Abstract
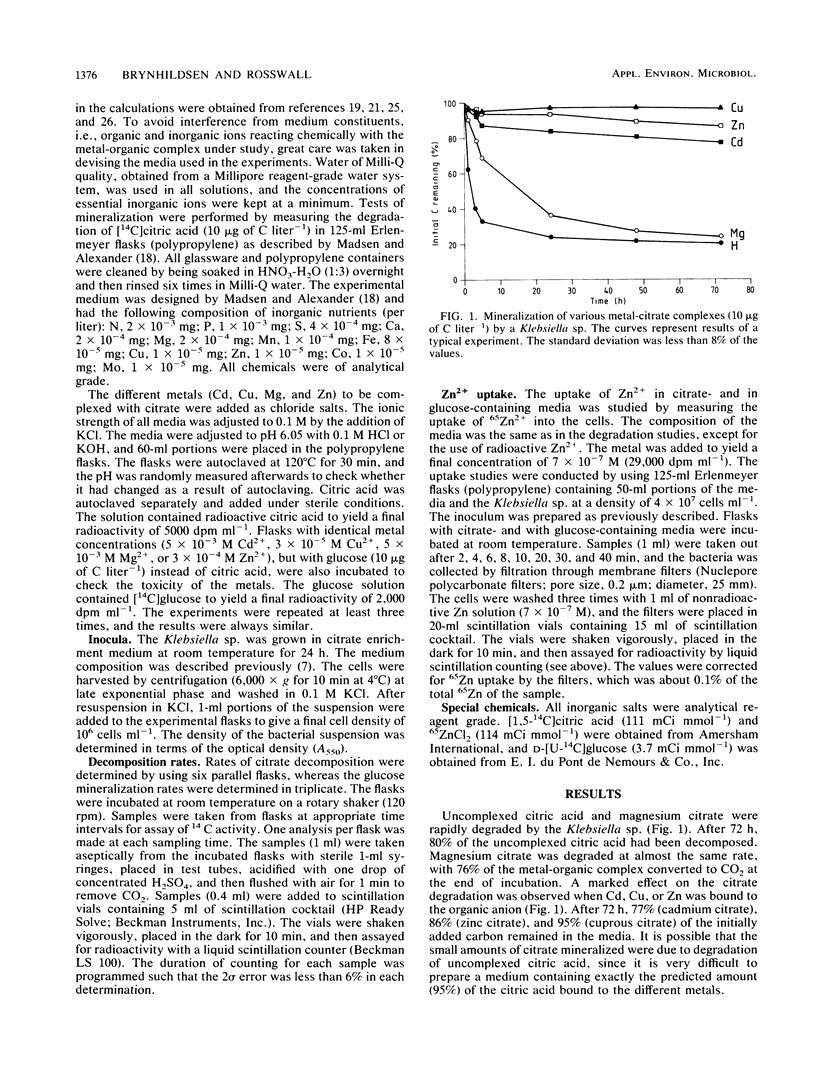
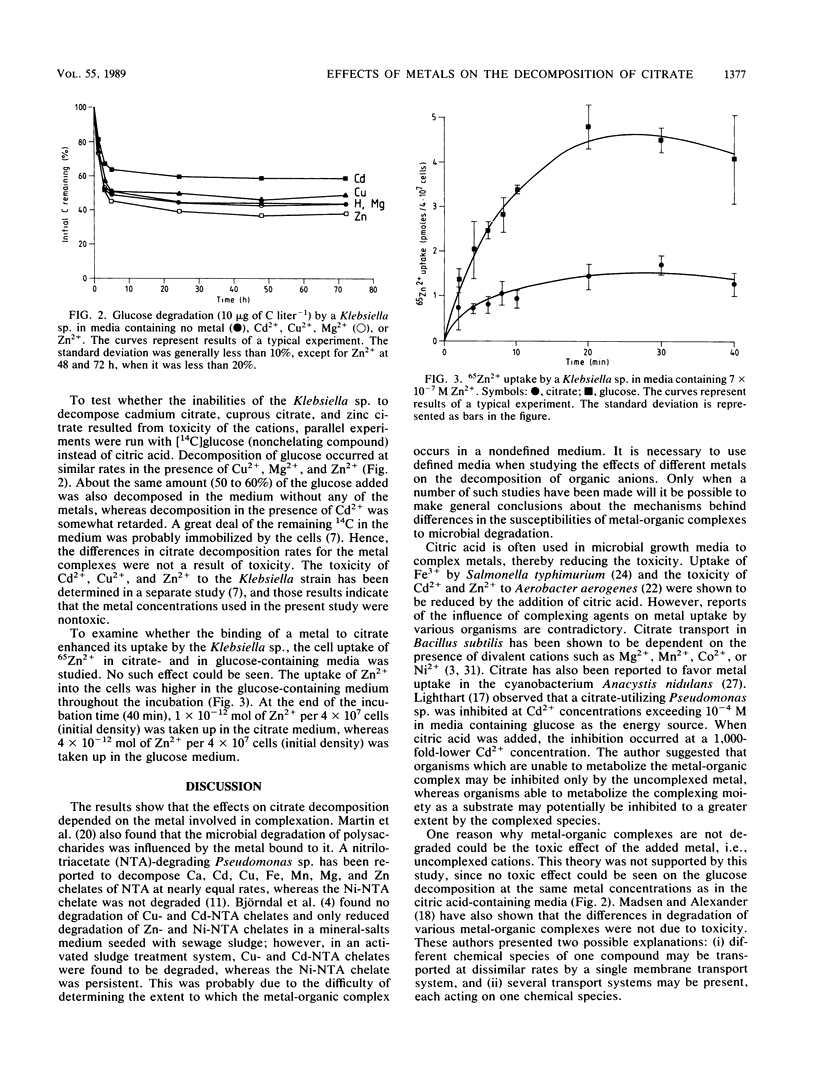
The effects of Cd2+, Cu2+, Mg2+, and Zn2+ on the decomposition of citric acid by a Klebsiella sp. were studied by monitoring the degradation of [14C]citrate. The carbon concentration used was 10 micrograms of C liter-1, and the media were designed to provide at least 95% of the citrate complexed to the metal studied. After 72 h of incubation, 80% of the uncomplexed citric acid and 76% of the magnesium citrate had been decomposed. A marked inhibition was observed when Cd2+, Cu2+, or Zn2+ was bound to the organic anion; only 23% of the cadmium citrate, 14% of the zinc citrate, and 5% of the cuprous citrate had been decomposed. The effects were not the result of toxicity, since experiments run with [14C]glucose (nonchelating compound) instead of citrate resulted in similar decomposition rates regardless of the presence of the metal. To examine whether the binding of a metal to citrate enhanced its uptake by the Klebsiella sp., we studied the relative uptake of 65Zn in citrate- and in glucose-containing media. No such effect could be observed, with the uptake of Zn2+ being higher in the glucose-containing media. The study shows that metals may render low-molecular-weight organic acids, such as citric acid, resistant to bacterial degradation. This stresses the importance of metals in influencing microbial decomposition of organic compounds, not only as a result of toxicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergsma J., Konings W. N. The properties of citrate transport in membrane vesicles from Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brynhildsen L., Lundgren B. V., Allard B., Rosswall T. Effects of Glucose Concentrations on Cadmium, Copper, Mercury, and Zinc Toxicity to a Klebsiella sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1689–1693. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1689-1693.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone M. K., Tiedje J. M. Biodegradation of metal-nitrilotriacetate complexes by a Pseudomonas species: mechanism of reaction. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):758–764. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.758-764.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lighthart B. Effects of certain cadmium species on pure and litter populations of microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(2):161–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00444071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen E. L., Alexander M. Effects of chemical speciation on the mineralization of organic compounds by microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):342–349. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.342-349.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett A. W., Dean A. C. Cadmium and zinc sensitivity and tolerance in Klebsiella (Aerobacter) aerogenes. Microbios. 1976;15(60):79–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Ames B. N., Neilands J. B. Iron transport in Salmonella typhimurium: mutants blocked in the biosynthesis of enterobactin. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.635-639.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Gries E. M., Oehr P. Coupled transport of citrate and magnesium in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


