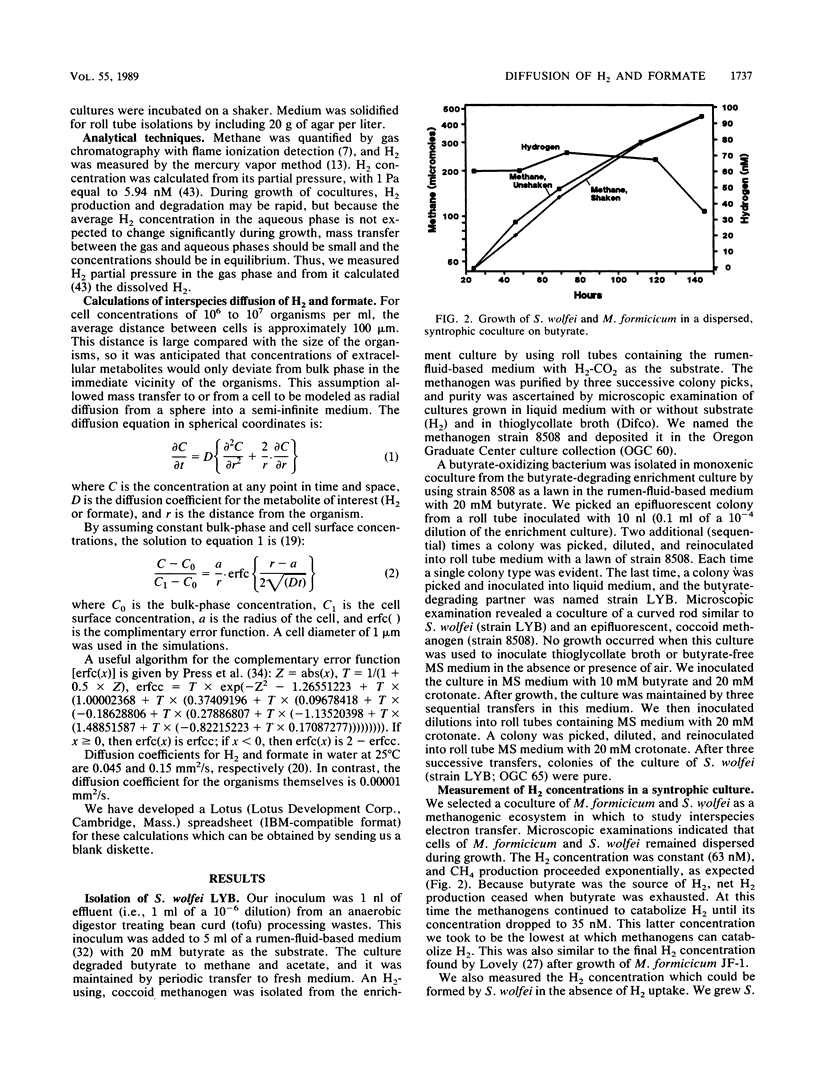
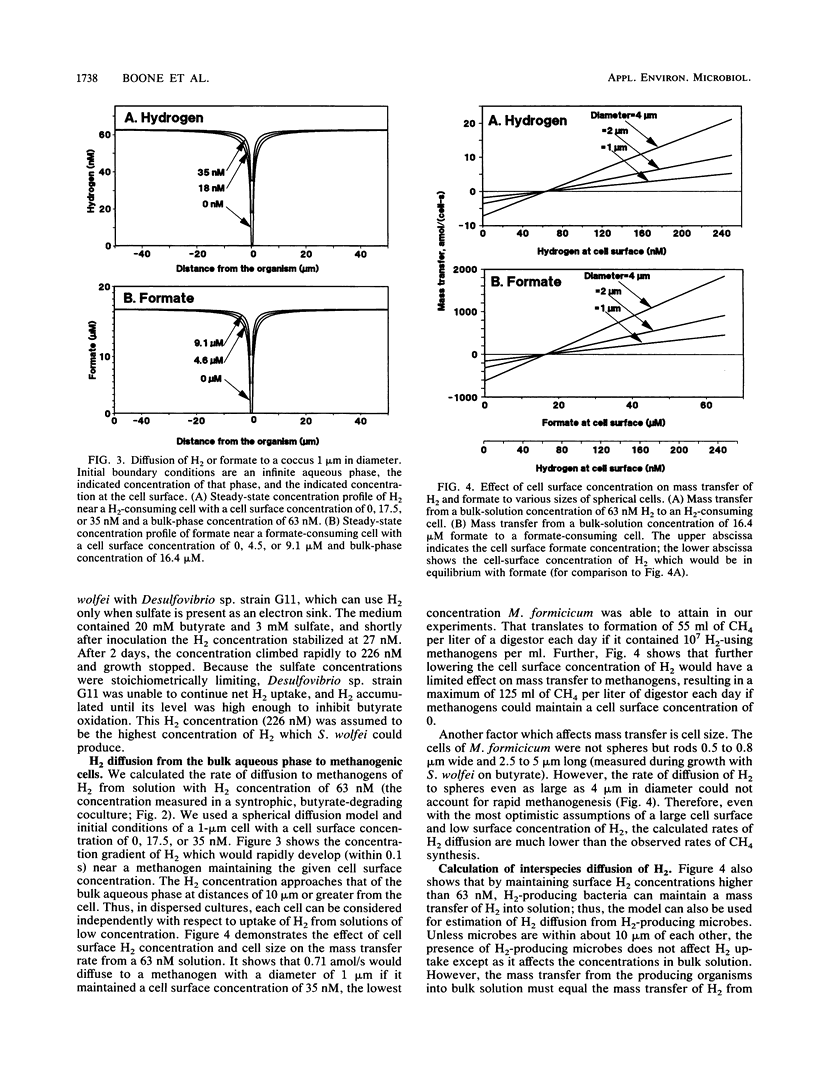
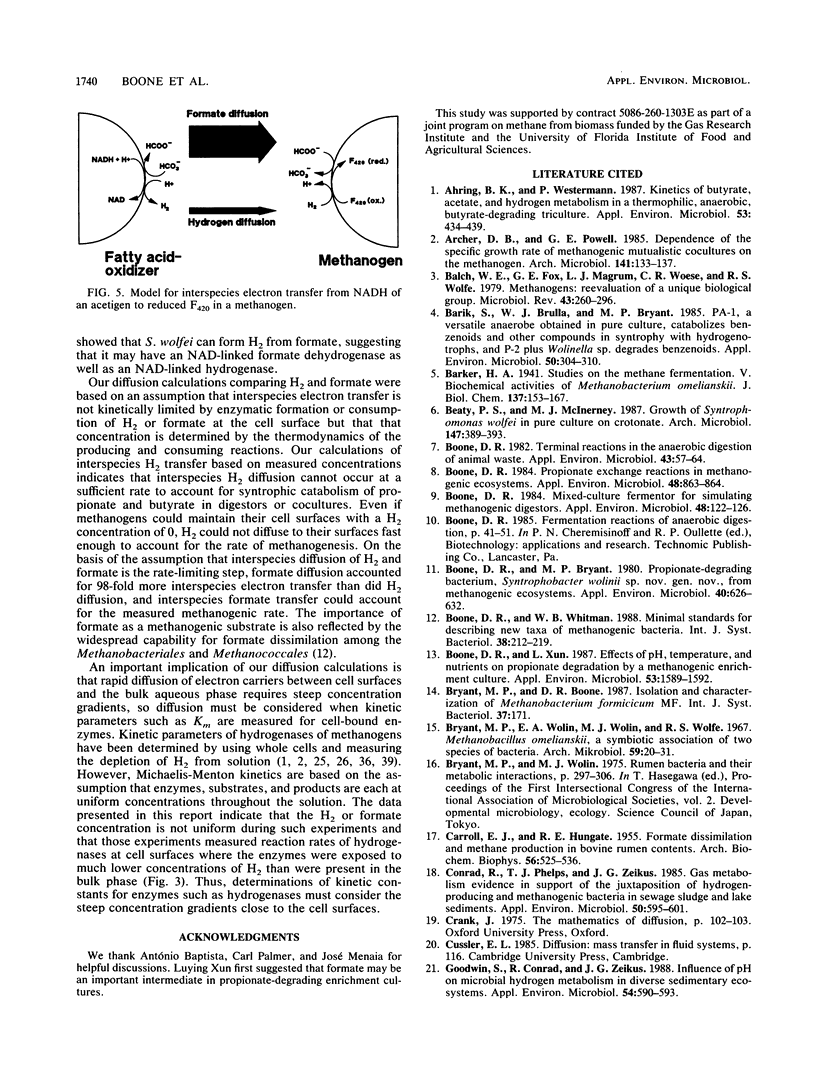
Abstract
We calculated the potential H2 and formate diffusion between microbes and found that at H2 concentrations commonly found in nature, H2 could not diffuse rapidly enough to dispersed methanogenic cells to account for the rate of methane synthesis but formate could. Our calculations were based on individual organisms dispersed in the medium, as supported by microscopic observations of butyrate-degrading cocultures. We isolated an axenic culture of Syntrophomonas wolfei and cultivated it on butyrate in syntrophic coculture with Methanobacterium formicicum; during growth the H2 concentration was 63 nM (10.6 Pa). S. wolfei contained formate dehydrogenase activity (as does M. formicicum), which would allow interspecies formate transfer in that coculture. Thus, interspecies formate transfer may be the predominant mechanism of syntrophy. Our diffusion calculations also indicated that H2 concentration at the cell surface of H2-consuming organisms was low but increased to approximately the bulk-fluid concentration at a distance of about 10 μm from the surface. Thus, routine estimation of kinetic parameters would greatly overestimate the Km for H2 or formate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahring B. K., Westermann P. Kinetics of butyrate, acetate, and hydrogen metabolism in a thermophilic, anaerobic, butyrate-degrading triculture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):434–439. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.434-439.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Brulla W. J., Bryant M. P. PA-1, a Versatile Anaerobe Obtained in Pure Culture, Catabolizes Benzenoids and Other Compounds in Syntrophy with Hydrogenotrophs, and P-2 plus Wolinella sp. Degrades Benzenoids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):304–310. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.304-310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Bryant M. P. Propionate-Degrading Bacterium, Syntrophobacter wolinii sp. nov. gen. nov., from Methanogenic Ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):626–632. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.626-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R. Mixed-culture fermentor for simulating methanogenic digestors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):122–126. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.122-126.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R. Propionate exchange reactions in methanogenic ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):863–864. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.863-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R. Terminal reactions in the anaerobic digestion of animal waste. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.57-64.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Xun L. Effects of pH, Temperature, and Nutrients on Propionate Degradation by a Methanogenic Enrichment Culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1589–1592. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1589-1592.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL E. J., HUNGATE R. E. Formate dissimilation and methane production in bovine rumen contents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jun;56(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Gas metabolism evidence in support of the juxtaposition of hydrogen-producing and methanogenic bacteria in sewage sludge and lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):595–601. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.595-601.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin S., Conrad R., Zeikus J. G. Influence of pH on microbial hydrogen metabolism in diverse sedimentary ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):590–593. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.590-593.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. M., Smith P. H. Isolation of a Butyrate-Utilizing Bacterium in Coculture with Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum from a Thermophilic Digester. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1461–1466. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1461-1466.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E., Smith W., Bauchop T., Yu I., Rabinowitz J. C. Formate as an intermediate in the bovine rumen fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.389-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Wuhrmann K. Kinetic parameters and relative turnovers of some important catabolic reactions in digesting sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.1-7.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R. Minimum threshold for hydrogen metabolism in methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1530–1531. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1530-1531.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie R. I., Bryant M. P. Metabolic Activity of Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacteria and the Contribution of Acetate, Propionate, Butyrate, and CO(2) to Methanogenesis in Cattle Waste at 40 and 60 degrees C. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1363–1373. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1363-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah R. A., Smith M. R., Baresi L. Studies on an acetate-fermenting strain of Methanosarcina. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1174–1184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1174-1184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Bryant M. P., Hespell R. B., Costerton J. W. Syntrophomonas wolfei gen. nov. sp. nov., an Anaerobic, Syntrophic, Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1029-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. A., Bryant M. P., Wolin M. J. Ferredoxin- and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent H 2 production from ethanol and formate in extracts of S organism isolated from "Methanobacillus omelianskii". J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.126-132.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteria in an anaerobic consortium that mineralizes 3-chlorobenzoic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):840–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.840-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Mah R. A. Kinetics of acetate metabolism during sludge digestion. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.368-371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer R. F., Tiedje J. M. Kinetic parameters of the conversion of methane precursors to methane in a hypereutrophic lake sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):330–340. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.330-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele Jurgen H., Chartrain M., Zeikus J. Gregory. Control of Interspecies Electron Flow during Anaerobic Digestion: Role of Floc Formation in Syntrophic Methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):10–19. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.10-19.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele Jurgen H., Zeikus J. Gregory. Control of Interspecies Electron Flow during Anaerobic Digestion: Significance of Formate Transfer versus Hydrogen Transfer during Syntrophic Methanogenesis in Flocs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):20–29. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.20-29.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


