Abstract
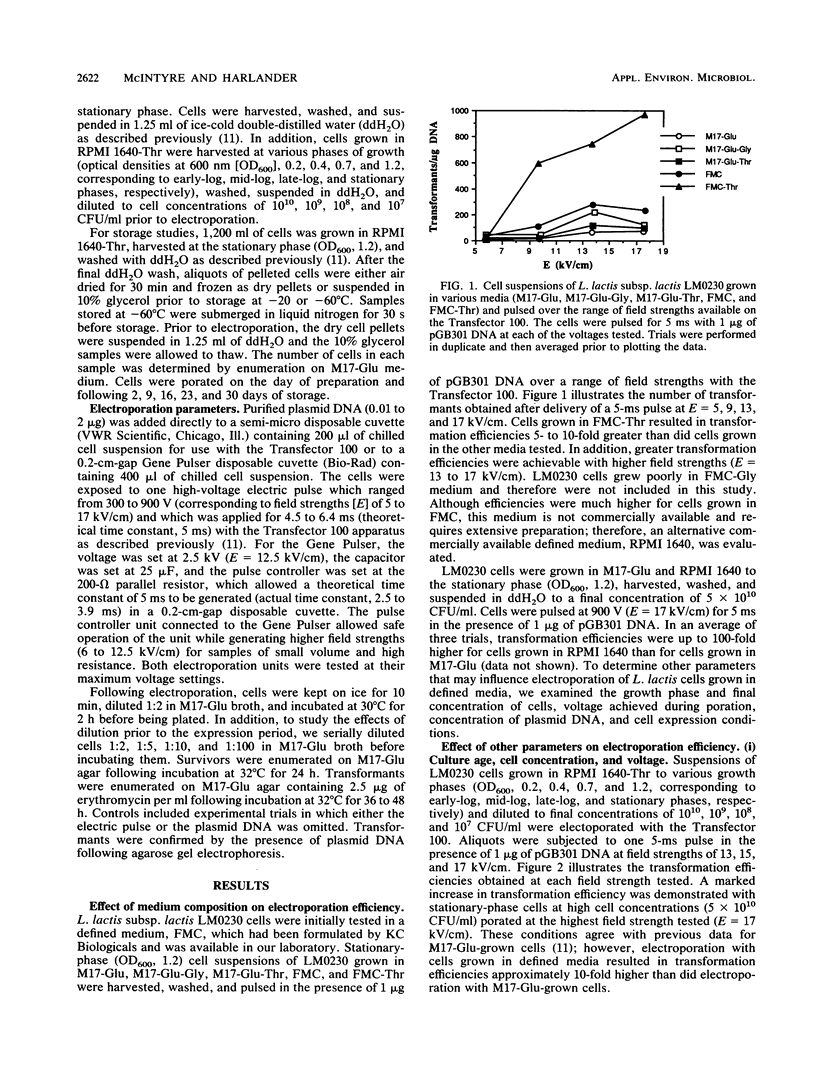
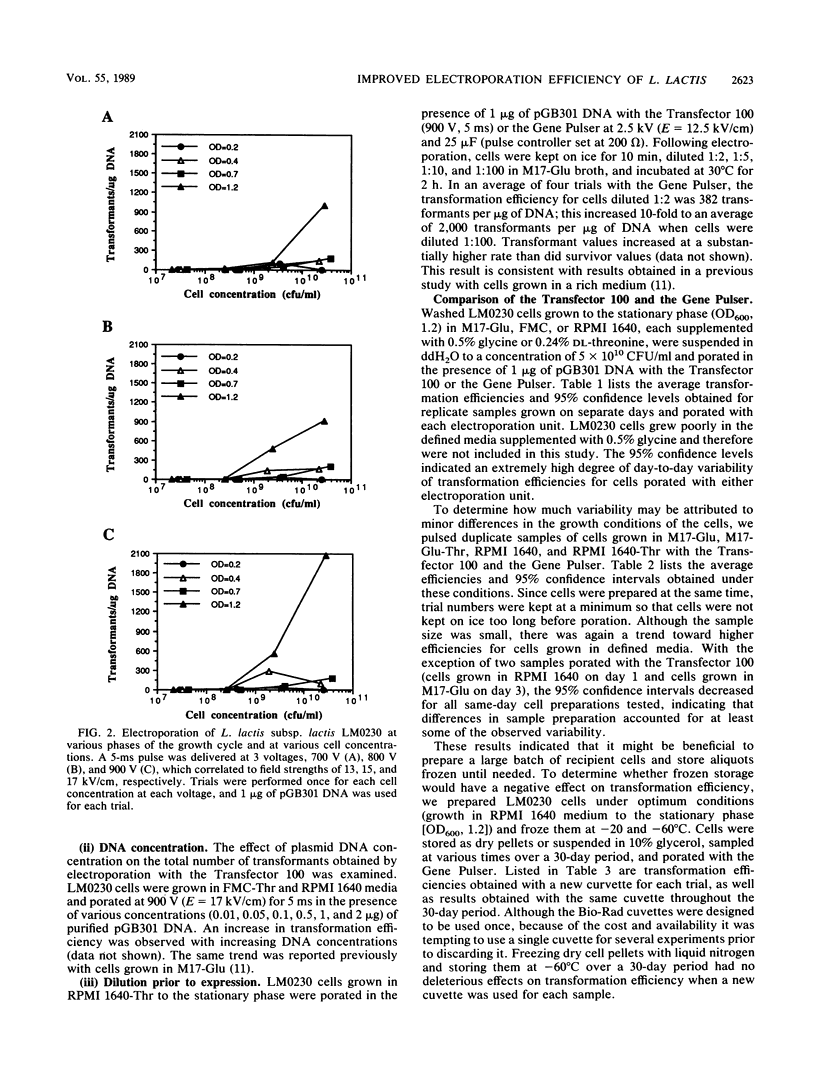
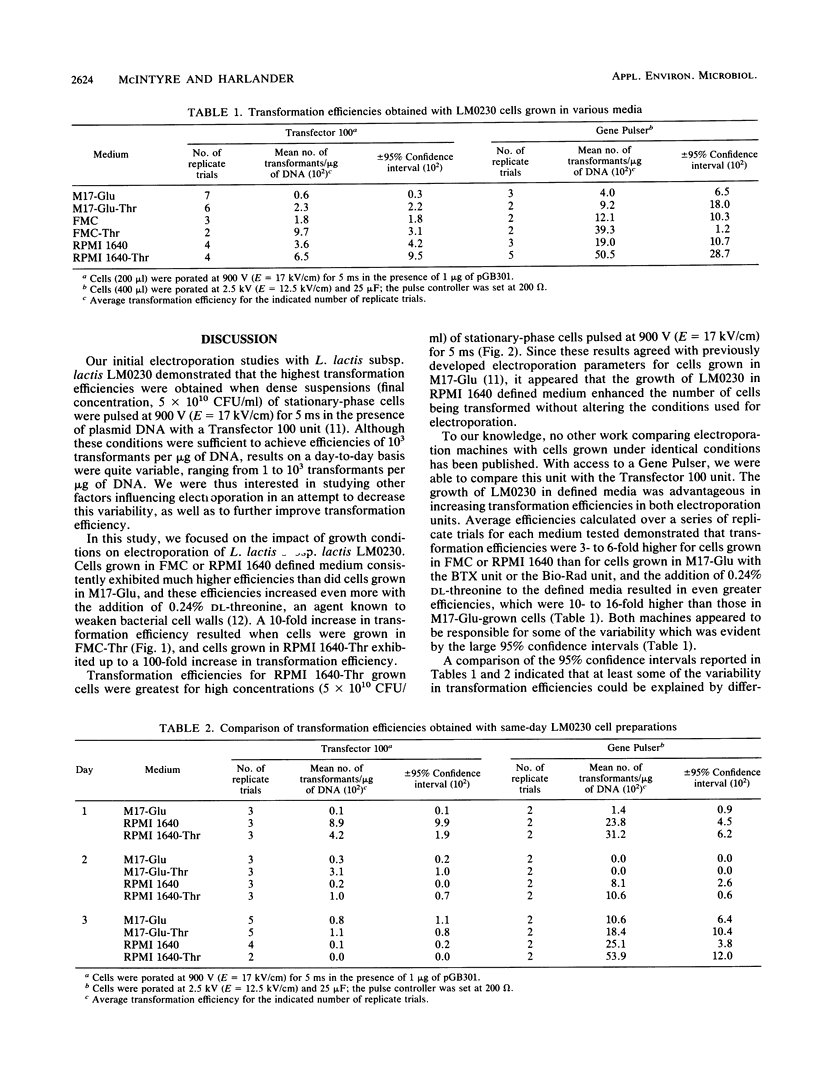
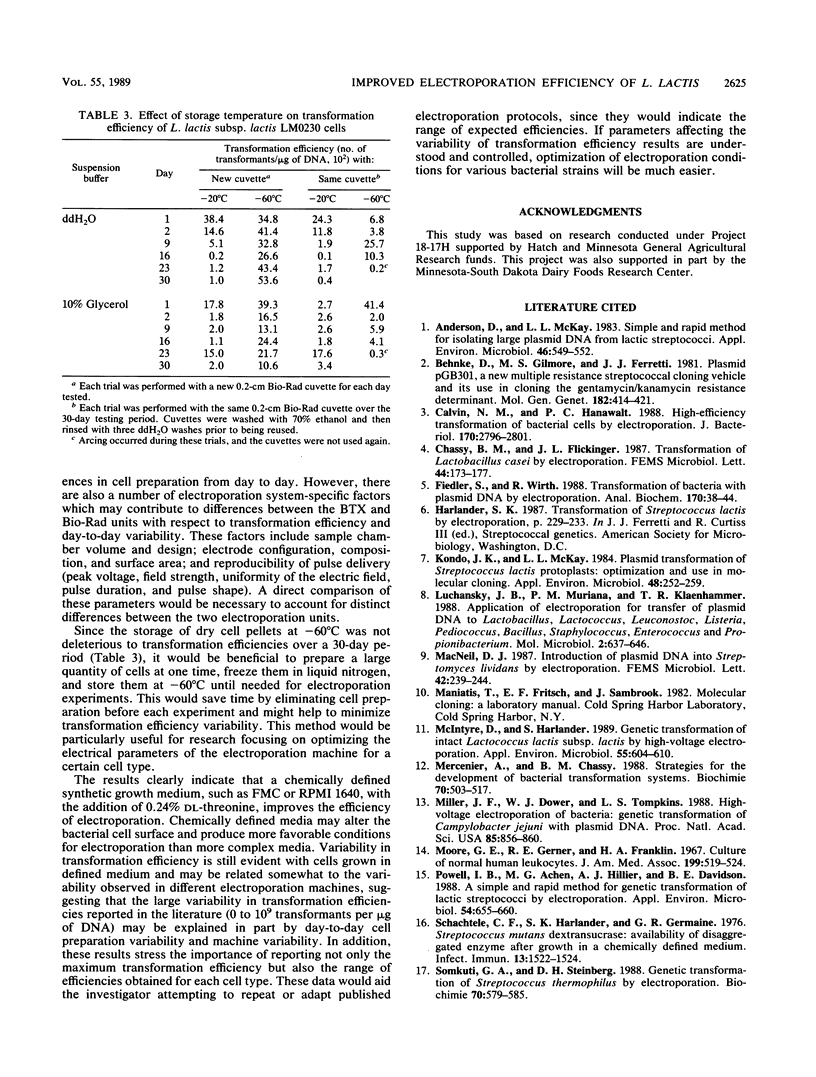
The impact of growth conditions on electroporation of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis LM0230 (previously designated Streptococcus lactis LM0230) was evaluated. Cells grown in M17 broth supplemented with 0.5% glucose (M17-Glu) and two chemically defined synthetic media, FMC and RPMI 1640, all supplemented with 0.24% DL-threonine or 0.5% glycine, were harvested, washed with double-distilled water, diluted, and porated in the presence of 1 microgram of pGB301 DNA with a Transfector 100 (BTX, Inc., San Diego, Calif.) or a Gene Pulser (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Richmond, Calif.). Transformants were recovered at consistently higher efficiencies for cells grown in FMC or RPMI 1640 (10(3) to 10(4) transformants per micrograms of DNA) than for cells grown in M17-Glu (10(1) to 10(2) transformants per micrograms of DNA). Other parameters influencing electroporation of L. lactis cells grown in chemically defined media were growth phase and final concentration of cells, concentration of plasmid DNA, voltage achieved during poration, and expression conditions. A high degree of variability in transformation efficiencies was evident for replicate samples of cells pulsed with either electroporation machine. A trend toward decreased variability was observed for duplicate samples of cells prepared on the same day. In addition, storage studies done with a large batch of cells prepared on the same day indicated that freezing dry cell pellets at -60 degrees C had no deleterious effect on transformation efficiencies over a 30-day period when a new 0.2-cm cuvette was used for porating each sample.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke D., Gilmore M. S., Ferretti J. J. Plasmid pGB301, a new multiple resistance streptococcal cloning vehicle and its use in cloning of a gentamicin/kanamycin resistance determinant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):414–421. doi: 10.1007/BF00293929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin N. M., Hanawalt P. C. High-efficiency transformation of bacterial cells by electroporation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2796–2801. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2796-2801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler S., Wirth R. Transformation of bacteria with plasmid DNA by electroporation. Anal Biochem. 1988 Apr;170(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchansky J. B., Muriana P. M., Klaenhammer T. R. Application of electroporation for transfer of plasmid DNA to Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Listeria, Pediococcus, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus and Propionibacterium. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):637–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre D. A., Harlander S. K. Genetic transformation of intact Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis by high-voltage electroporation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):604–610. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.604-610.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercenier A., Chassy B. M. Strategies for the development of bacterial transformation systems. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Dower W. J., Tompkins L. S. High-voltage electroporation of bacteria: genetic transformation of Campylobacter jejuni with plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Gerner R. E., Franklin H. A. Culture of normal human leukocytes. JAMA. 1967 Feb 20;199(8):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell Ian B., Achen Marc G., Hillier Alan J., Davidson Barrie E. A Simple and Rapid Method for Genetic Transformation of Lactic Streptococci by Electroporation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):655–660. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.655-660.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Harlander S. K., Germaine G. R. Streptococcus mutans dextransucrase: availability of disaggregated enzyme after growth in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1522–1524. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1522-1524.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somkuti G. A., Steinberg D. H. Genetic transformation of Streptococcus thermophilus by electroporation. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. DNA transfection of Escherichia coli by electroporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 31;949(3):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Guchte M., van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Construction of a lactococcal expression vector: expression of hen egg white lysozyme in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):224–228. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.224-228.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


