled with [32P]phosphate and used as a probe in subsequent colony and Southern hybridization studies. We concluded that pIMVS1 from isolates obtained from humans was genetically different from plasmids of a similar size found in isolates from chickens. Studies to characterize pIMVS1 were undertaken to determine if it codes for known virulence factors. It did not appear to be associated with the formation of attachment pili or major outer membrane proteins. By using transposon mutagenesis techniques, Tn3(Apr) was inserted into pIMVS1, and the existence of a restriction and modification system was deduced.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber W. Host-controlled modification of bacteriophage. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:365–378. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W. DNA restriction and modification mechanisms in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:153–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner F., Margadant A., Peduzzi R., Piffaretti J. C. The plasmid pattern as an epidemiologic tool for Salmonella typhimurium epidemics: comparison with the lysotype. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):7–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLOW B. R. A new phage-typing scheme for Salmonella typhi-murium. J Hyg (Lond) 1959 Sep;57:346–359. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Cohen M. L. Comparison of plasmid profile analysis, phage typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing in characterizing Salmonella typhimurium isolates from outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.100-104.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. A., Mayhall C. G., Spadora A. C., Markowitz S. M., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Dalton H. P. Outbreak of Salmonella typhimurium gastroenteritis due to an imported strain resistant to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in a nursery. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1076–1079. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1076-1079.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Bartowsky E. J., Leavesly D. I., Hackett J. A., Heuzenroeder M. W. Molecular cloning using immune sera of a 22-kDal minor outer membrane protein of Vibrio cholerae. Gene. 1985;34(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Sato S., Ohya T., Suzuki S., Ikeda S. Plasmid profile analysis in epidemiological studies of animal Salmonella typhimurium infection in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):360–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.360-365.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Sato S., Ohya T., Suzuki S., Ikeda S. Possible relationship of a 36-megadalton Salmonella enteritidis plasmid to virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):831–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.831-833.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Sørum H., Birkness K., Wachsmuth K., Fjølstad M., Lassen J., Fossum K., Feeley J. C. Plasmid characterization of Salmonella typhimurium transmitted from animals to humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):336–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.336-338.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt D. J., Brown D. J., Munro D. S. The distribution of plasmids among a representative collection of Scottish strains of Salmonellae. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Oct;97(2):199–204. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006527x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J. Two mannose-resistant haemagglutinins on enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serotype O6:K15:H16 or H-isolated from travellers' and infantile diarrhoea. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2081–2096. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]