Abstract
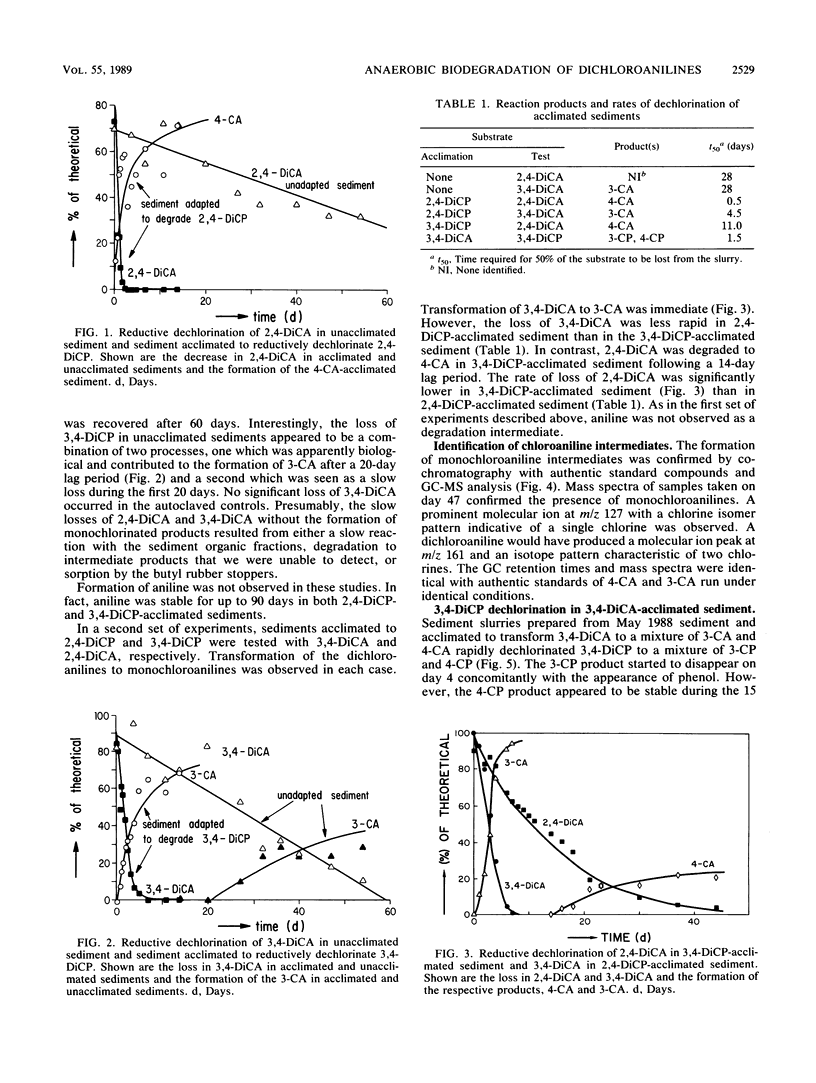
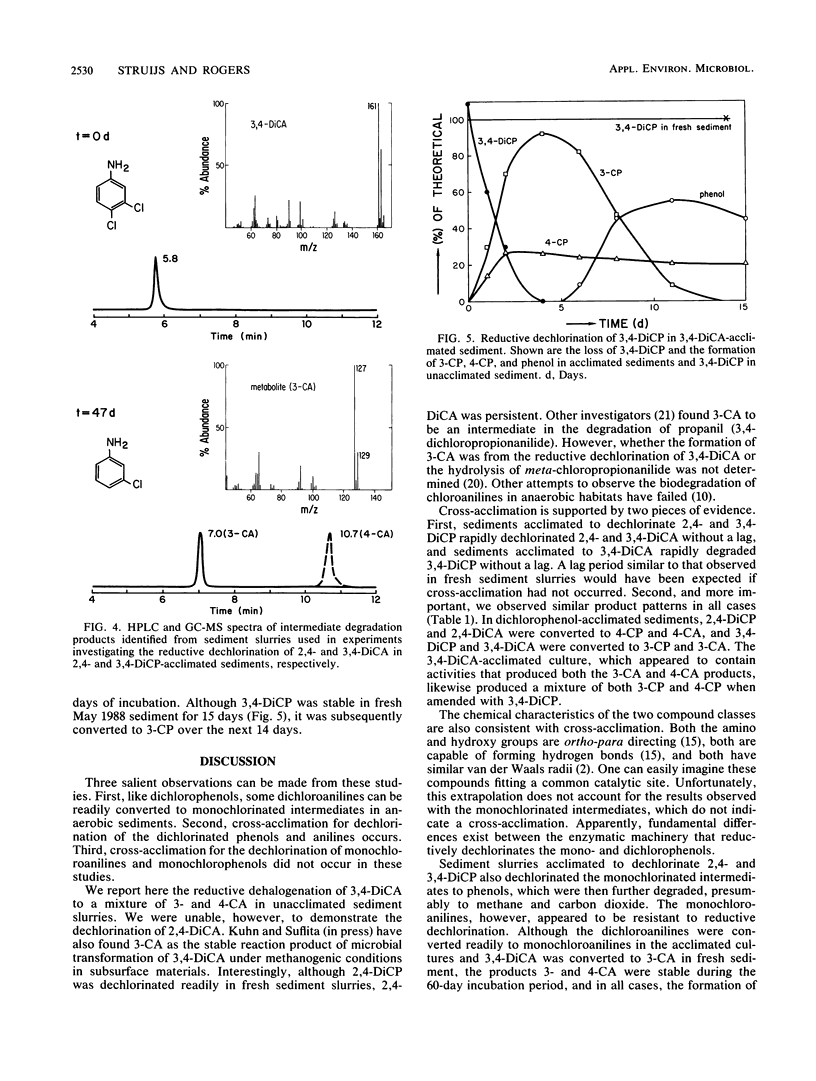
We investigated the transformation of 2,4-dichloroaniline (2,4-DiCA) and 3,4-DiCA to monochloroanilines (CA) in anaerobic pond sediment. Dechlorination of 3,4-DiCA to 3-CA started after a lag period of 3 weeks and was complete after an additional 5 weeks. Although 2,4-DiCA disappeared over 8 weeks, the appearance of a CA product could not be detected. In contrast, anaerobic bacteria in pond sediment acclimated to dehalogenate 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DiCP) or 3,4-DiCP rapidly dechlorinated 2,4-DiCA and 3,4-DiCA without any lag time. By comparison, anaerobic sediment bacteria acclimated to 3,4-DiCA rapidly degraded 3,4-DiCP without a lag. In all cases, the CA products were stable for the duration of the experiments. It is concluded that cross-acclimation occurred.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouwer E. J., McCarty P. L. Transformations of 1- and 2-carbon halogenated aliphatic organic compounds under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1286–1294. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1286-1294.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esaac E. G., Matsumura F. Metabolism of insecticides by reductive systems. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;9(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathepure B. Z., Tiedje J. M., Boyd S. A. Reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene to tri- and dichlorobenzenes in anaerobic sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):327–330. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.327-330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerike P., Fischer W. K. A correlation study of biodegradability determinations with various chemicals in various tests. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1979 Jun;3(2):159–173. doi: 10.1016/0147-6513(79)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Extrapolation of biodegradation results to groundwater aquifers: reductive dehalogenation of aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):681–688. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.681-688.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenzi W. D., Beard W. E. Anaerobic biodegradation of DDT to DDD in soil. Science. 1967 May 26;156(3778):1116–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3778.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A., Suflita J. M., Tiedje J. M. Reductive dehalogenations of halobenzoates by anaerobic lake sediment microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1459-1465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagnow G., Haider K., Ellwardt P. C. Anaerobic dechlorination and degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Dec 15;115(3):285–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00446454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney P. C., Kaufman D. D. Enzyme from Soil Bacterium Hydrolyzes Phenylcarbamate Herbicides. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):740–741. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter H. A., King E. F. A respirometric method for the assessment of ready biodegradability: results of a ring test. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1985 Feb;9(1):6–16. doi: 10.1016/0147-6513(85)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Wasserfallen A., Timmis K. N. Microbial mineralization of ring-substituted anilines through an ortho-cleavage pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):447–453. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.447-453.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



