Abstract
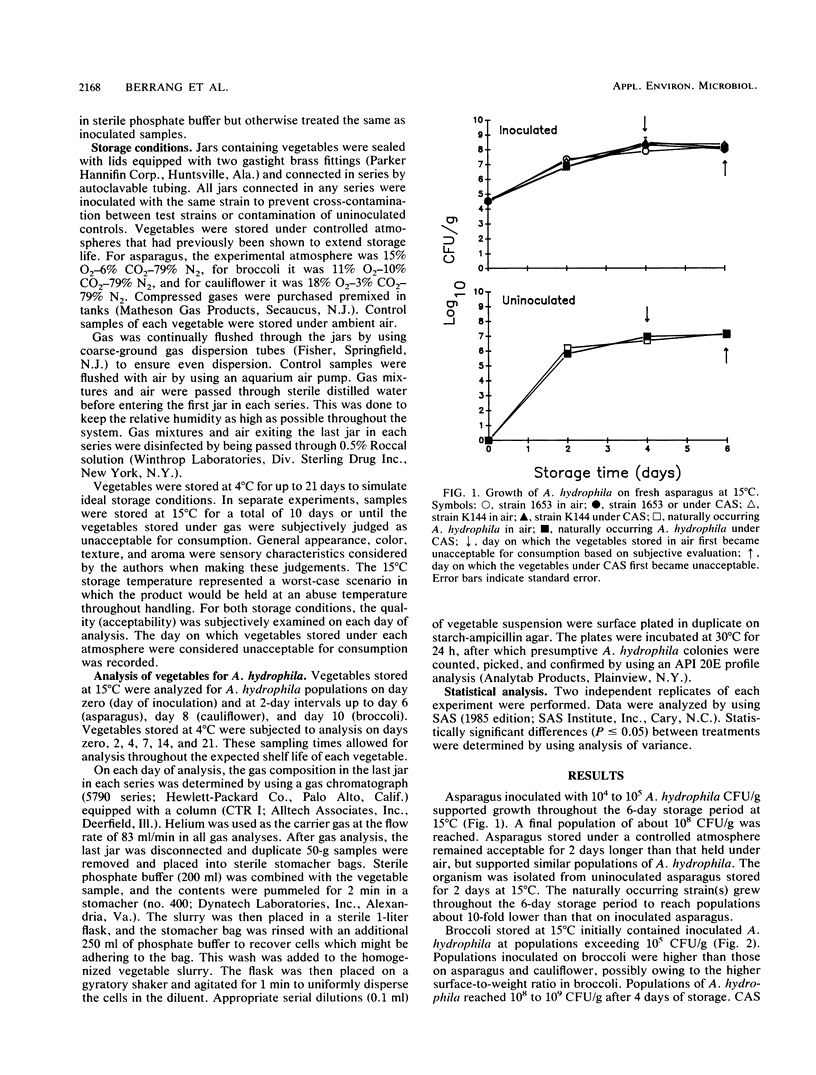
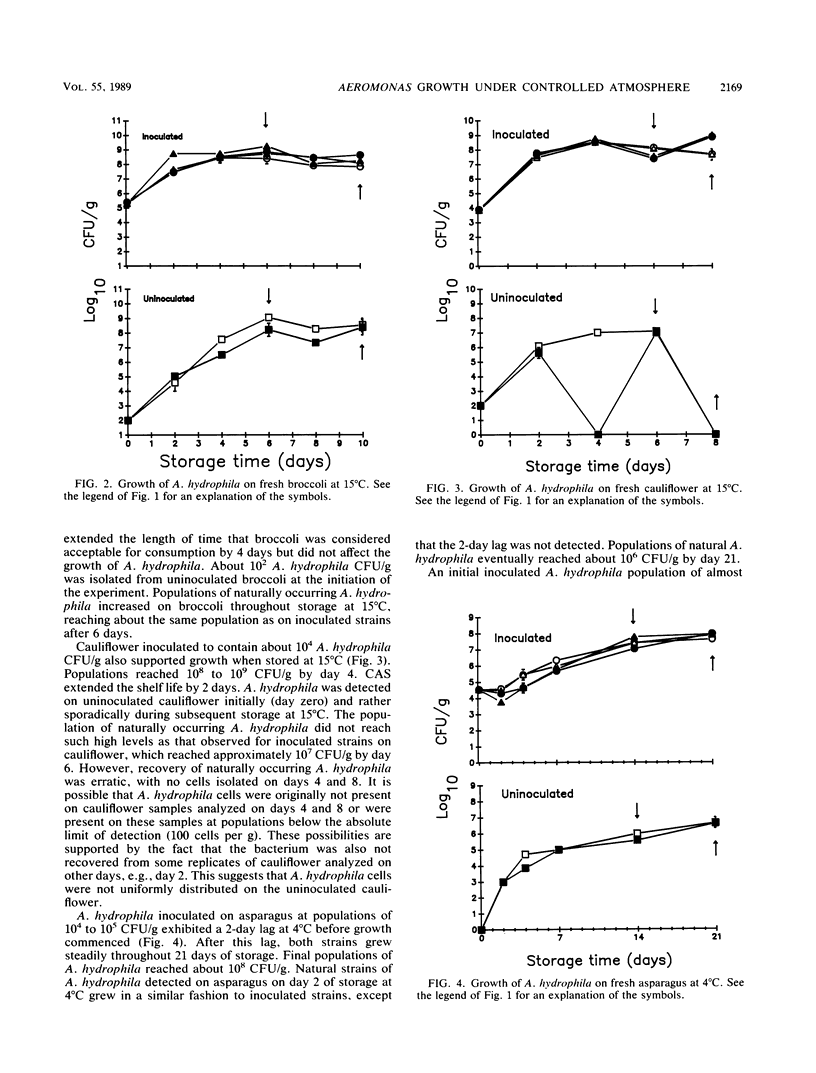
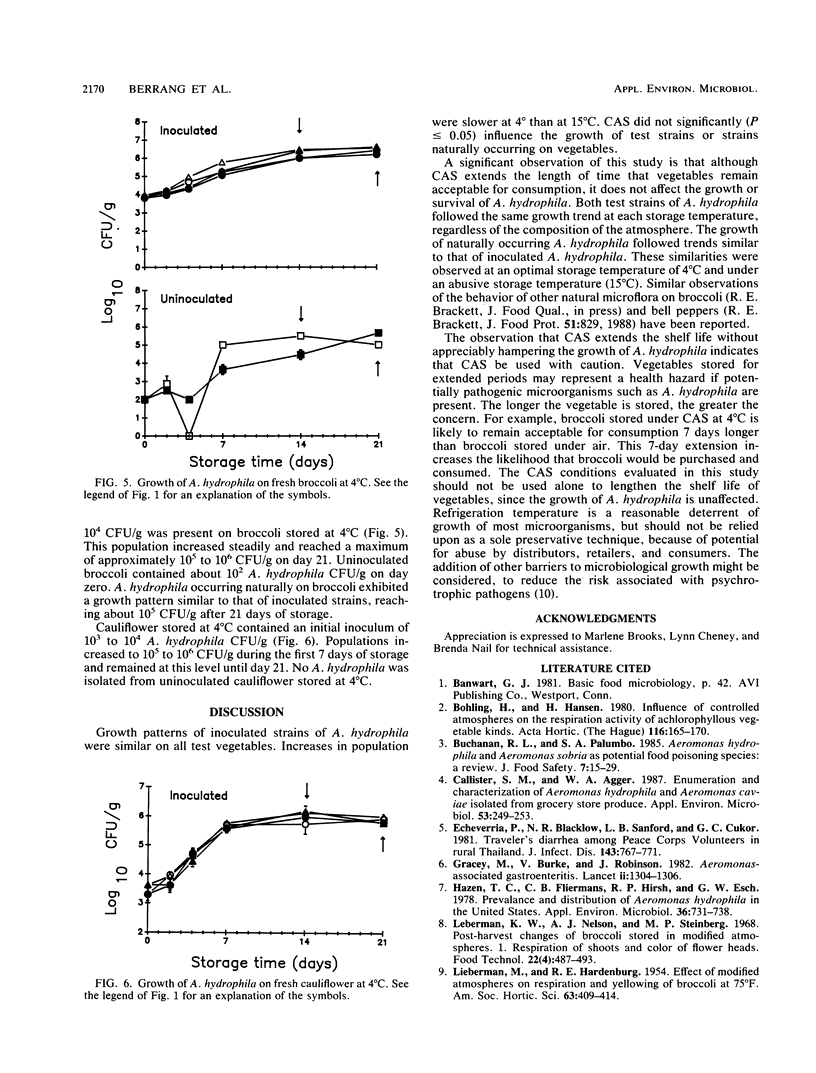
The effects of controlled-atmosphere storage (CAS) on the survival and growth of Aeromonas hydrophila on fresh asparagus, broccoli, and cauliflower were examined. Two lots of each vegetable were inoculated with A. hydrophila 1653 or K144. A third lot served as an uninoculated control. Following inoculation, vegetables were stored at 4 or 15 degrees C under a CAS system previously shown to extend the shelf life of each commodity or under ambient air. Populations of A. hydrophila were enumerated on the initial day of inoculation and at various intervals for 10 days (15 degrees C) or 21 days (4 degrees C) of storage. Direct plating of samples with selective media was used to enumerate A. hydrophila. The organism was detected on most lots of vegetables as they were received from a commercial produce supplier. Without exception, the CAS system lengthened the time vegetables were subjectively considered acceptable for consumption. However, CAS did not significantly affect populations of A. hydrophila which survived or grew on inoculated vegetables.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callister S. M., Agger W. A. Enumeration and characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas caviae isolated from grocery store produce. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):249–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.249-253.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Sanford L. B., Cukor G. G. Travelers' diarrhea among American Peace Corps volunteers in rural Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):767–771. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo S. A., Maxino F., Williams A. C., Buchanan R. L., Thayer D. W. Starch-Ampicillin Agar for the Quantitative Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1027-1030.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo S. A. The growth of Aeromonas hydrophila K144 in ground pork at 5 degrees C. Int J Food Microbiol. 1988 Aug;7(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platenius H. EFFECT OF OXYGEN CONCENTRATION ON THE RESPIRATION OF SOME VEGETABLES. Plant Physiol. 1943 Oct;18(4):671–684. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.4.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


