Abstract
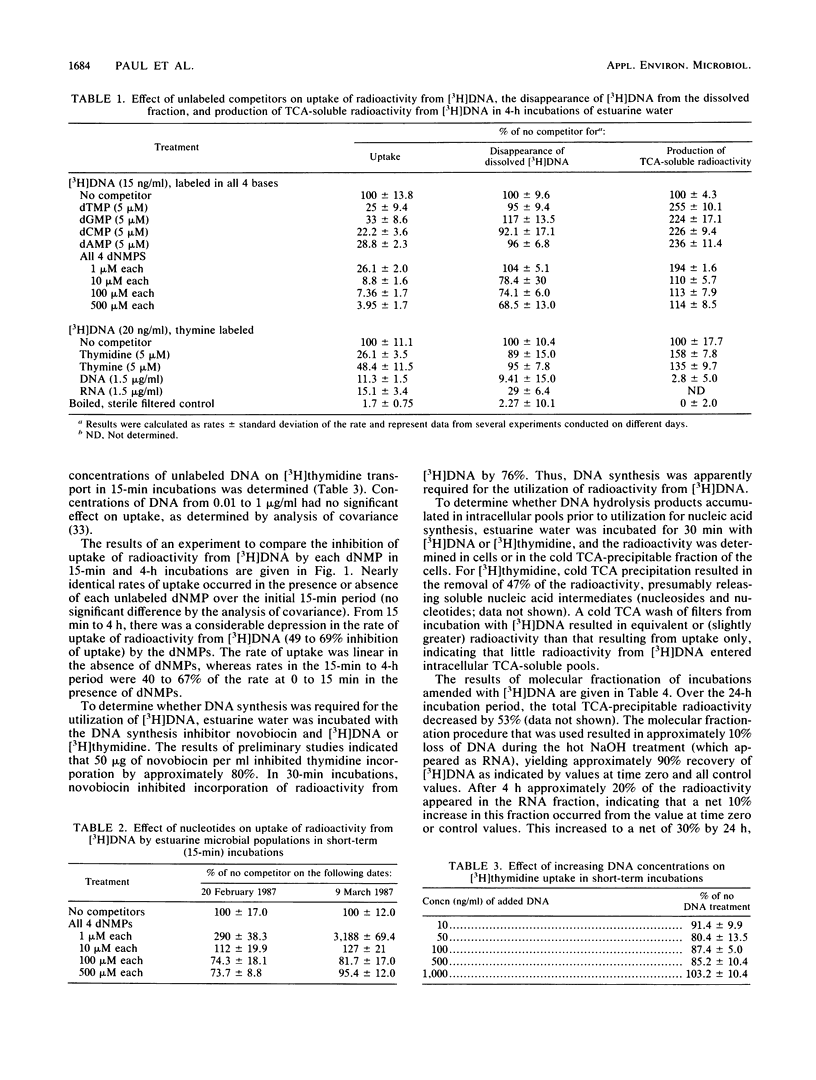
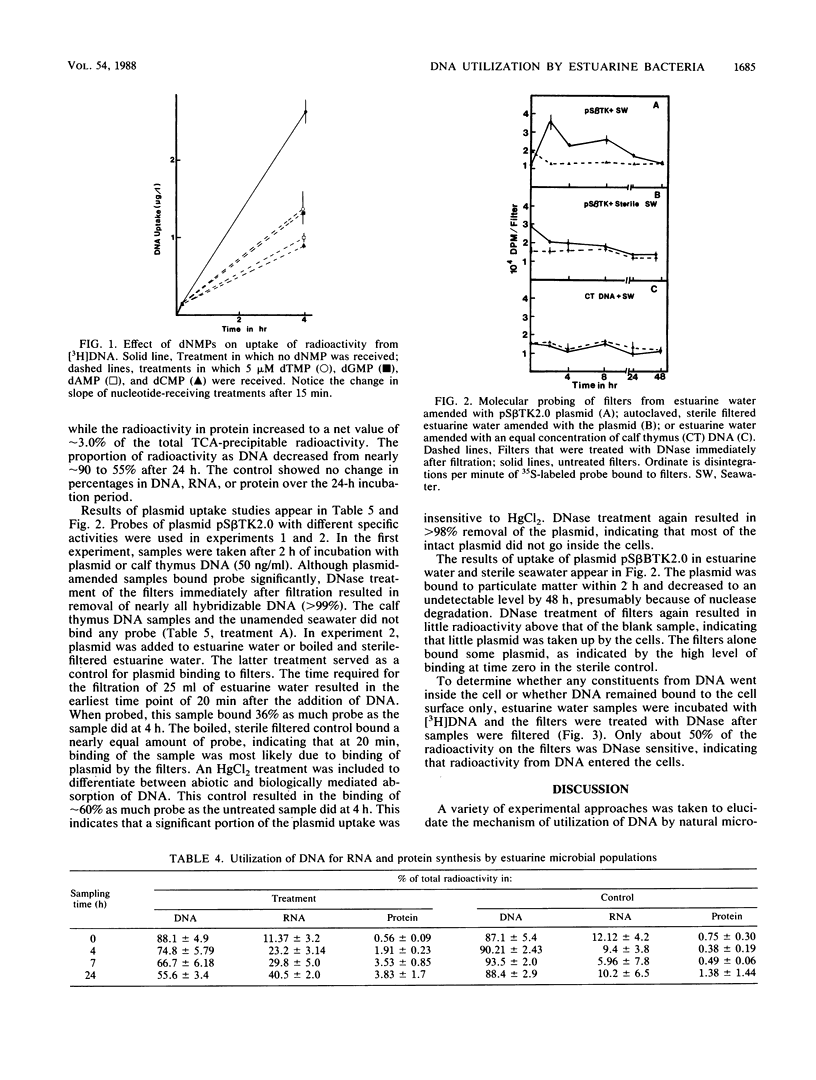
The mechanisms of utilization of DNA by estuarine microbial populations were investigated by competition experiments and DNA uptake studies. Deoxyribonucleoside monophosphates, thymidine, thymine, and RNA all competed with the uptake of radioactivity from [3H]DNA in 4-h incubations. In 15-min incubations, deoxyribonucleoside monophosphates had no effect or stimulated [3H]DNA binding, depending on the concentration. The uptake of radioactivity from [3H]DNA resulted in little accumulation of trichloroacetic acid-soluble intracellular radioactivity and was inhibited by the DNA synthesis inhibitor novobiocin. Molecular fractionation studies indicated that some radioactivity from [3H]DNA appeared in the RNA (10 and 30% at 4 and 24 h, respectively) and protein (approximately 3%) fractions. The ability of estuarine microbial assemblages to transport gene sequences was investigated by plasmid uptake studies, followed by molecular probing. Although plasmid DNA was detected on filters after filtration of plasmid-amended incubations, DNase treatment of filters removed this DNA, indicating that there was little transport of intact gene sequences. These observations led to the following model for DNA utilization by estuarine microbial populations. (i) DNA is rapidly bound to the cell surface and (ii) hydrolyzed by cell-associated and extracellular nonspecific nucleases. (iii) DNA hydrolysis products are transported, and (iv) the products are rapidly salvaged into nucleic acids, with little accumulation into intracellular nucleotide pools.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammerman J. W., Azam F. Bacterial 5-nucleotidase in aquatic ecosystems: a novel mechanism of phosphorus regeneration. Science. 1985 Mar 15;227(4692):1338–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4692.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Fouts D. L., Olson B. H. Preparation of a DNA gene probe for detection of mercury resistance genes in gram-negative bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):686–692. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.686-692.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengis-Garber C., Kushner D. J. Purification and properties of 5'-nucleotidase from the membrane of Vibrio costicola, a moderately halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.24-32.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengis-Garber C., Kushner D. J. Role of membrane-bound 5'-nucleotidase in nucleotide uptake by the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):808–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.808-815.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deflaun M. F., Paul J. H., Davis D. Simplified method for dissolved DNA determination in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):654–659. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.654-659.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doddema H. J., Claesen C. A., Kell D. B., van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. An adenine nucleotide translocase in the procaryote Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1288–1293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91613-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Al-Hossainy E., Silverman J. A. Adenine nucleotide and lysine transport in Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.662-670.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey W. H., Paul J. H. Activity measurements of planktonic microbial and microfouling communities in a eutrophic estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):157–162. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.157-162.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M., Craven D. B. Effects of alkaline phosphatase activity on nucleotide measurements in aquatic microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):549–561. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.549-561.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Taga N. Extracellular nuclease produced by a marine bacterium. II. Purification and properties of extracellular nuclease from a marine Vibrio sp. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;22(10):1443–1452. doi: 10.1139/m76-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale G. A., Mitchell A., Finch L. R. Uptake and utilization of deoxynucleoside 5'-monophosphates by Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):943–947. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.943-947.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patni N. J., Dhawale S. W., Aaronson S. Extracellular phosphatases of Chlamydomonas reinhardi and their regulation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):205–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.205-211.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Jeffrey W. H., DeFlaun M. F. Dynamics of extracellular DNA in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):170–179. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.170-179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robarts R. D., Wicks R. J., Sephton L. M. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Bacterial Macromolecule Labeling with [methyl-H]Thymidine in a Hypertrophic Lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1368–1373. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1368-1373.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Danner D. B., Deich R. A. Genetic transformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:41–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Carlson C. A. The biology of natural transformation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:211–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Green M. L., Happold F. C. Cation-activated nucleotidase in cell envelopes of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):834–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.834-841.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


