Abstract
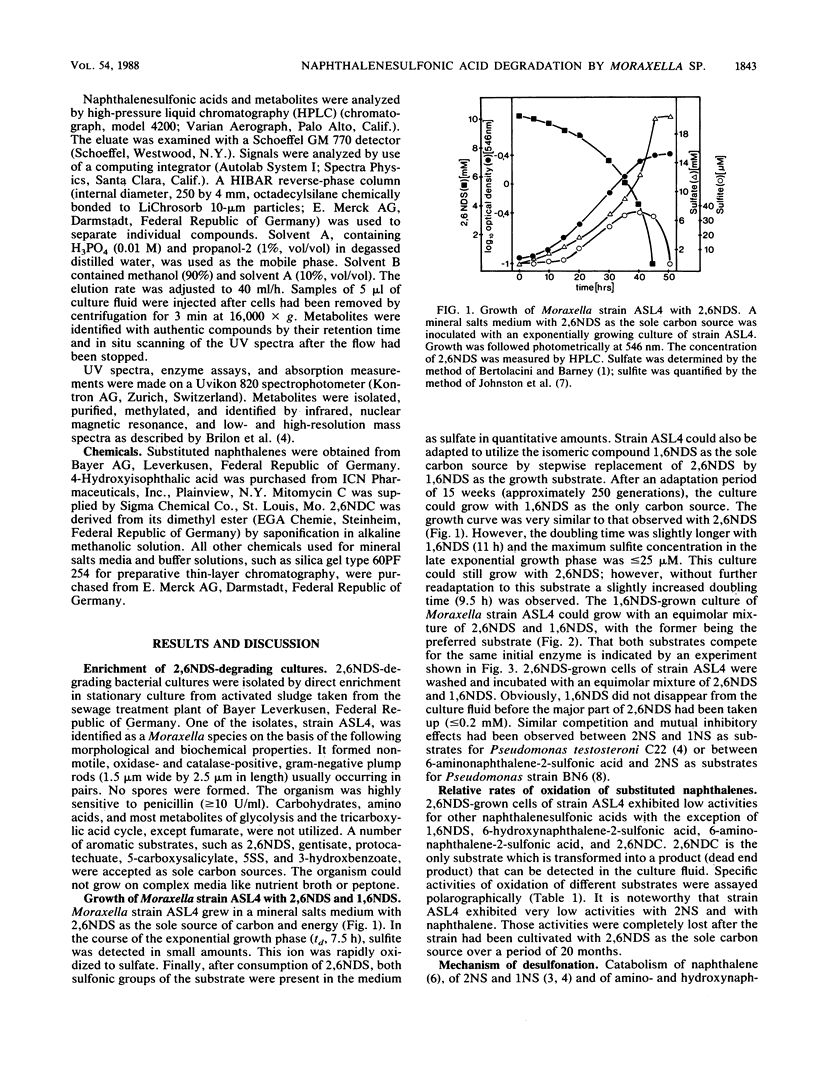
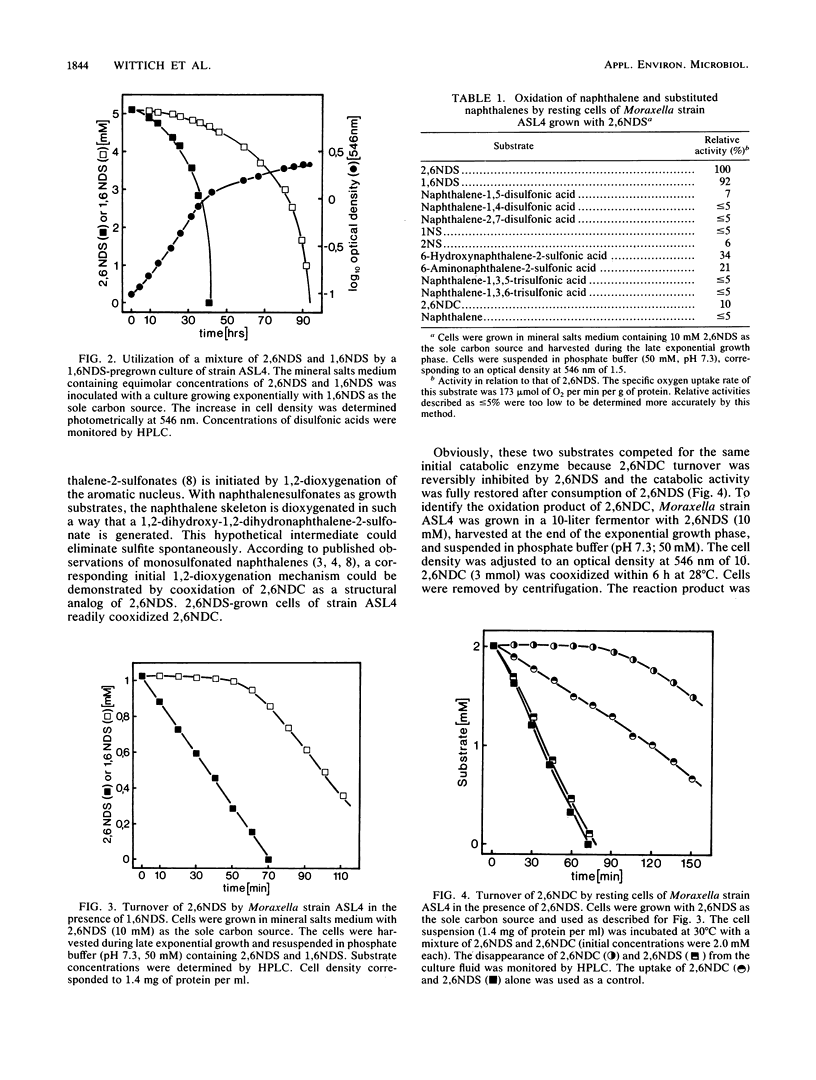
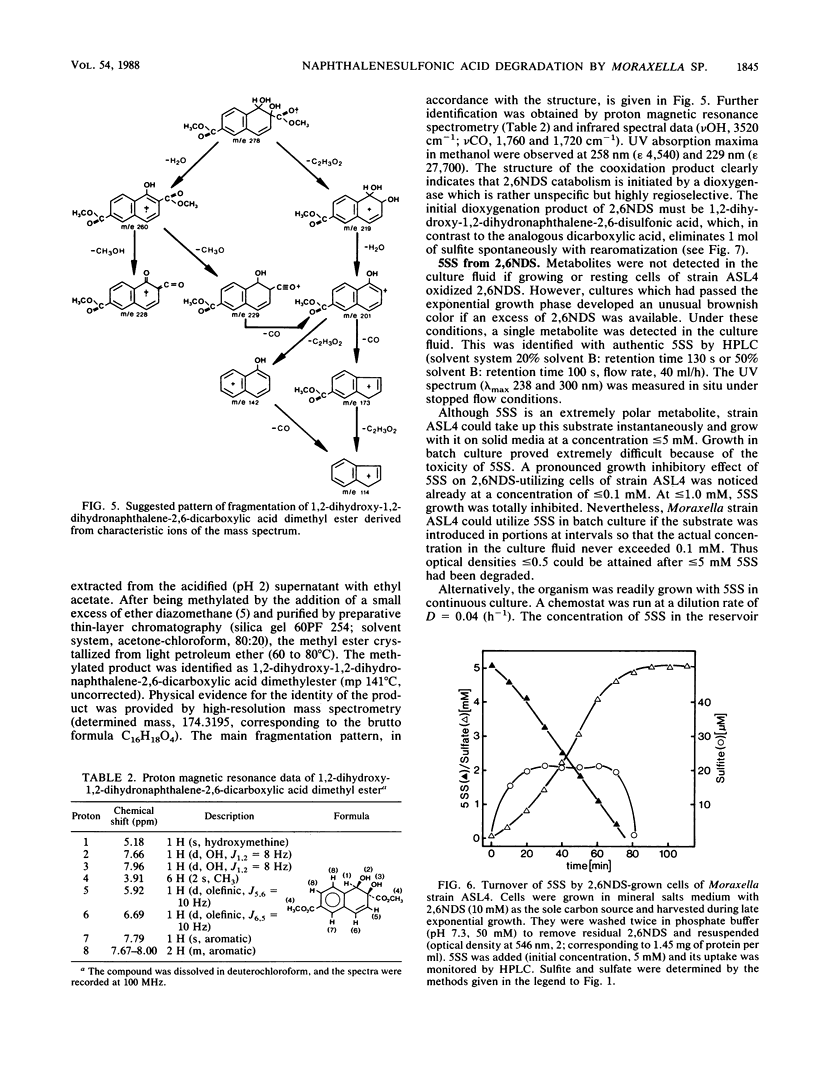
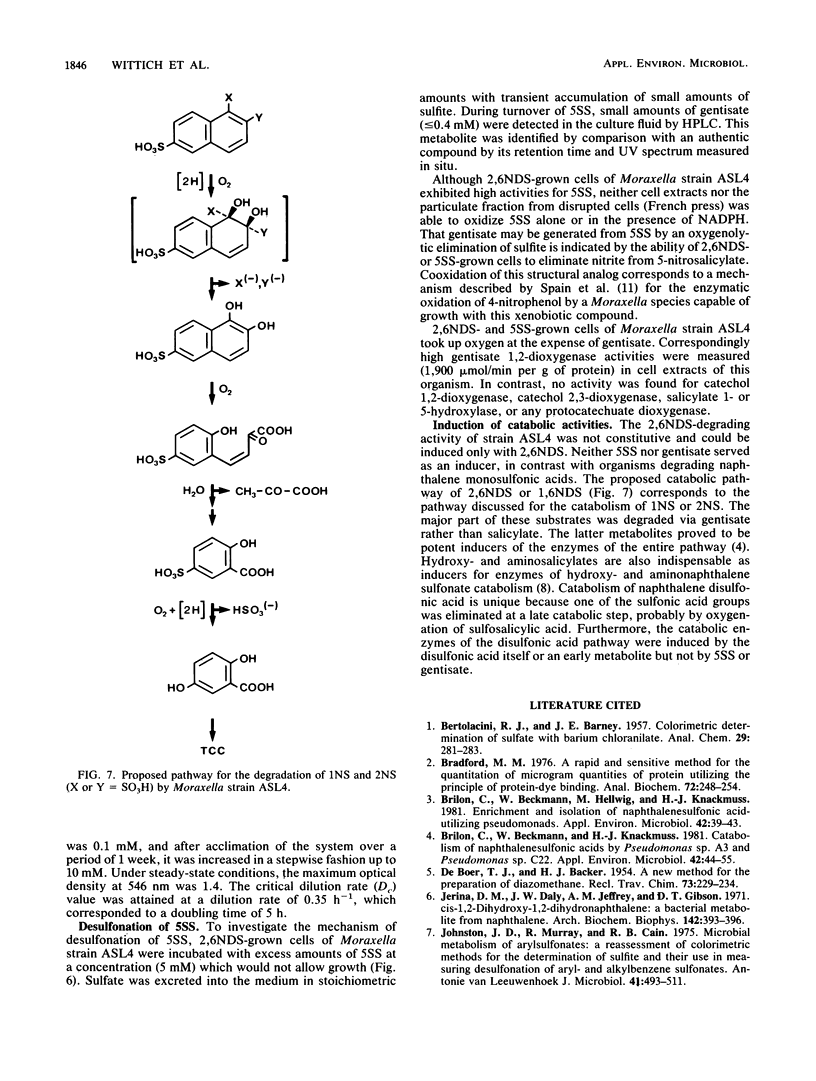
A naphthalene-2,6-disulfonic acid (2,6NDS)-degrading Moraxella strain was isolated from an industrial sewage plant. This culture could also be adapted to naphthalene-1,6-disulfonic acid as growth substrate. Regioselective 1,2-dioxygenation effected desulfonation and catabolism to 5-sulfosalicylic acid (5SS), which also could be used as the sole carbon source. 5SS-grown cells exhibited high gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase activity. Neither 5SS- nor gentisate-grown cells oxidized 2,6NDS; therefore, 2,6NDS or an early metabolite must serve as an inducer of the initial catabolic enzyme(s).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Hellwig M., Knackmuss H. J. Enrichment and isolation of naphthalenesulfonic Acid-utilizing pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.39-43.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Knackmuss H. J. Catabolism of Naphthalenesulfonic Acids by Pseudomonas sp. A3 and Pseudomonas sp. C22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.44-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Jeffrey A. M., Gibson D. T. Cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene: a bacterial metabolite from naphthalene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jan;142(1):394–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. B., Murray K., Cain R. B. Microbial metabolism of aryl sulphonates a re-assessment of colorimetric methods for the determination of sulphite and their use in measuring desulphonation of aryl and alkylbenzene sulphonates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(4):493–511. doi: 10.1007/BF02565092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nörtemann B., Baumgarten J., Rast H. G., Knackmuss H. J. Bacterial communities degrading amino- and hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulfonates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1195-1202.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT K., LIAAENJENSEN S., SCHLEGEL H. G. DIE CAROTINOIDE DER THIORHODACEAE. I. OKENON ALS HAUPTEAROTINOID VON CHROMATIUM OKENII PERTY. Arch Mikrobiol. 1963 Aug 1;46:117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Wyss O., Gibson D. T. Enzymatic oxidation of p-nitrophenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):634–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


