Abstract
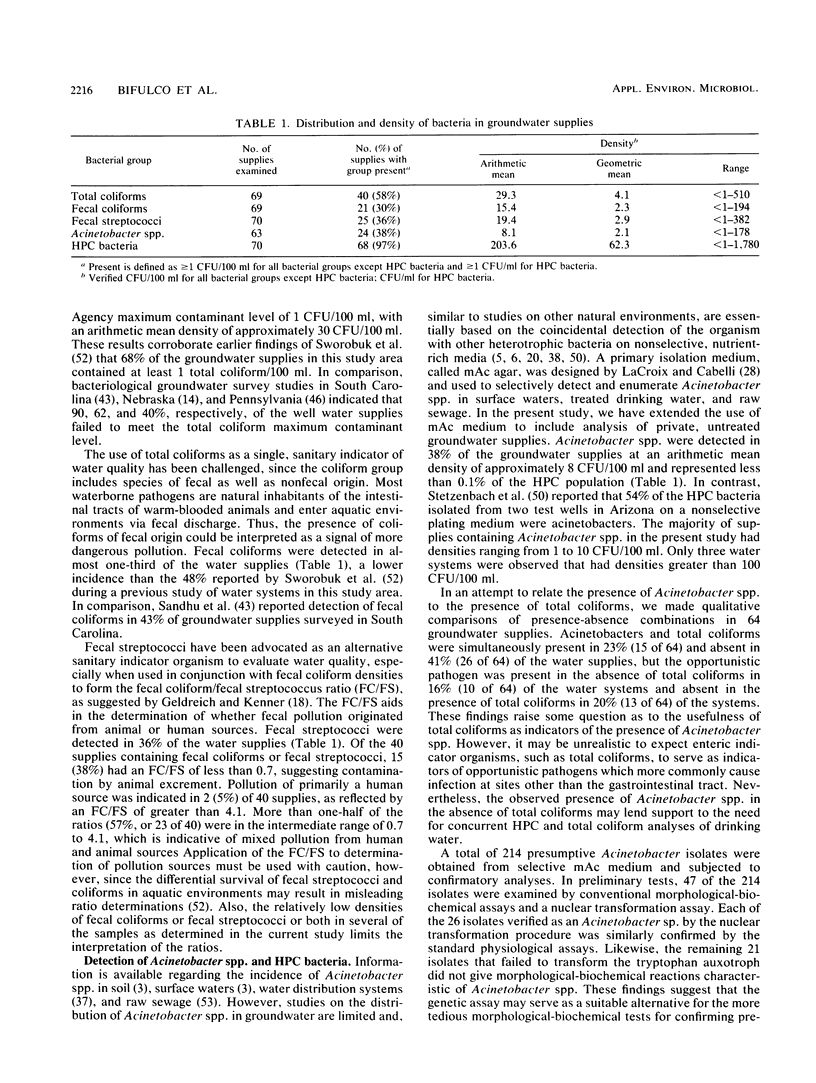
A bacteriological survey was conducted of untreated, individual groundwater supplies in Preston County, W.Va. Nearly 60% of the water supplies contained total coliforms in excess of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency maximum contaminant level of 1 CFU/100 ml. Approximately one-third of the water systems contained fecal coliforms and/or fecal streptococci. Acinetobacter spp. were detected in 38% of the groundwater supplies at an arithmetic mean density of 8 CFU/100 ml and were present in 16% of the water supplies in the absence of total coliforms, posing some concern about the usefulness of total coliforms as indicators of the presence of this opportunistic pathogen. Slime production, a virulence factor for A. calcoaceticus, was not significantly different between well water isolates and clinical strains, suggesting some degree of pathogenic potential for strains isolated from groundwater. In addition, several Acinetobacter isolates were able to interfere with sheen production by some coliform bacteria on M-Endo medium, adding further to the possible significance of Acinetobacter spp. in groundwater supplies.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrell R. A., Rowland M. G. The relationship between rainfall and well water pollution in a West African (Gambian) village. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Aug;83(1):143–150. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P. Isolation of Acinetobacter from soil and water. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.39-42.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Jones K. C., James T. W. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame G. A., McElhaney J., Bennett M., Pipes W. O. Bacterial interference with coliform colony sheen production on membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):56–60. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.56-60.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Brink E. W., Checko P. J., Lentnek A., Lyons R. W., Hayes P. S., Wu T. C., Tharr D. G., Fraser D. W. A cluster of Acinetobacter Pneumonia in foundry workers. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Dec;95(6):688–693. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-6-688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALY A. K., POSTIC B., KASS E. H. Infections due to organisms of the genus Herellea. B5W and B. anitratum. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Nov;110:580–591. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620230026006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. M., Seidler R. J., LeChevallier M. W. Impact of verification media and resuscitation on accuracy of the membrane filter total coliform enumeration technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1144–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1144-1151.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszer-Szafarz B., Szafarz D., Guevara de Murillo A. A general, fast, and sensitive micromethod for DNA determination application to rat and mouse liver, rat hepatoma, human leukocytes, chicken fibroblasts, and yeast cells. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G., Hinnebusch B. J., Kelley L. M., Sinclair N. A. Effect of noncoliforms on coliform detection in potable groundwater: improved recovery with an anaerobic membrane filter technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.142-148.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich E. E., Kenner B. A. Concepts of fecal streptococci in stream pollution. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1969 Aug;41(8 Suppl):R336+–R336+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J. Infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (Herellea vaginicola): clinical and laboratory studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Mar;56(2):79–97. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197703000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González C., Gutiérrez C., Grande T. Bacterial flora in bottled uncarbonated mineral drinking water. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Dec;33(12):1120–1125. doi: 10.1139/m87-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D. Moraxella, Acinetobacter, and the Mimeae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):522–561. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.522-561.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith A. K., Feeley J. C., Skaliy P., Wells J. G., Wood B. T. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from well water and growth in distilled water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):745–750. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.745-750.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann S., Mabeck C. E., Vejlsgaard R. Bacteriuria caused by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus biovars in a normal population and in general practice. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):443–451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.443-451.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving W. R., Jr, Herrick W. C. The bacteria Mima-herellea. Isolation and clinical significance in a general hospital. Am J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jun;47(6):729–733. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/47.6.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E. Interspecies transformation of Acinetobacter: genetic evidence for a ubiquitous genus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):917–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.917-931.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V. Survey of hemolysin production among species of pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):718–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.718-727.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix S. J., Cabelli V. J. Membrane Filter Method for Enumeration of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus from Environmental Waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.90-96.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamka K. G., LeChevallier M. W., Seidler R. J. Bacterial contamination of drinking water supplies in a modern rural neighborhood. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):734–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.734-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Seidler R. J., Evans T. M. Enumeration and characterization of standard plate count bacteria in chlorinated and raw water supplies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):922–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.922-930.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell S. S., Quinn P. Shigella sonnei isolated from well water. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):424–425. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.424-425.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means E. G., Olson B. H. Coliform inhibition by bacteriocin-like substances in drinking water distribution systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):506–512. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.506-512.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obana Y., Nishino T., Tanino T. In-vitro and in-vivo activities of antimicrobial agents against Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Apr;15(4):441–448. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obana Y., Nishino T., Tanino T. The virulence of glucose non-fermentative organisms in experimental pyelonephritis in mice. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1985 Jun;59(6):580–587. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.59.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obana Y. Pathogenic significance of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus: analysis of experimental infection in mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):645–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quevedo-Sarmiento J., Ramos-Cormenzana A., Gonzalez-Lopez J. Isolation and characterization of aerobic heterotrophic bacteria from natural spring waters in the Lanjaron area (Spain). J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;61(4):365–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS R. C., CLUFF L. E. Infection of man with Mimeae. Ann Intern Med. 1963 May;58:759–767. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-58-5-759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON R. G., GARRISON R. G., BROWN R. W. EVALUATION OF THE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THE GENUS HERELLEA. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Jan;60:19–27. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S. L. Sources of pseudomonas and acinetobacter species found in human culture materials. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Dec;62(6):807–811. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.6.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu S. S., Warren W. J., Nelson P. Magnitude of pollution indicator organisms in rural potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):744–749. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.744-749.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from surface and well waters in Ontario. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Sep;24(9):1048–1052. doi: 10.1139/m78-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spino D. F. Characterization of dysgonic, heterotrophic bacteria from drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1213–1218. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1213-1218.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warskow A. L., Juni E. Nutritional requirements of Acinetobacter strains isolated from soil, water, and sewage. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.1014-1016.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. C. The seasonality of bacterial quality of water in a tropical developing country (Sierra Leone). J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Feb;96(1):75–82. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


