Abstract
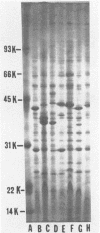
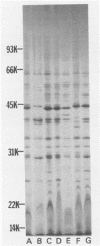
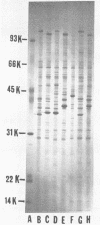
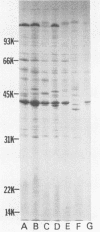
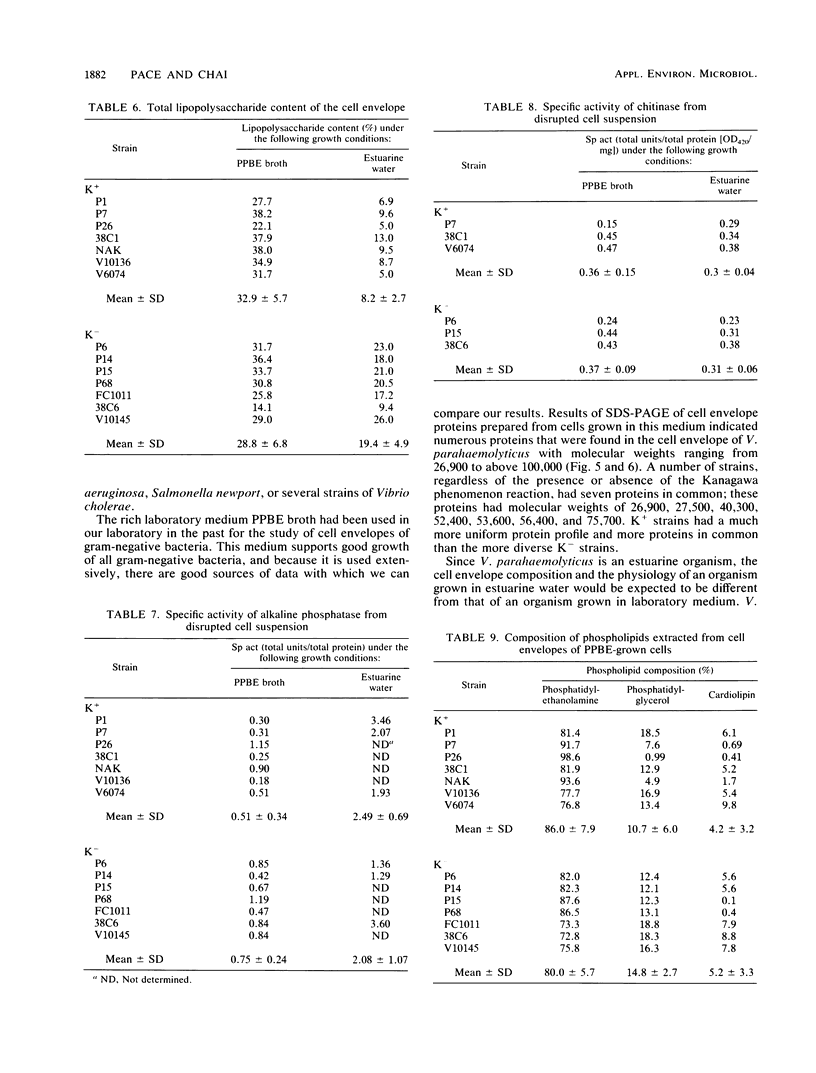
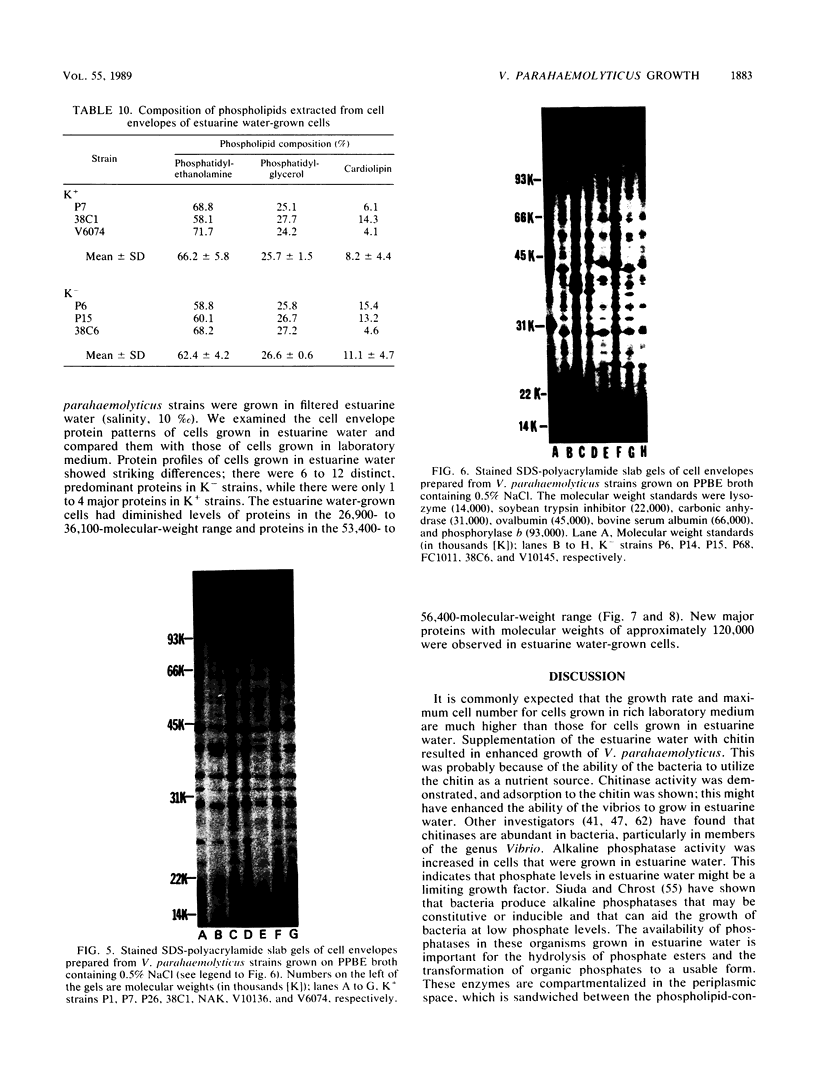
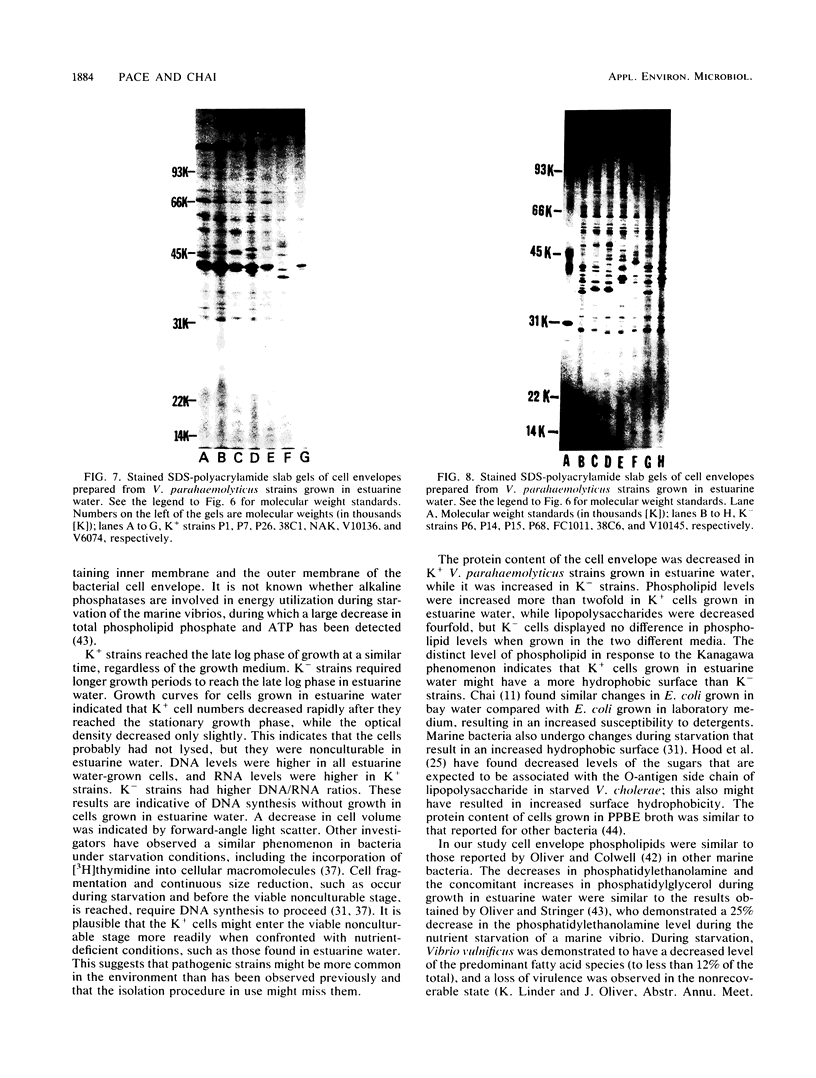
Cell envelope composition and selected physiological traits of Vibrio parahaemolyticus were studied in regard to the Kanagawa phenomenon and growth conditions. Cell envelopes were prepared from cells cultured in Proteose Peptone-beef extract (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Mich.) medium or filtered estuarine water. Protein, phospholipid, and lipopolysaccharide contents varied with culture conditions. The phospholipids present in the cell envelopes were identified as phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, and cardiolipin. Phosphatidylethanolamine decreased and phosphatidylglycerol increased in cells grown in estuarine water. Profiles of proteins separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis demonstrated numerous protein species, with four to six predominant proteins ranging from 26,000 to 120,000 in molecular weight. The profile of V. parahaemolyticus cell envelope proteins was unique and might be useful in the identification of the organism. Alkaline phosphatase activity was slightly higher in Kanagawa-negative strains and was higher in cells grown in estuarine water than in cells grown in rich laboratory medium. The DNA levels in estuarine water-grown cells increased, while RNA levels and cell volume decreased. Bacteriophage sensitivity typing demonstrated a close intraspecies relationship. Results indicated that Kanagawa-positive and -negative strains were closely related, but they could be grouped separately and may have undergone starvation-related physiological changes when cultured in estuarine water.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baross J. A., Liston J., Morita R. Y. Ecological relationship between Vibrio parahaemolyticus and agar-digesting vibrios as evidenced by bacteriophage susceptibility patterns. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.500-505.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baross J. A., Liston J., Morita R. Y. Incidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophages and other Vibrio bacteriophages in marine samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):492–499. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.492-499.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai T. J. Characteristics of Escherichia coli grown in bay water as compared with rich medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1316–1323. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1316-1323.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai T. J., Foulds J. Escherichia coli K-12 tolF mutants: alterations in protein composition of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):781–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.781-786.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. W., Sizemore R. K. Incidence of Vibrio species associated with blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) collected from Galveston Bay, Texas. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1092–1097. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1092-1097.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke C. F., Colwell R. R. Studies of the cell envelope of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Feb;19(2):241–245. doi: 10.1139/m73-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckert J. B., Hood M. A., White D. C. Phospholipid ester-linked fatty acid profile changes during nutrient deprivation of Vibrio cholerae: increases in the trans/cis ratio and proportions of cyclopropyl fatty acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):794–801. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.794-801.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., Kiuye A., Kondo S. A comparative study of the sugar composition of O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides isolated from Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(2):127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., Kiuye A., Kondo S. Sugar composition of O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides isolated from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(8):691–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Goshima K., Takeda Y., Sugino Y., Miwatani T. Demonstration of the cardiotoxicity of the thermostable direct hemolysin (lethal toxin) produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):163–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.163-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Guckert J. B., White D. C., Deck F. Effect of nutrient deprivation on lipid, carbohydrate, DNA, RNA, and protein levels in Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):788–793. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.788-793.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from Vibrio cholerae 395 (Ogawa). Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1263–1272. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1263-1272.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Incidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.251-257.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. T., Parker C. D. Identification and preliminary characterization of Vibrio cholerae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1018-1024.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M. Starvation-induced effects on bacterial surface characteristics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.497-503.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Kawata T. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3185–3196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Toyoshima S., Kawata T. Morphological varieties and host ranges of Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophages isolated from seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):466–470. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.466-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J. Effects of monovalent and divalent salts on the phospholipid and fatty acid compositions of a halotolerant Planococcus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):580–582. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.580-582.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J. Effects of temperature and sodium chloride concentration on the phospholipid and fatty acid compositions of a halotolerant Planococcus sp. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):263–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.263-270.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Colwell R. R. Extractable lipids of gram-negative marine bacteria: phospholipid composition. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):897–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.897-908.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Stringer W. F. Lipid Composition of a Psychrophilic Marine Vibrio sp. During Starvation-Induced Morphogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):461–466. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.461-466.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Rick P. D., Lehmann V., Rupprecht E., Singh M. Structure and biogenesis of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):52–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitmeyer J. C., Peterson J. W., Wilson K. J. Salmonella cytotoxin: a component of the bacterial outer membrane. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Palin W. J., Watson D. W. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in lipopolysaccharides from Vibrio metchnikovii and Vibrio parahemolyticus. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):116–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi O., Yokota K., Koshi T. Acid and alkaline phosphatases of vibrio parahaemolyticus. Jpn J Microbiol. 1972 Sep;16(5):351–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1972.tb00670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar B. L., Nair G. B., Banerjee A. K., Pal S. C. Seasonal distribution of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in freshwater environs and in association with freshwater fishes in Calcutta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.132-136.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Nelson J. D., Jr, Justice A., Colwell R. R. Incidence of Salmonella spp., Clostridium botulinum, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in an estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):723–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.723-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Formation of a defective alkaline phosphatase subunit by a mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1604–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Payne S. M. Effect of iron limitation on growth, siderophore production, and expression of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.148-155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R. W., Jangi M. S., Colwell R. R. Influence of salinity and organic nutrient concentration on survival and growth of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1080-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiano-Coico L., Darzynkiewicz Z., Melamed M. R., Weksler M. Changes in DNA content of human blood mononuclear cells with senescence. Cytometry. 1982 Sep;3(2):79–83. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Colwell R. R. Effects of microcosm salinity and organic substrate concentration on production of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):297–301. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.297-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traganos F., Darzynkiewicz Z., Sharpless T., Melamed M. R. Simultaneous staining of ribonucleic and deoxyribonucleic acids in unfixed cells using acridine orange in a flow cytofluorometric system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jan;25(1):46–56. doi: 10.1177/25.1.64567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. W., Novitsky T. J., Quinby H. L., Valois F. W. Determination of bacterial number and biomass in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):940–946. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.940-946.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortman A. T., Somerville C. C., Colwell R. R. Chitinase determinants of Vibrio vulnificus: gene cloning and applications of a chitinase probe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):142–145. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.142-145.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]