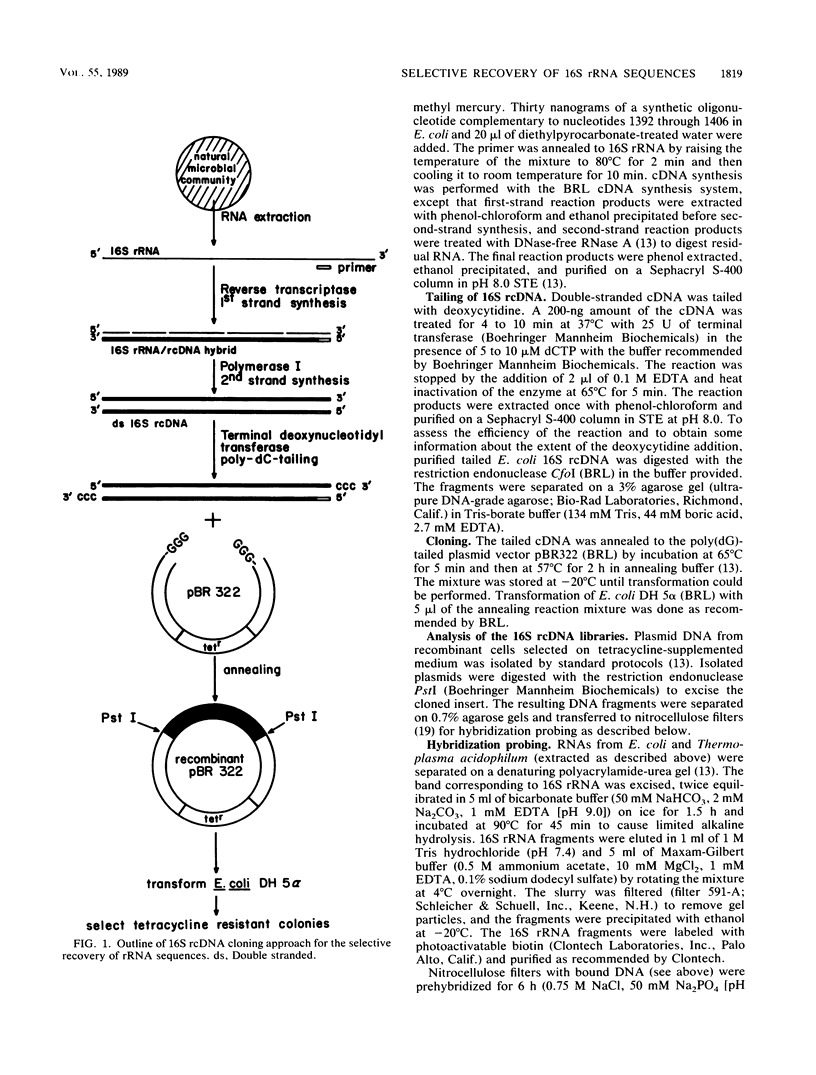
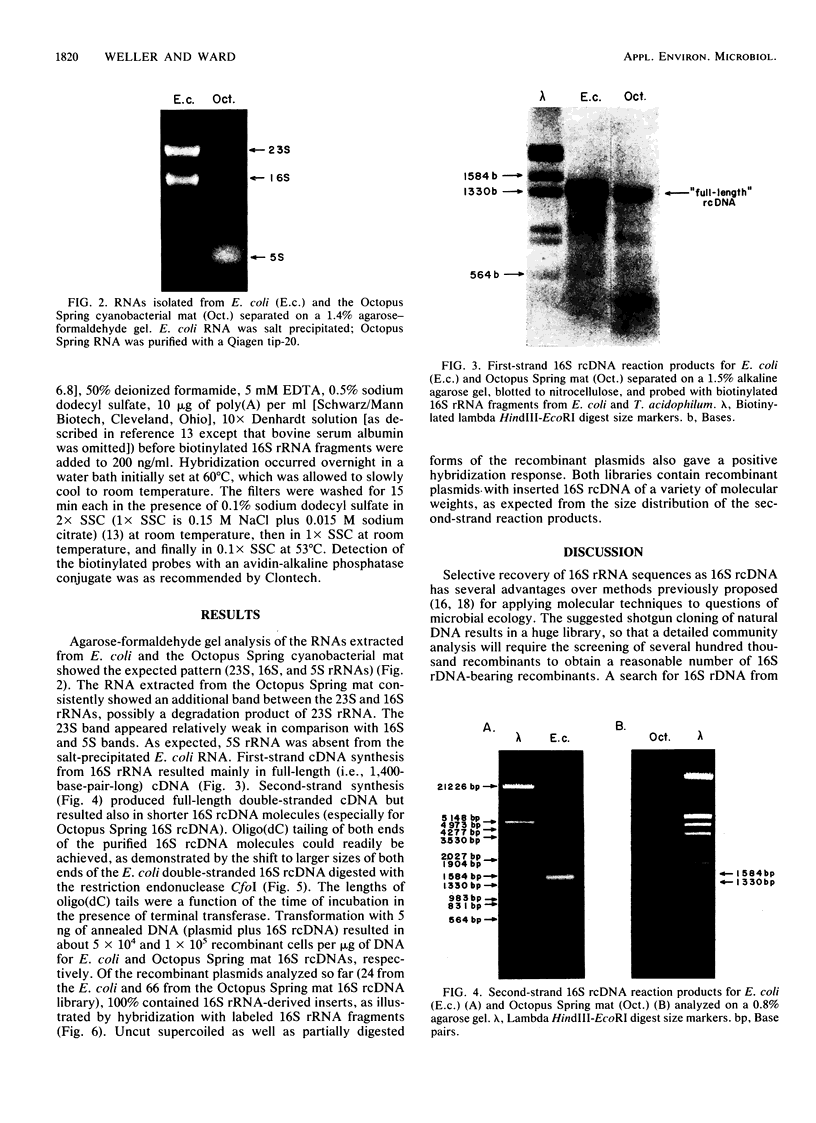
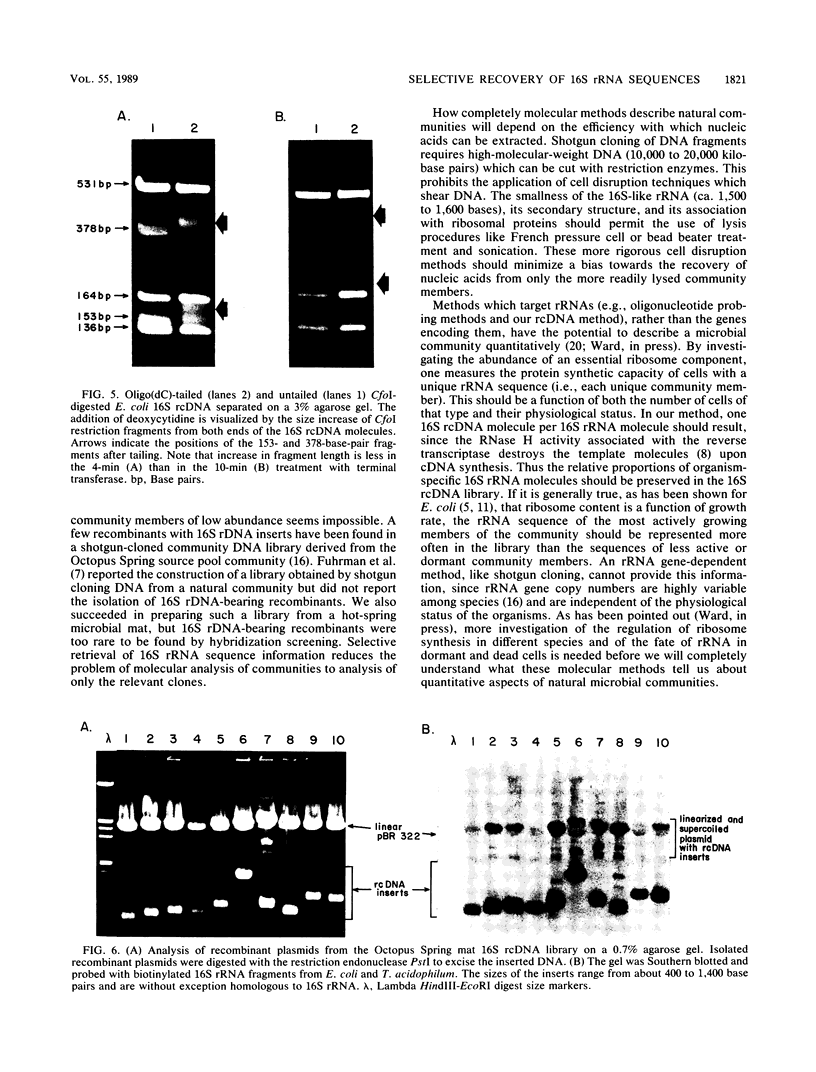
Abstract
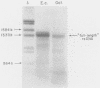
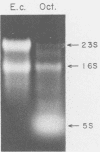
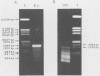
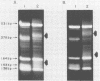
Cloning of cDNA obtained from 16S rRNA (16S rcDNA) selectively retrieves species-specific sequence information useful for analyzing the composition and structure of natural microbial communities. With this technique we obtained recombinant 16S rcDNA libraries from Escherichia coli and from a model hot-spring cyanobacterial-mat community. The recombinant plasmids contained exclusively 16S rRNA-derived inserts. This selective approach is independent of biasing culture techniques and eliminates the laborious screening required to locate 16S rRNA gene-bearing recombinants in genomic DNA libraries obtained from natural communities.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg D. D. Creating a ribonuclease-free environment. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:20–24. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doemel W. N., Brock T. D. Structure, growth, and decomposition of laminated algal-bacterial mats in alkaline hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):433–452. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.433-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Comeau D. E., Hagström A., Chan A. M. Extraction from natural planktonic microorganisms of DNA suitable for molecular biological studies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1426–1429. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1426-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard G. F. Mechanism of action of Moloney murine leukemia virus RNA-directed DNA polymerase associated RNase H (RNase H I). Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):256–265. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill T. J., Jurka J., Sobieski J. M., Pickett M. H., Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Characteristic archaebacterial 16S rRNA oligonucleotides. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:194–197. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace B., Matthews E. A., Johnson K. D., Cantor C. R., Pace N. R. Conserved 5S rRNA complement to tRNA is not required for protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Flesher B., Mansfield H. R., Montgomery L. Use of phylogenetically based hybridization probes for studies of ruminal microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1079-1084.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. M. Large- and small-scale phenol extractions. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:33–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. M. Precipitation of nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:41–48. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Macke T. J., Fox G. E. A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:143–151. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(85)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]