Abstract
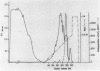
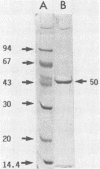
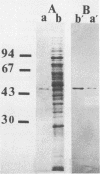
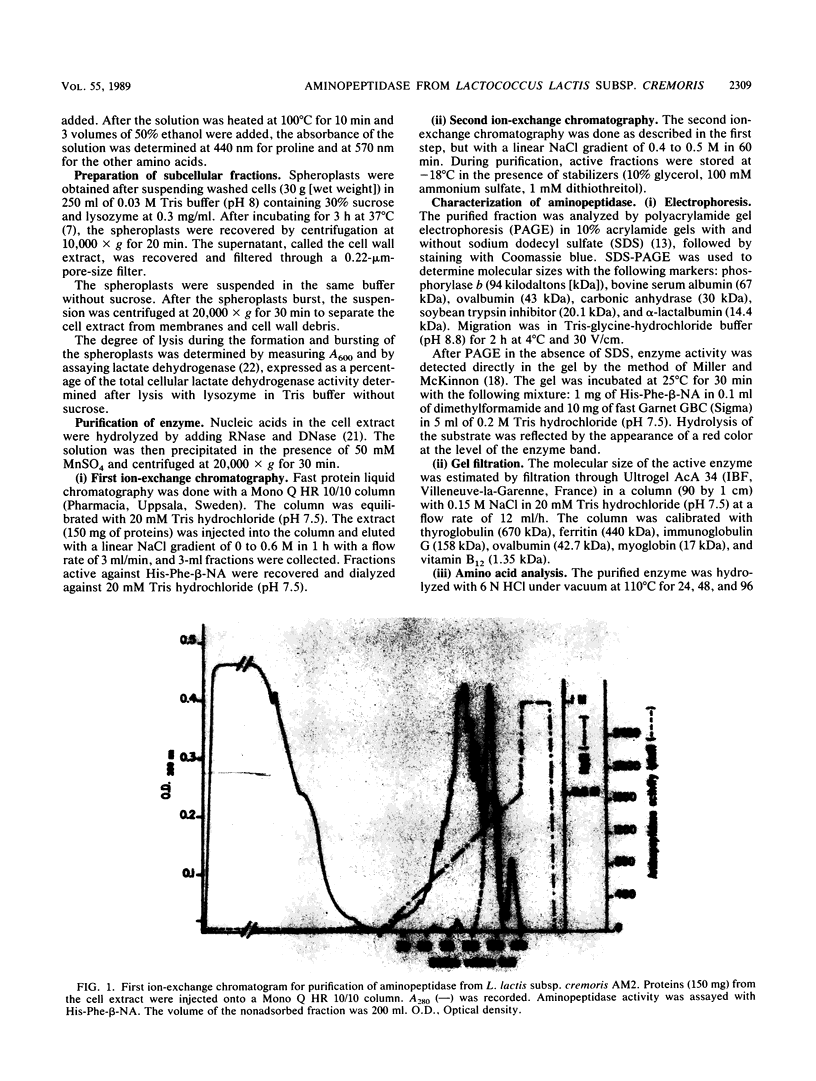
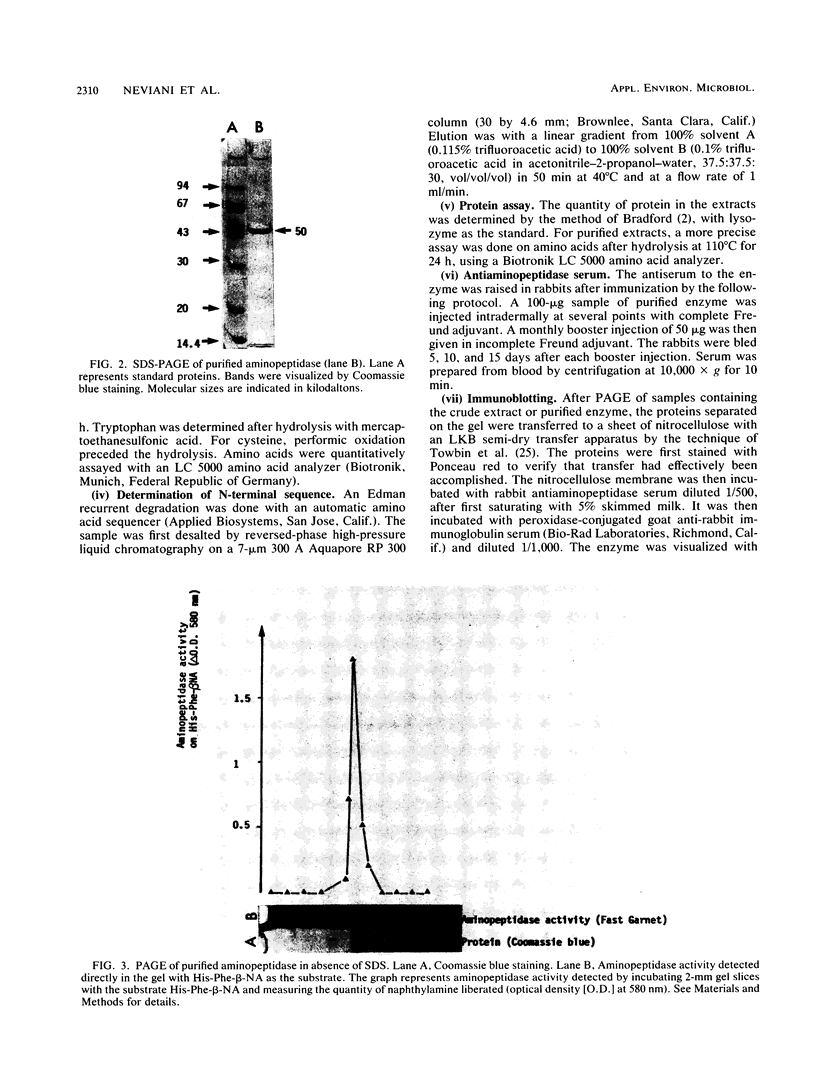
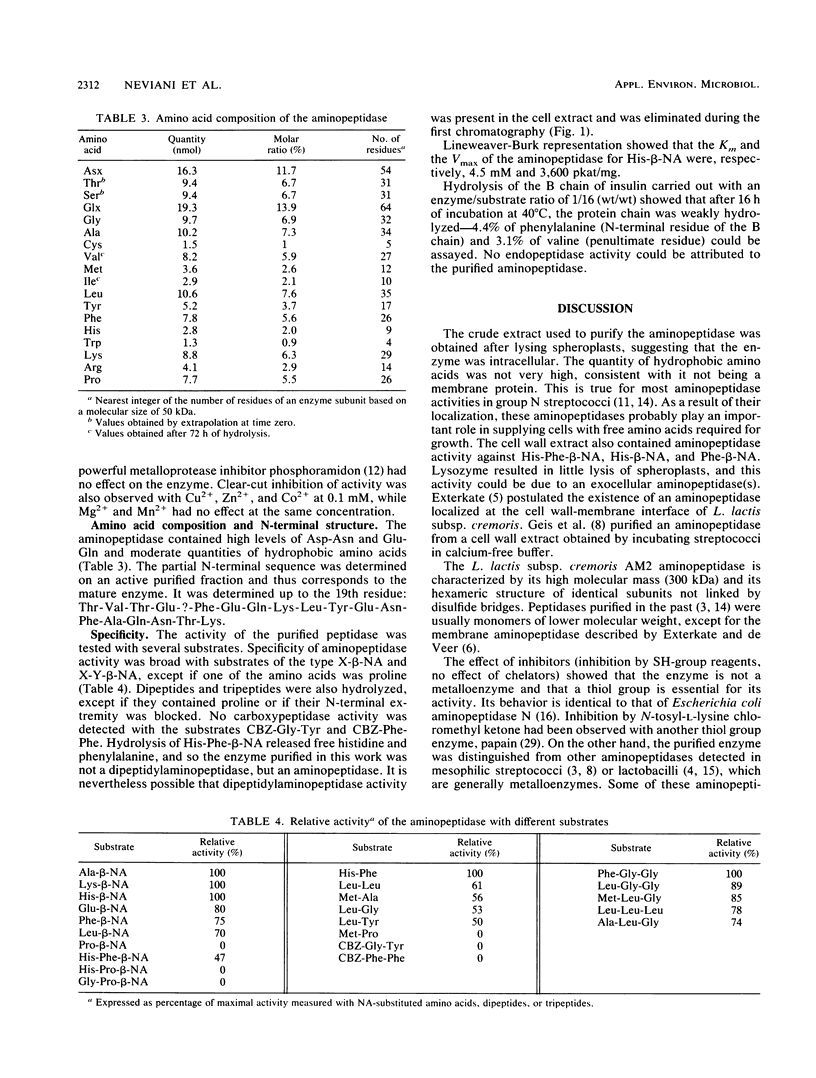
An aminopeptidase was purified from cell extracts of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris AM2 by ion-exchange chromatography. After electrophoresis of the purified enzyme in the presence or absence of sodium dodecyl sulfate, one protein band was detected. The enzyme was a 300-kilodalton hexamer composed of identical subunits not linked by disulfide bridges. Activity was optimal at 40°C and pH 7 and was inhibited by classical thiol group inhibitors. The aminopeptidase hydrolyzed naphthylamide-substituted amino acids, as well as dipeptides and tripeptides. Longer protein chains such as the B chain of insulin were hydrolyzed, but at a much slower rate. The Michaelis constant (Km) and the maximal rate of hydrolysis (Vmax) were, respectively, 4.5 mM and 3,600 pkat/mg for the substrate l-histidyl-β-naphthylamide. Amino acid analysis showed that the enzyme contained low levels of hydrophobic residues. The partial N-terminal sequence of the first 19 residues of the mature enzyme was determined. Polyclonal antibodies were obtained from the purified enzyme, and after immunoblotting, there was no cross-reaction between these antibodies and other proteins in the crude extract.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggimann B., Bachmann M. Purification and Partial Characterization of an Aminopeptidase from Lactobacillus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):876–882. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.876-882.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. Location of Peptidases Outside and Inside the Membrane of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.177-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., de Veer G. J. Purification and Some Properties of a Membrane-Bound Aminopeptidase A from Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):577–583. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.577-583.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolstad J., Law B. A. Comparative peptide specificity of cell wall, membrane and intracellular peptidases of group N streptococci. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 May;58(5):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama T., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Inhibitory effects of phosphoramidon on neutral metalloendopeptidases and its application on affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):352–357. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machuga E. J., Ives D. H. Isolation and characterization of an aminopeptidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus R-26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 28;789(1):26–36. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman M. T., Villarejo M. R. Structured and catalytic properties of peptidase N from Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):384–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Jordi R. Purification and characterization of X-prolyl-dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase from Lactobacillus lactis and from Streptococcus thermophilus. J Dairy Sci. 1987 Apr;70(4):738–745. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(87)80068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Mackinnon K. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.355-363.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabier D., Desmazeaud M. J. Inventaire des différentes activités peptidasiques intracellulaires de Streptococcus thermophilus. Purification et propriétés d'une dipeptide-hydrolase et d'une aminopeptidase. Biochimie. 1973;55(4):389–404. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Tagatose-1, 6-diphosphate activation of lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus cremoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser S., Exterkate F. A., Slangen C. J., de Veer G. J. Comparative Study of Action of Cell Wall Proteinases from Various Strains of Streptococcus cremoris on Bovine alpha(s1)-, beta-, and kappa-Casein. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1162–1166. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1162-1166.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. R., Perez-Villase ñor J. Chemical modification of papain. I. Reaction with the chloromethyl ketones of phenylalanine and lysine and with phenylmethyl-sulfonyl fluoride. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]