Abstract
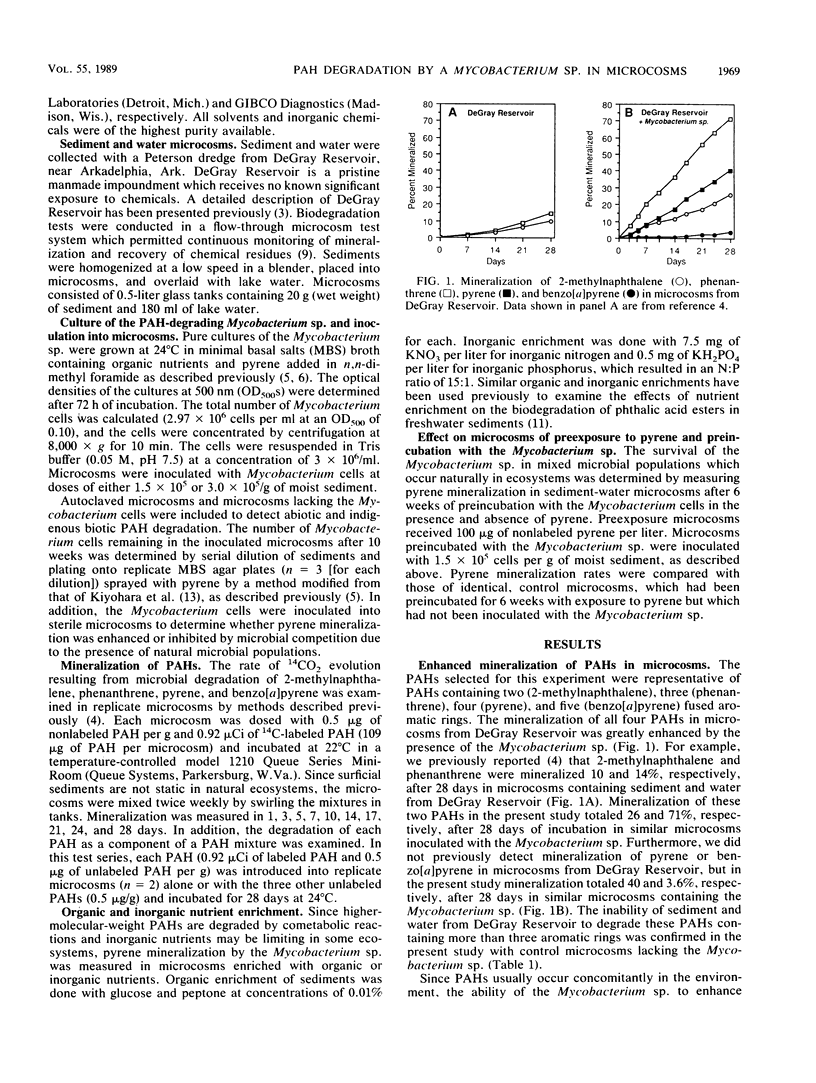
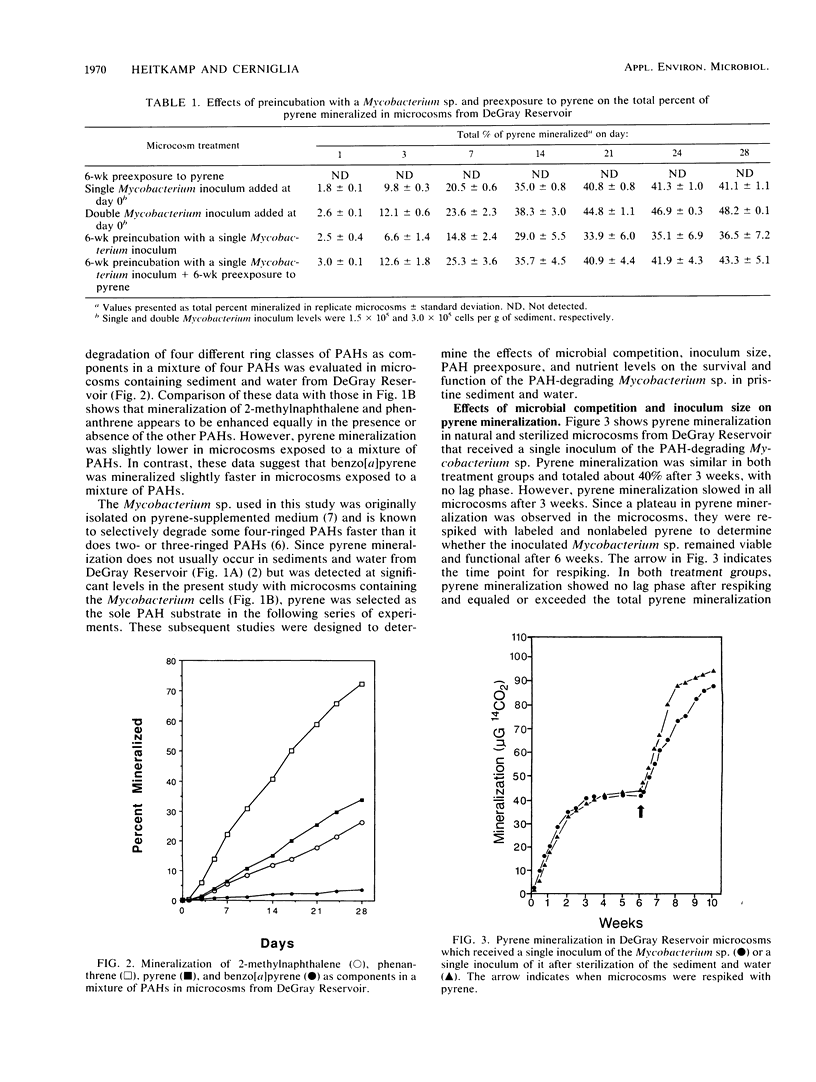
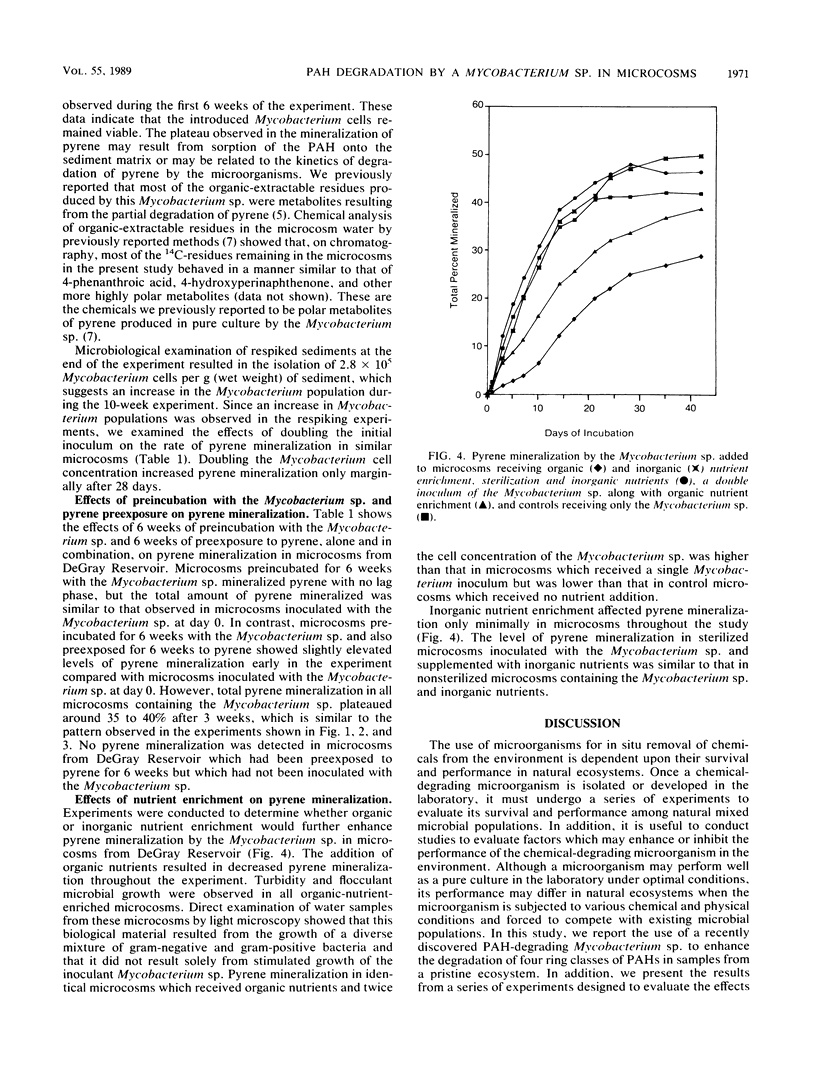
Microcosm studies were conducted to evaluate the survival and performance of a recently discovered polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading Mycobacterium sp. when this organism was added to sediment and water from a pristine ecosystem. Microcosms inoculated with the Mycobacterium sp. showed enhanced mineralization, singly and as components in a mixture, of 2-methylnaphthalene, phenanthrene, pyrene, and benzo[alpha]pyrene. Studies utilizing pyrene as the sole added PAH showed that the Mycobacterium sp. survived in microcosms for 6 weeks both with and without preexposure to PAH and mineralized multiple doses of pyrene. Pyrene mineralization rates for sterilized microcosms inoculated with the Mycobacterium sp. showed that competition with indigenous microorganisms did not adversely affect survival of or pyrene degradation by the Mycobacterium sp. Pyrene mineralization by the Mycobacterium sp. was not enhanced by inorganic nutrient enrichment and was hindered by organic nutrient enrichment, which appeared to result from overgrowth of indigenous bacteria. This study demonstrates the versatility of the PAH-degrading Mycobacterium sp. and expands its potential applications to include the degradation of two-, three-, four-, and five-ringed PAHs in sediments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Guerin W. F., Jones G. E. Mineralization of phenanthrene by a Mycobacterium sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):937–944. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.937-944.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitkamp M. A., Cerniglia C. E. Mineralization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a bacterium isolated from sediment below an oil field. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1612–1614. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1612-1614.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitkamp M. A., Franklin W., Cerniglia C. E. Microbial metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: isolation and characterization of a pyrene-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2549–2555. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2549-2555.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitkamp M. A., Freeman J. P., Miller D. W., Cerniglia C. E. Pyrene degradation by a Mycobacterium sp.: identification of ring oxidation and ring fission products. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2556–2565. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2556-2565.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyohara H., Nagao K., Yana K. Rapid screen for bacteria degrading water-insoluble, solid hydrocarbons on agar plates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):454–457. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.454-457.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Hodson R. E., Freeman L. F., 3rd Effects of microbial community interactions on transformation rates of xenobiotic chemicals. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):561–565. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.561-565.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Shields M. S., Tedford E. T., Breen A., Hooper S. W., Sirotkin K. M., Davis J. W. Application of DNA-DNA colony hybridization to the detection of catabolic genotypes in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1295–1303. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1295-1303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Pritchard P. H., Bourquin A. W. Effects of adaptation on biodegradation rates in sediment/water cores from estuarine and freshwater environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):726–734. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.726-734.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Babich H. Survival of, and genetic transfer by, genetically engineered bacteria in natural environments. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1986;31:93–138. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



