Abstract
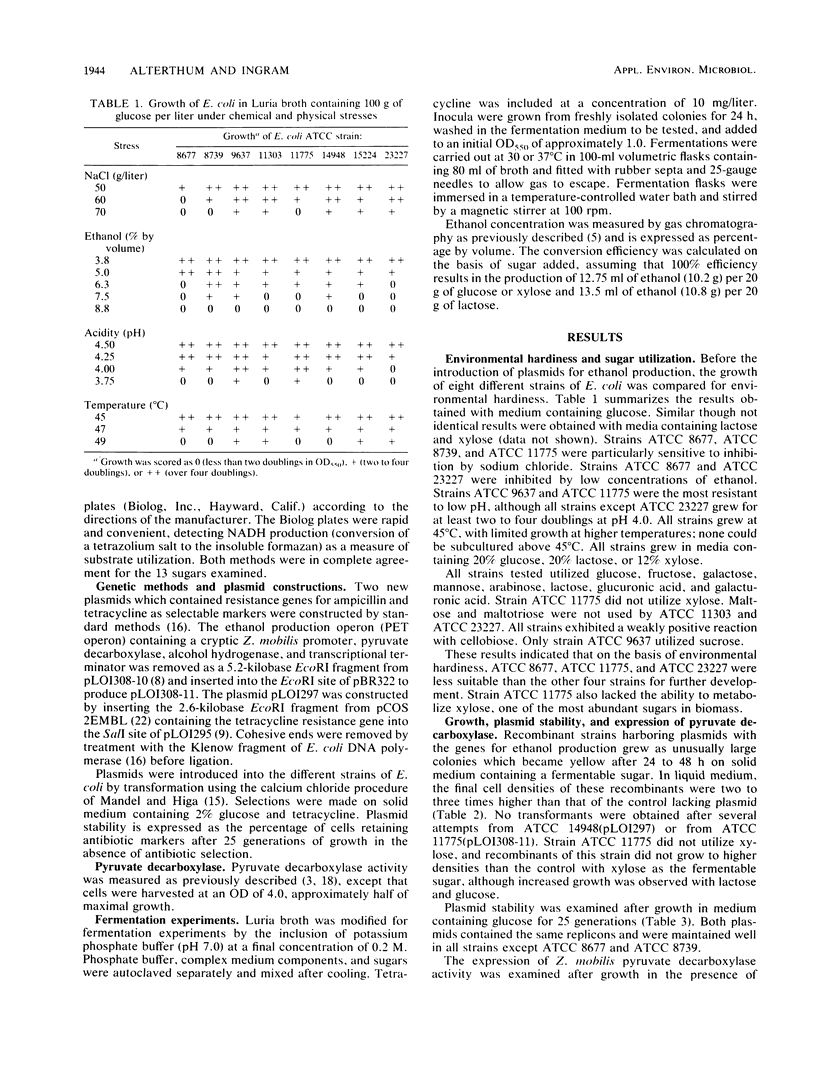
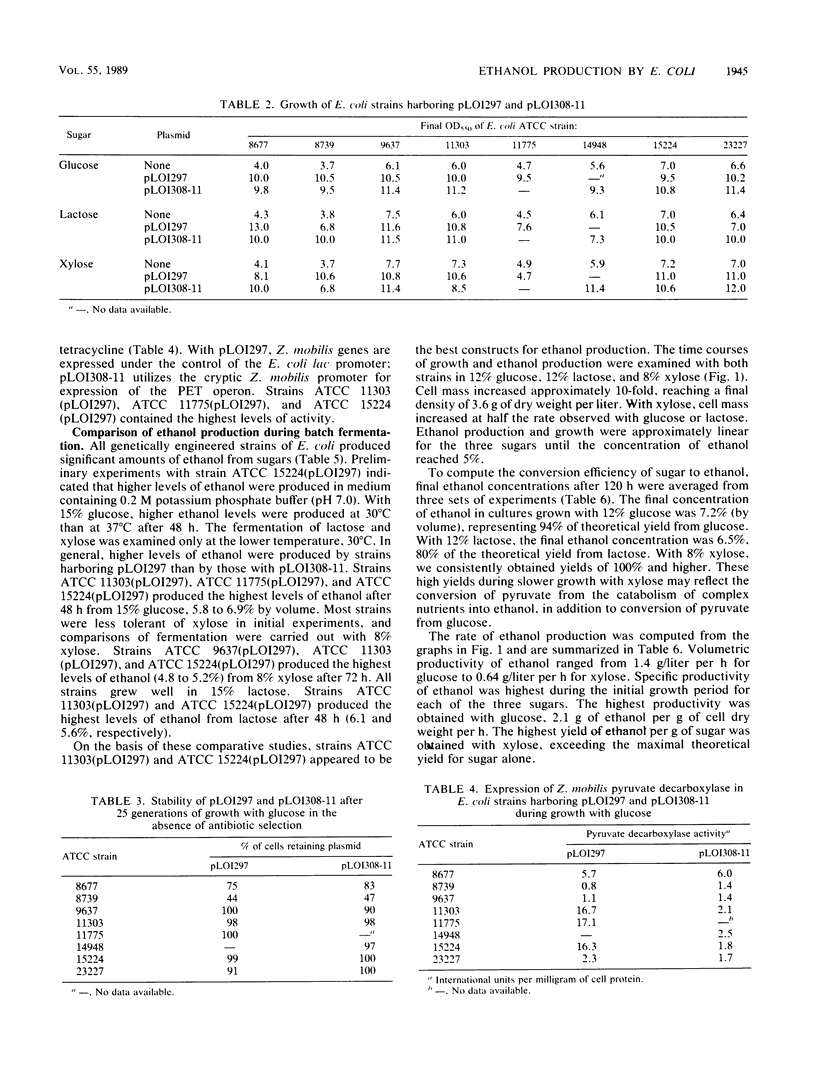
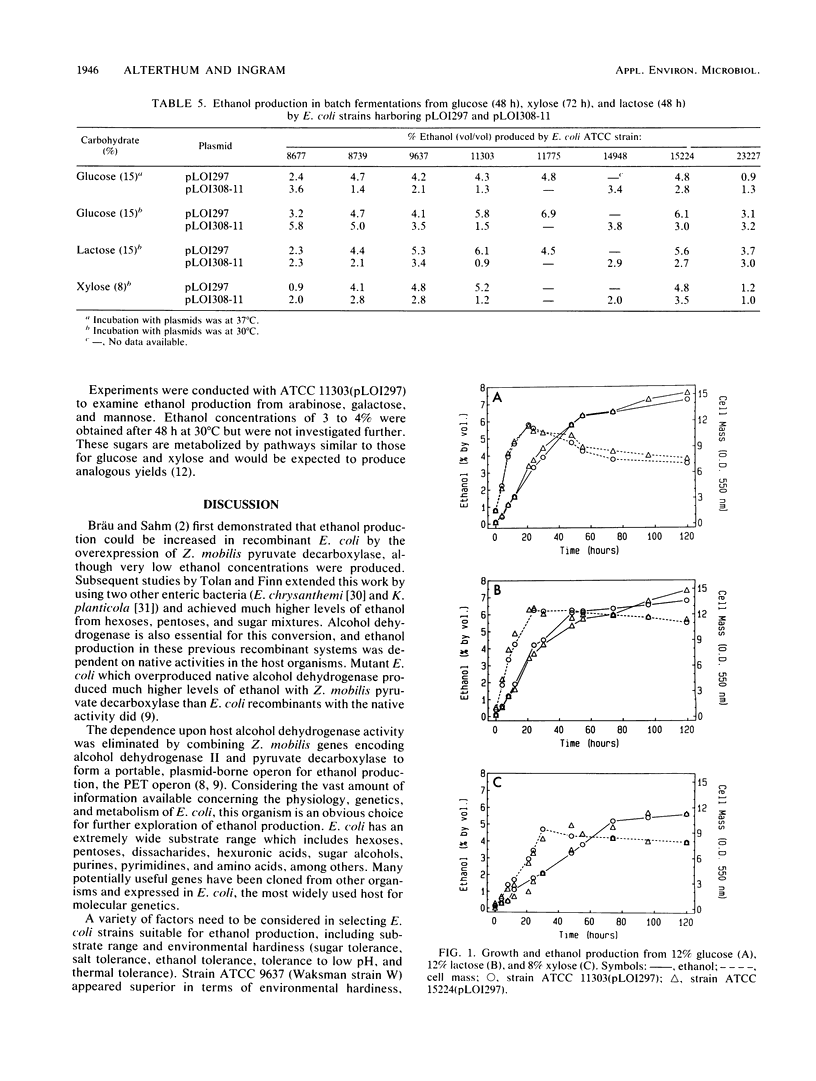
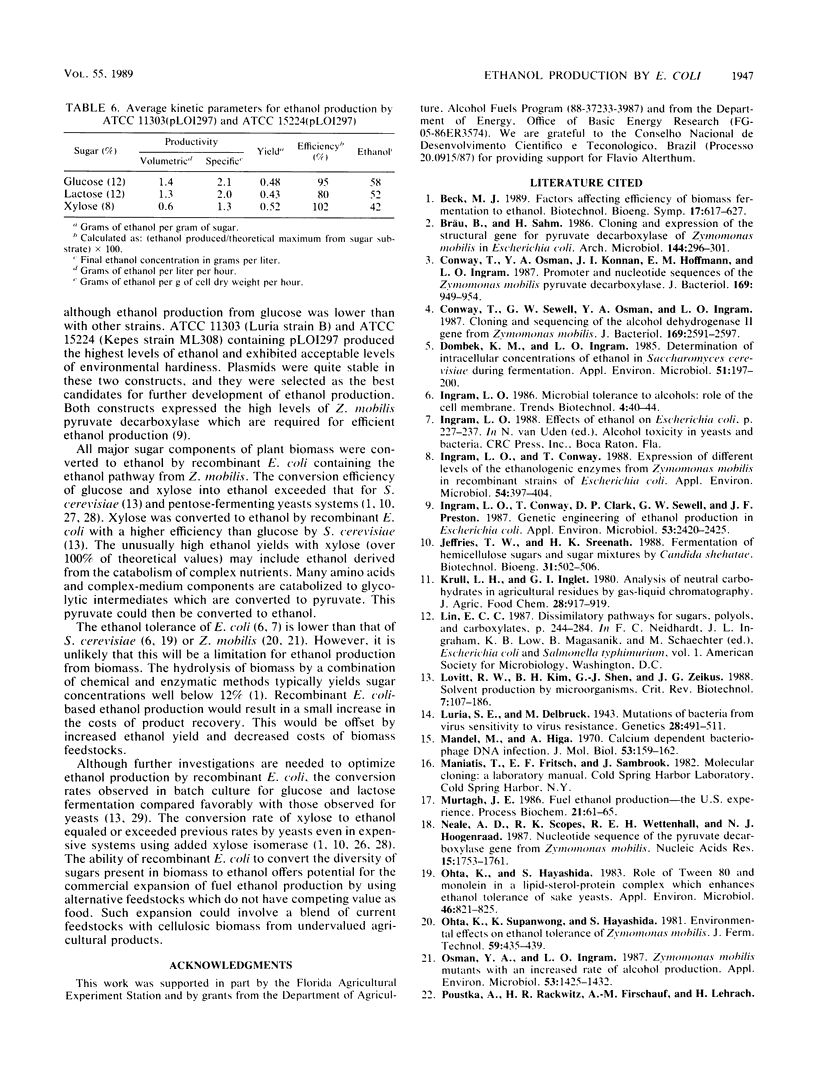
Lactose and all of the major sugars (glucose, xylose, arabinose, galactose, and mannose) present in cellulose and hemicellulose were converted to ethanol by recombinant Escherichia coli containing plasmid-borne genes encoding the enzymes for the ethanol pathway from Zymomonas mobilis. Environmental tolerances, plasmid stability, expression of Z. mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase, substrate range, and ethanol production (from glucose, lactose, and xylose) were compared among eight American Type Culture Collection strains. E. coli ATCC 9637(pLO1297), ATCC 11303(pLO1297), and ATCC 15224(pLO1297) were selected for further development on the basis of environmental hardiness and ethanol production. Volumetric ethanol productivities per hour in batch culture were 1.4 g/liter for glucose (12%), 1.3 g/liter for lactose (12%), and 0.64 g/liter for xylose (8%). Ethanol productivities per hour ranged from 2.1 g/g of cell dry weight with 12% glucose to 1.3 g/g of cell dry weight with 8% xylose. The ethanol yield per gram of xylose was higher for recombinant E. coli than commonly reported for Saccharomyces cerevisiae with glucose. Glucose (12%), lactose (12%), and xylose (8%) were converted to (by volume) 7.2% ethanol, 6.5% ethanol, and 5.2% ethanol, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conway T., Osman Y. A., Konnan J. I., Hoffmann E. M., Ingram L. O. Promoter and nucleotide sequences of the Zymomonas mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.949-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Sewell G. W., Osman Y. A., Ingram L. O. Cloning and sequencing of the alcohol dehydrogenase II gene from Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2591–2597. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2591-2597.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombek K. M., Ingram L. O. Determination of the intracellular concentration of ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae during fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):197–200. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.197-200.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Conway T., Clark D. P., Sewell G. W., Preston J. F. Genetic engineering of ethanol production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2420–2425. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2420-2425.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Conway T. Expression of Different Levels of Ethanologenic Enzymes from Zymomonas mobilis in Recombinant Strains of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):397–404. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.397-404.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krull L. H., Inglett G. E. Analysis of neutral carbohydrates in agricultural residues by gas-liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem. 1980 Sep-Oct;28(5):917–919. doi: 10.1021/jf60231a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale A. D., Scopes R. K., Wettenhall R. E., Hoogenraad N. J. Nucleotide sequence of the pyruvate decarboxylase gene from Zymomonas mobilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1753–1761. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta K., Hayashida S. Role of tween 80 and monoolein in a lipid-sterol-protein complex which enhances ethanol tolerance of sake yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):821–825. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.821-825.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osman Y. A., Ingram L. O. Zymomonas mobilis Mutants with an Increased Rate of Alcohol Production. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1425–1432. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1425-1432.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynen M., Sahm H. Comparison of the structural genes for pyruvate decarboxylase in different Zymomonas mobilis strains. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3310–3313. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3310-3313.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Uses of lac fusions for the study of biological problems. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):398–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.398-418.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrell S. L., Bernard A., Bailey R. B. Ethanol from Whey: Continuous Fermentation with a Catabolite Repression-Resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):577–580. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.577-580.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolan J. S., Finn R. K. Fermentation of d-Xylose and l-Arabinose to Ethanol by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2033–2038. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2033-2038.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolan J. S., Finn R. K. Fermentation of d-Xylose to Ethanol by Genetically Modified Klebsiella planticola. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2039–2044. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2039-2044.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


