Abstract
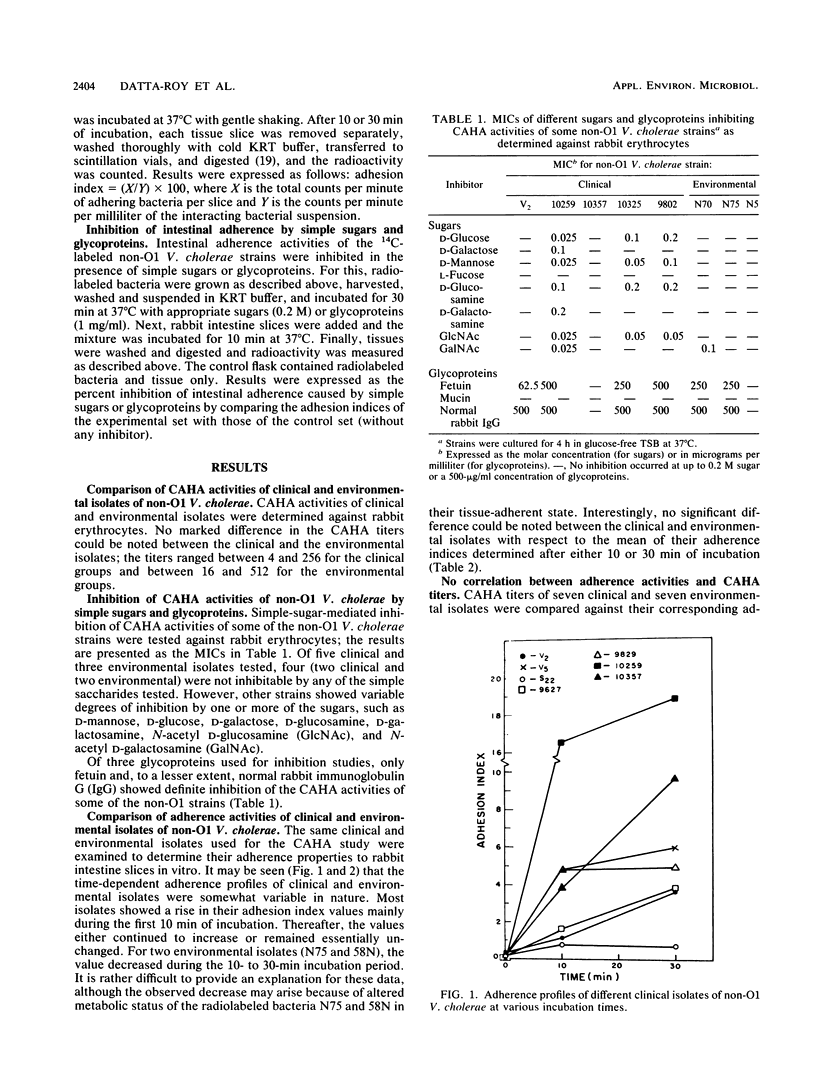
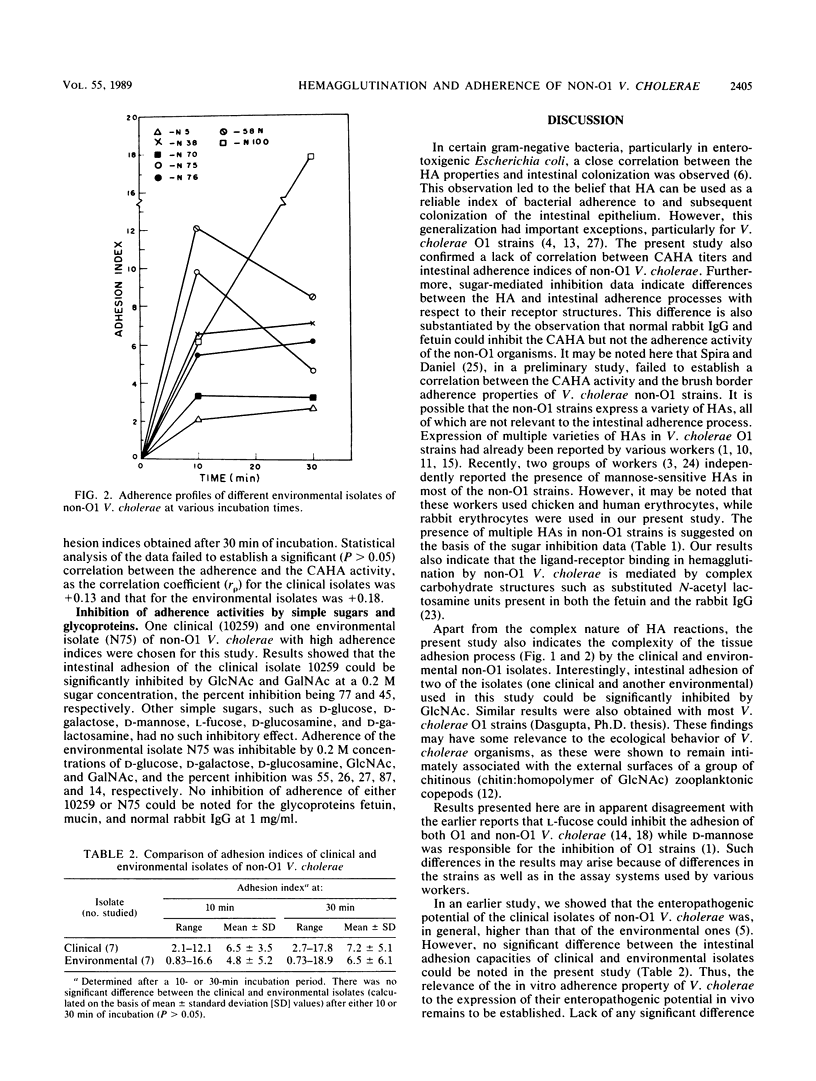
Hemagglutination and intestinal adherence properties of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae were studied in vitro. No definite correlation between the cell-associated hemagglutinin titers and the intestinal adhesion indices was noted. Sugar- and glycoprotein-mediated inhibition data also indicated differences between the hemagglutination and adherence processes in respect to the receptor structures. Intestinal adherence of most V. cholerae strains could be inhibited to various extents by N-acetyl D-glucosamine. This observation provides a likely explanation for the ecological behavior of these organisms, which are known to associate themselves with chitinous (chitin:homopolymer of N-acetyl D-glucosamine) surfaces of zooplankton. The absence of any significant difference between the intestinal adherence indices of clinical and environmental isolates suggests that intestinal adhesion may be an essential but not sufficient prerequisite for colonization by and subsequent expression of pathogenicity of these microorganisms.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharjee J. W., Srivastava B. S. Mannose-sensitive haemagglutinins in adherence of Vibrio cholerae eltor to intestine. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Aug;107(2):407–410. doi: 10.1099/00221287-107-2-407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Presence of hemagglutinin/protease and other potential virulence factors in O1 and non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):183–186. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta-Roy K., Banerjee K., De S. P., Ghose A. C. Comparative study of expression of hemagglutinins, hemolysins, and enterotoxins by clinical and environmental isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae in relation to their enteropathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):875–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.875-879.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R. Mechanisms of association of bacteria with mucosal surfaces. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:36–55. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyobu Y., Kodama H., Uetake H., Katsuda S. Studies on the enteropathogenic mechanism of non-O 1 Vibrio cholerae isolated from the environment and fish in Toyama Prefecture. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(7):735–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Finkelstein R. A. Characterization and distribution of the hemagglutinins produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):209–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.209-214.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Lindblad M. Receptor-like glycocompounds in human milk that inhibit classical and El Tor Vibrio cholerae cell adherence (hemagglutination). Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):147–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.147-154.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq A., Small E. B., West P. A., Huq M. I., Rahman R., Colwell R. R. Ecological relationships between Vibrio cholerae and planktonic crustacean copepods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.275-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S., Ali S. Characterization of surface properties of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1048-1058.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levett P. N., Daniel R. R. Adhesion of vibrios and aeromonads to isolated rabbit brush borders. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):167–172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta D., Datta-Roy K., Banerjee K., Ghose A. C. Identification of some antigenically related outer-membrane proteins of strains of Vibrio cholerae O1 and non-O1 serovars involved in intestinal adhesion and the protective role of antibodies to them. J Med Microbiol. 1989 May;29(1):33–39. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehabi A. A., Drexler H., Richardson S. H. Virulence mechanisms associated with clinical isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Apr;261(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Fedorka-Cray P. J., Pettebone P. Colonization of the rabbit small intestine by clinical and environmental isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1175–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1175-1183.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton W. C., 3rd, Wawrukiewicz A., Melo J. C., Schiller M. G., Raff M. J. Anaerobic osteomyelitis of long bones. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):692–712. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppema J. S., Guinée P. A., Ibrahim A. A., Pâques M., Ruitenberg E. J. In vivo adherence and colonization of Vibrio cholerae strains that differ in hemagglutinating activity and motility. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2093–2102. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2093-2102.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twedt R. M., Madden J. M., Hunt J. M., Francis D. W., Peeler J. T., Duran A. P., Hebert W. O., McCay S. G., Roderick C. N., Spite G. T. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae isolated from oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1475–1478. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1475-1478.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


