Abstract
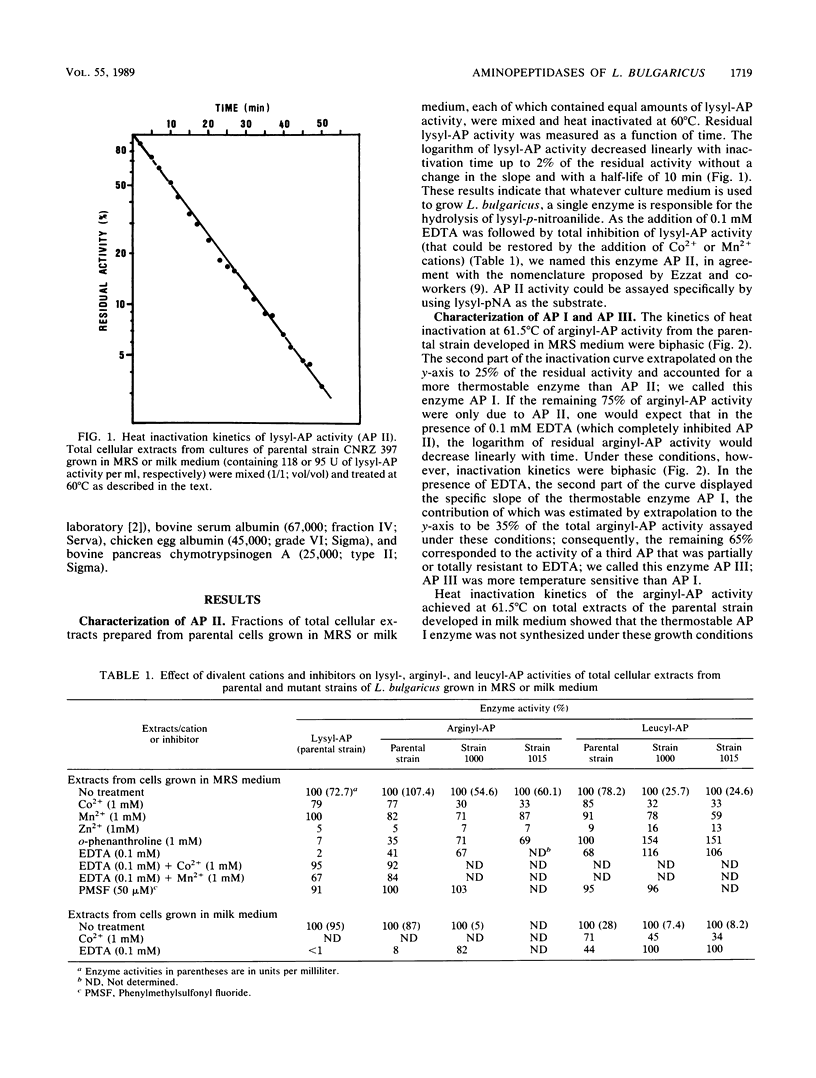
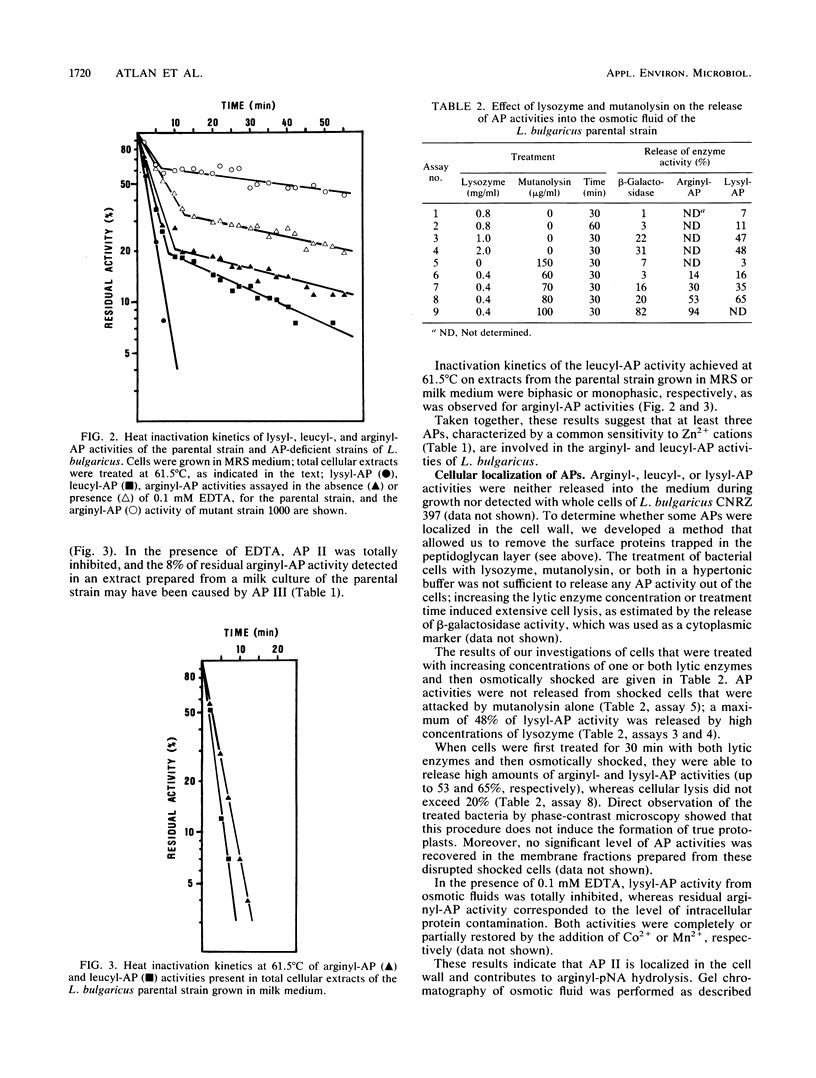
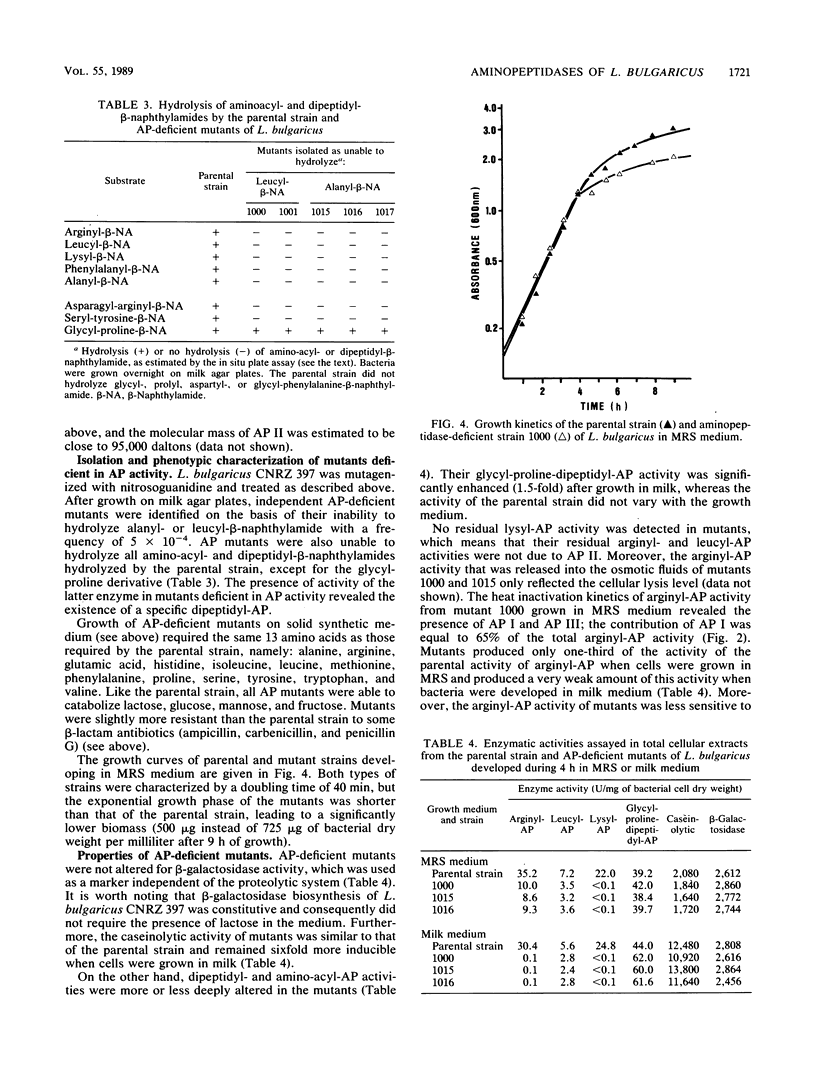
Lactobacillus bulgaricus CNRZ 397 is able to hydrolyze many amino-acyl- and dipeptidyl-β-naphthylamides. Analysis of heat inactivation kinetics, protease inhibitor effects, and the subcellular location of aminopeptidase (AP) activities from the parental strain and mutant derivatives dificient in alanyl- or leucyl-β-naphthylamide hydrolysis pointed out the existence of four APs. All mutants isolated were totally deficient in AP II, a cell wall metallo-enzyme with a broad substrate specificity but that is specifically responsible for lysyl-AP activity and is characterized by a molecular mass of 95,000 daltons. AP I and AP III are cytoplasmic enzymes that exhibit arginyl-AP activity; both enzymes are inducible during growth in rich peptide MRS medium (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Mich.). The existence of a fourth AP (AP IV) that is involved in leucyl-AP activity was suggested. Moreover, we showed that X-prolyl-dipeptidyl-AP activity, which was not catalyzed by an AP, involved an enzyme(s) that is controlled by a regulatory mechanism that is common to that of AP II.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argyle P. J., Mathison G. E., Chandan R. C. Production of cell-bound proteinase by Lactobacillus bulgaricus and its location in the bacterial cell. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;41(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey M. G., Meyer J. Presence of X-prolyl-dipeptidyl-peptidase in lactic acid bacteria. J Dairy Sci. 1985 Dec;68(12):3212–3215. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(85)81229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggimann B., Bachmann M. Purification and Partial Characterization of an Aminopeptidase from Lactobacillus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):876–882. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.876-882.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Soda M., Desmazeaud M. J. Les peptide-hydrolases des lactobacilles du groupe Thermobacterium. I. Mise en évidence de ces activités chez Lactobacillus helveticus, L. acidophilus, L. lactis et L. bulgaricus. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Oct;28(10):1181–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., de Veer G. J. Purification and Some Properties of a Membrane-Bound Aminopeptidase A from Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):577–583. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.577-583.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A., Kolstad J. Proteolytic systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):225–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00399500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledesma O. V., De Ruiz Holgado A. P., Oliver G., De Giori G. S., Raibaud P., Galpin J. V. A synthetic medium for comparative nutritional studies of lactobacilli. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;42(1):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Mackinnon K. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.355-363.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G. Peptidases and proteases of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:485–504. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled casein assay for proteolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;143(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90553-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



