Abstract
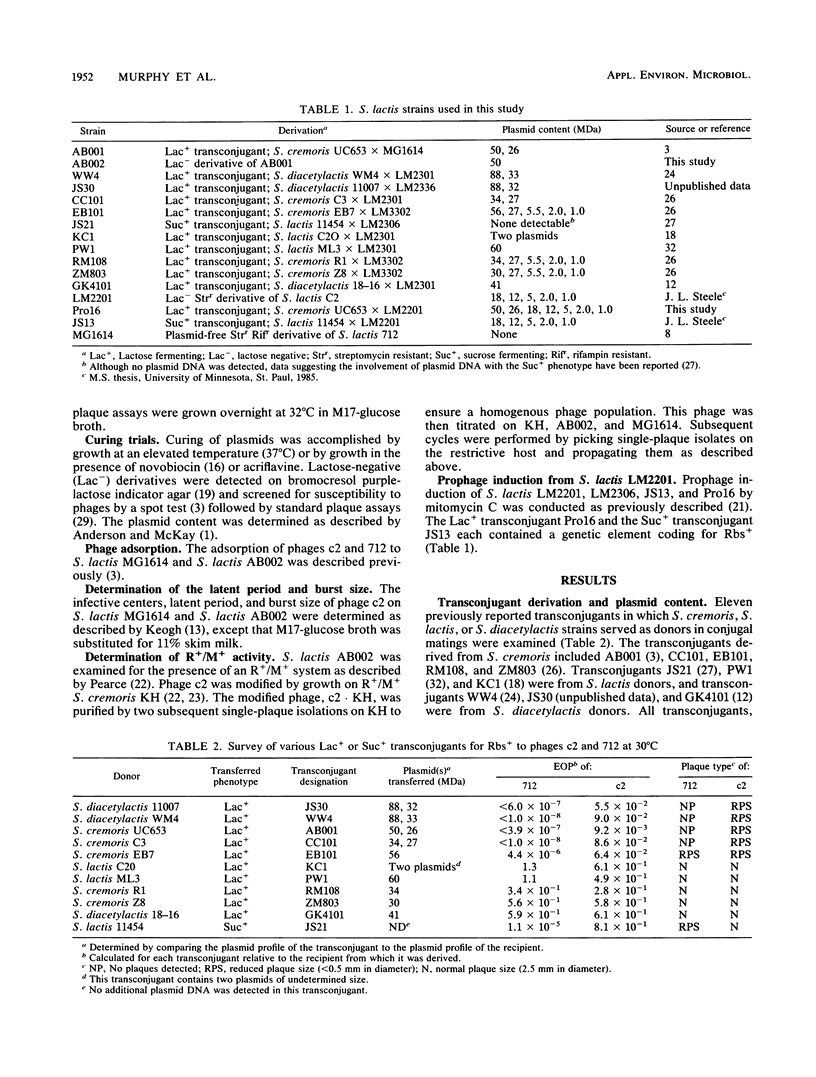
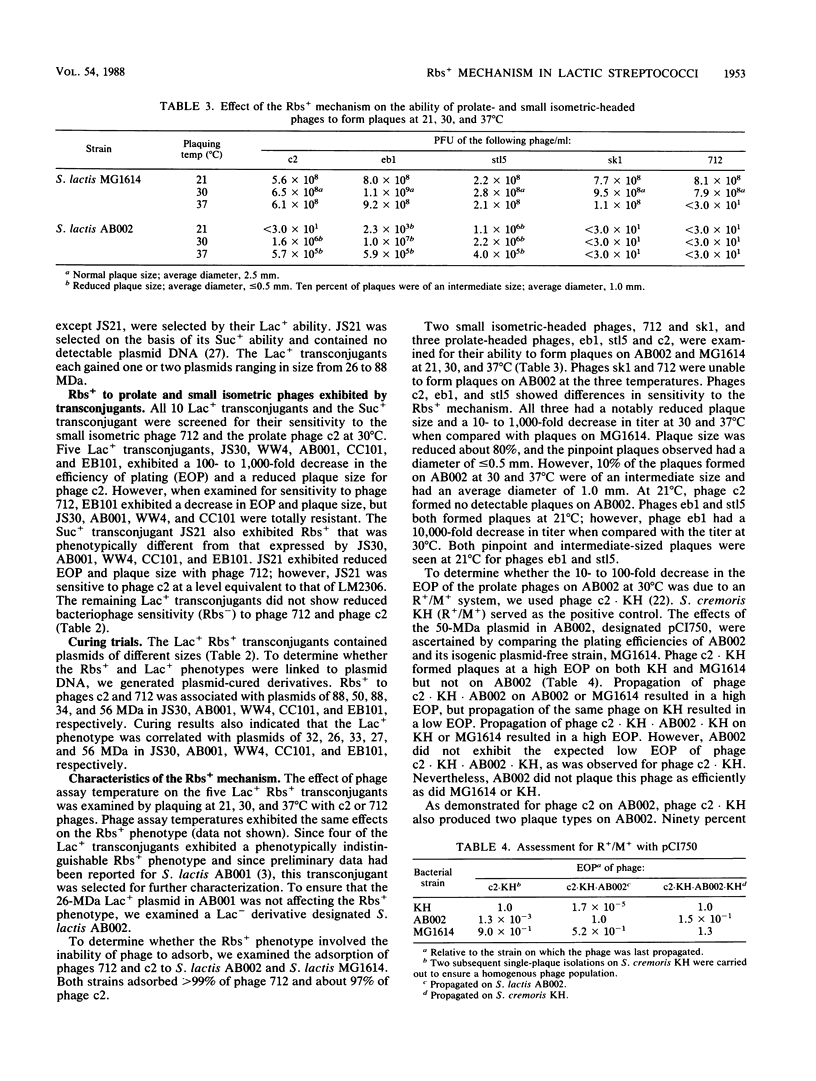
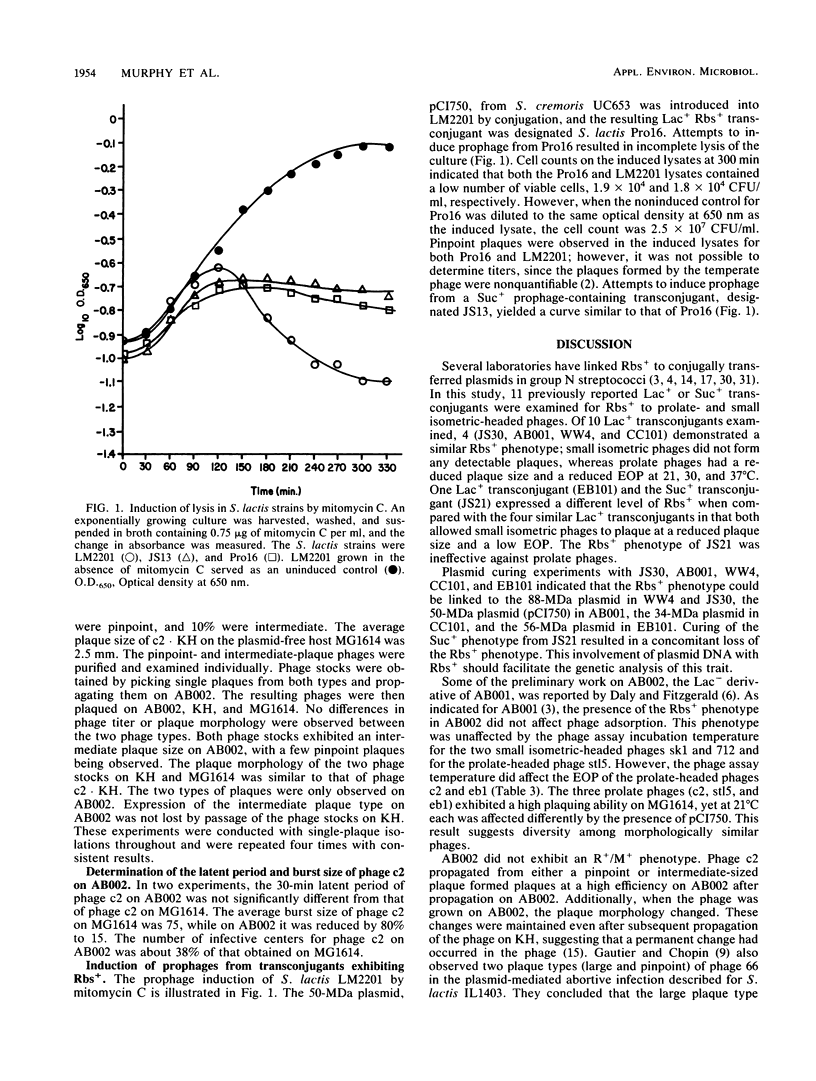
Ten previously reported lactose-positive (Lac+) transconjugants from Streptococcus lactis, S. cremoris, and S. lactis subsp. diacetylactis and one sucrose-positive (Suc+) transconjugant from S. lactis were examined for their sensitivity to prolate- and small isometric-headed bacteriophages. Four of the Lac+ transconjugants showed a 10- to 100-fold reduction in the efficiency of plating (EOP) as well as a reduced plaque size for the prolate phage c2 and were insensitive to the small isometric phage 712. A fifth Lac+ transconjugant demonstrated a similar reduced sensitivity to phage c2; however, this transconjugant was able to plaque phage 712, but with a reduced plaque size and EOP. The other five Lac+ transconjugants were sensitive to both c2 and 712 phages. The Suc+ transconjugant plaqued phage 712 with a reduced plaque size and EOP, but no reduction in plaque size or EOP was observed for phage c2. The Lac+ and reduced bacteriophage sensitivity (Rbs+) phenotypes were correlated with specific plasmids in the Lac+ transconjugants. As four of the Lac+ transconjugants exhibited a phenotypically indistinguishable Rbs+, one (AB001) was selected for further study. The Rbs+ in AB001 for both small isometric- and prolate-headed phages was not related to adsorption, and the reduced EOP for phage c2 was not related to the presence of a restriction and modification system. The latent period for phage c2 was unchanged, but the burst size was reduced 80%. The presence of the plasmid coding for Rbs+ retarded the lysis of a mitomycin C-induced prophage-containing strain. The Rbs+ mechanism appears to be abortive phage infection. This study supports previous observations that Rbs+ and conjugal transfer ability are physically linked among some group N streptococci. The results presented have implications in the identification of plasmids coding for Rbs+ and may also aid in explaining the dissemination of Rbs+ genes among lactic streptococci.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin K. A., McKay L. L. Spontaneous release of temperate phage by relysogenized lactose-positive transductants of Streptococcus lactis C2. J Dairy Sci. 1987 Oct;70(10):2005–2012. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(87)80247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin A., Chopin M. C., Moillo-Batt A., Langella P. Two plasmid-determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth D. H., Glenn J., McCorquodale D. J. Inhibition of bacteriophage replication by extrachromosomal genetic elements. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Mar;45(1):52–71. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.1.52-71.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier M., Chopin M. C. Plasmid-Determined Systems for Restriction and Modification Activity and Abortive Infection in Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):923–927. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.923-927.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriophage Resistance Conferred on Lactic Streptococci by the Conjugative Plasmid pTR2030: Effects on Small Isometric-, Large Isometric-, and Prolate-Headed Phages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1272–1277. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1272-1277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriophage Resistance Plasmid pTR2030 Inhibits Lytic Infection of r(1)t Temperate Bacteriophage but Not Induction of r(1)t Prophage in Streptococcus cremoris R1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):385–389. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.385-389.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempler G. M., McKay L. L. Characterization of Plasmid Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis: Evidence for Plasmid-Linked Citrate Utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):316–323. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.316-323.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger D. H., Bickle T. A. Bacteriophage survival: multiple mechanisms for avoiding the deoxyribonucleic acid restriction systems of their hosts. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):345–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.345-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Elimination of plasmids from several bacterial species by novobiocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Conjugative 40-megadalton plasmid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis DRC3 is associated with resistance to nisin and bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.68-74.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Walsh P. M. Conjugal transfer of genetic information in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.84-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Zottola E. A. Loss of lactose metabolism in lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1090–1096. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1090-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada J. L., La Vía M. I., Solari A. J. Isolation of Streptococcus lactis Bacteriophages and Their Interaction with the Host Cell. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1352–1354. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1352-1354.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Evidence for Plasmid Linkage of Restriction and Modification in Streptococcus cremoris KH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):944–950. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.944-950.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherwitz K. M., Baldwin K. A., McKay L. L. Plasmid linkage of a bacteriocin-like substance in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis strain WM4: transferability to Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1506–1512. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1506-1512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing W. D., Klaenhammer T. R. Conjugal Transfer of Bacteriophage Resistance Determinants on pTR2030 into Streptococcus cremoris Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1264–1271. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1264-1271.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snook R. J., McKay L. L. Conjugal Transfer of Lactose-Fermenting Ability Among Streptococcus cremoris and Streptococcus lactis Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):904–911. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.904-911.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. L., McKay L. L. Partial characterization of the genetic basis for sucrose metabolism and nisin production in Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.57-64.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenson L. R., Klaenhammer T. R. Streptococcus cremoris M12R transconjugants carrying the conjugal plasmid pTR2030 are insensitive to attack by lytic bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):851–858. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.851-858.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedamuthu E. R., Neville J. M. Involvement of a Plasmid in Production of Ropiness (Mucoidness) in Milk Cultures by Streptococcus cremoris MS. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):677–682. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.677-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedamuthu E. R., Neville J. M. Phage resistance in Streptococcus lactis ssp. diacetylactis transconjugant SLA3.2501 and its derivatives. J Dairy Sci. 1987 Feb;70(2):225–229. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(87)80001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., OKADA M. NEW TYPE OF SEX FACTOR-SPECIFIC BACTERIOPHAGE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:727–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.727-736.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. M., McKay L. L. Recombinant plasmid associated cell aggregation and high-frequency conjugation of Streptococcus lactis ML3. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.937-944.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



