Abstract
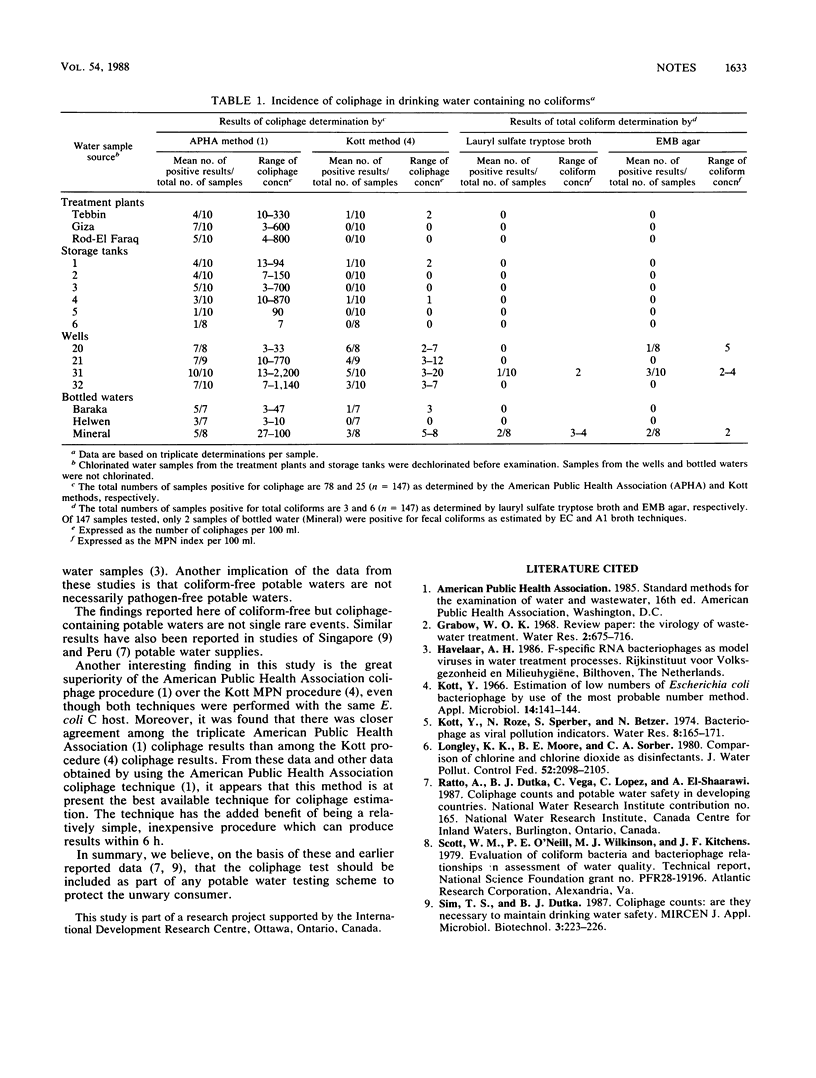
Samples of drinking water from different sources in greater Cairo, Egypt, and bottled drinking water were tested for total coliform, fecal coliform, and coliphage populations. Of the 147 samples tested, 4 samples were positive for both total coliforms and coliphage, 65 samples were negative for total coliforms, fecal coliforms, and coliphage, and 78 samples were positive for coliphage and negative for total coliforms and fecal coliforms. The incidence of coliphage in these potable water supplies reflects the probability of human pathogenic virus survival in these waters also.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kott Y. Estimation of low numbers of Escherichia coli bacteriophage by use of the most probable number method. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):141–144. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.141-144.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


