Abstract
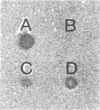
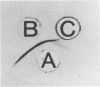
A vibrio isolated from the intestine of a coastal fish was identified as Vibrio hollisae by its biochemical characteristics. The isolate reacted with the gene probe for the thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The hemolysin produced by the isolate from the fish had traits identical to those of the thermostable direct hemolysin-like hemolysin produced by a clinical strain of V. hollisae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hollis D. G., Fanning G. R., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Brenner D. J. Identification of Vibrio hollisae sp. nov. from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.395-401.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry P. W., McFarland L. M., Threefoot H. K. Vibro hollisae septicemia after consumption of catfish. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):730–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Black R. E. Cholera and other vibrioses in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 7;312(6):343–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502073120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Miller H. G., Wilson R., Tacket C. O., Hollis D. G., Hickman F. W., Weaver R. E., Blake P. A. Illness caused by Vibrio damsela and Vibrio hollisae. Lancet. 1982 Jun 5;1(8284):1294–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92853-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Ishibashi M., Takeda Y., Kaper J. B. Detection of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene and related DNA sequences in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and other vibrio species by the DNA colony hybridization test. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):481–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.481-486.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.558-564.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Kato T., Obara Y., Yamai S. Studies on the enteropathogenic, facultatively halophilic bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus. 3. Enteropathogenicity. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):325–331. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Kelly M. T. Vibrio species of medical importance. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;2(4):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoh M., Honda T., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of a Vibrio hollisae hemolysin that relates to the thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Aug;32(8):632–636. doi: 10.1139/m86-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoh M., Honda T., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae hemolysin that cross-reacts with thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):319–322. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.319-322.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]