Abstract
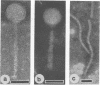
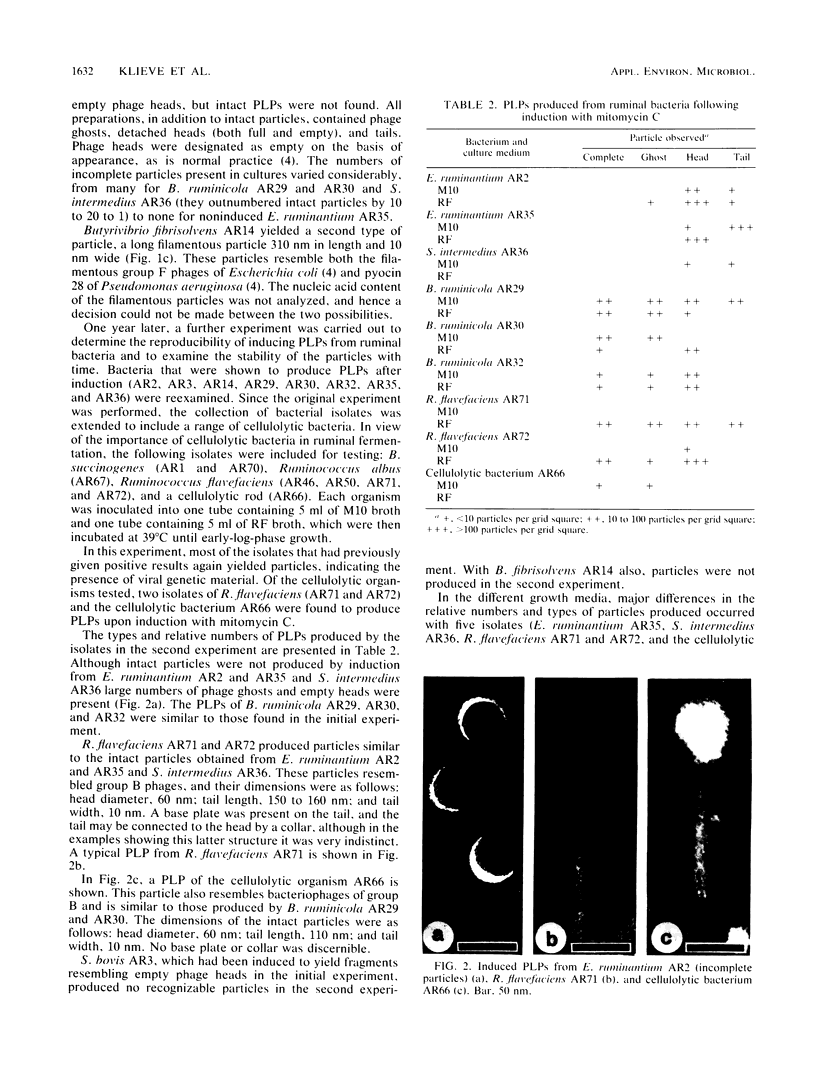
The incidence of temperate bacteriophage in a wide range of ruminal bacteria was investigated by means of induction with mitomycin C. Supernatant liquid from treated cultures was examined for phagelike particles by using transmission electron microscopy. Of 38 ruminal bacteria studied, nine organisms (23.7%) representing five genera (Eubacteria, Bacteroides, Butyrivibrio, Ruminococcus, and Streptococcus) produced phagelike particles. Filamentous particles from Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens are the first of this morphological type reported from ruminal bacteria. All of the other particles obtained possessed polyhedral heads and long, noncontractile tails (group B-type phage). The limited range of morphological types produced by mitomycin C induction cannot yet account for the much wider range of types found in ruminal contents by direct examination. The presence of viral genetic material in a significant percentage of the bacteria tested, as well as in a range of different genera, indicates that viral genetic material may be a normal constituent of the genome of appreciable numbers of ruminal bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barksdale L., Arden S. B. Persisting bacteriophage infections, lysogeny, and phage conversions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):265–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brailsford M. D., Hartman P. A. Characterization of Streptococcus durans bacteriophages. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):397–402. doi: 10.1139/m68-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. R., Bryant M. P. Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):794–801. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.794-801.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T. Interconversion of type C and D strains of Clostridium botulinum by specific bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.251-258.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T., Reed S. M., Smith C. A. Bacteriophage and the toxigenicity of Clostridium botulinum type C. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):480–482. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson W. G., Millis N. F. Characterization of Streptococcus bovis bacteriophages. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jun;22(6):847–852. doi: 10.1139/m76-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson W. G., Millis N. F. Lysogeny in Streptococcus bovis. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jun;22(6):853–857. doi: 10.1139/m76-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klieve A. V., Bauchop T. Morphological diversity of ruminal bacteriophages from sheep and cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1637–1641. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1637-1641.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockington R. A., Attwood G. T., Brooker J. D. Isolation and characterization of a temperate bacteriophage from the ruminal anaerobe Selenomonas ruminantium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1575–1580. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1575-1580.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteuzzi D., Sozzi T. Bifidobacterium bacteriophage from calf rumen. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1971;11(1):57–58. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630110108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orpin C. G., Munn E. A. The occurrence of bacteriophages in the rumen and their influence on rumen bacterial populations. Experientia. 1974 Sep 15;30(9):1018–1020. doi: 10.1007/BF01938983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paynter M. J., Ewert D. L., Chalupa W. Some morphological types of bacteriophages in bovine rumen contents. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):942–943. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.942-943.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privitera G., Dublanchet A., Sebald M. Transfer of multiple antibiotic resistance between subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):97–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamada H., Harasawa R., Shinjo T. Isolation of a bacteriophage in Fusobacterium necrophorum. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Jun;47(3):483–486. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarakanov B. V. Lizogeniia sredi kul'tur Streptococcus bovis, vydelennykh iz rubtsa korov i ovets. Mikrobiologiia. 1974 Mar;43(2):375–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M. Maintenance of Laboratory strains of obligately anaerobic rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):499–501. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.499-501.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]