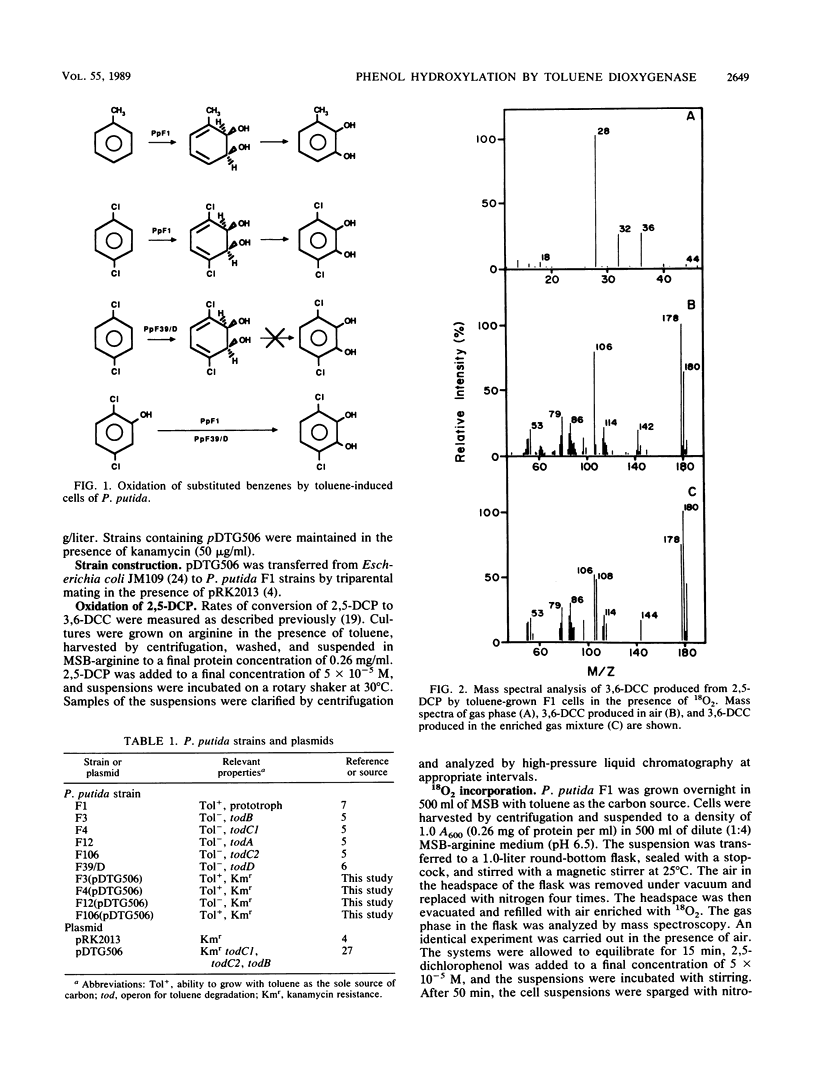
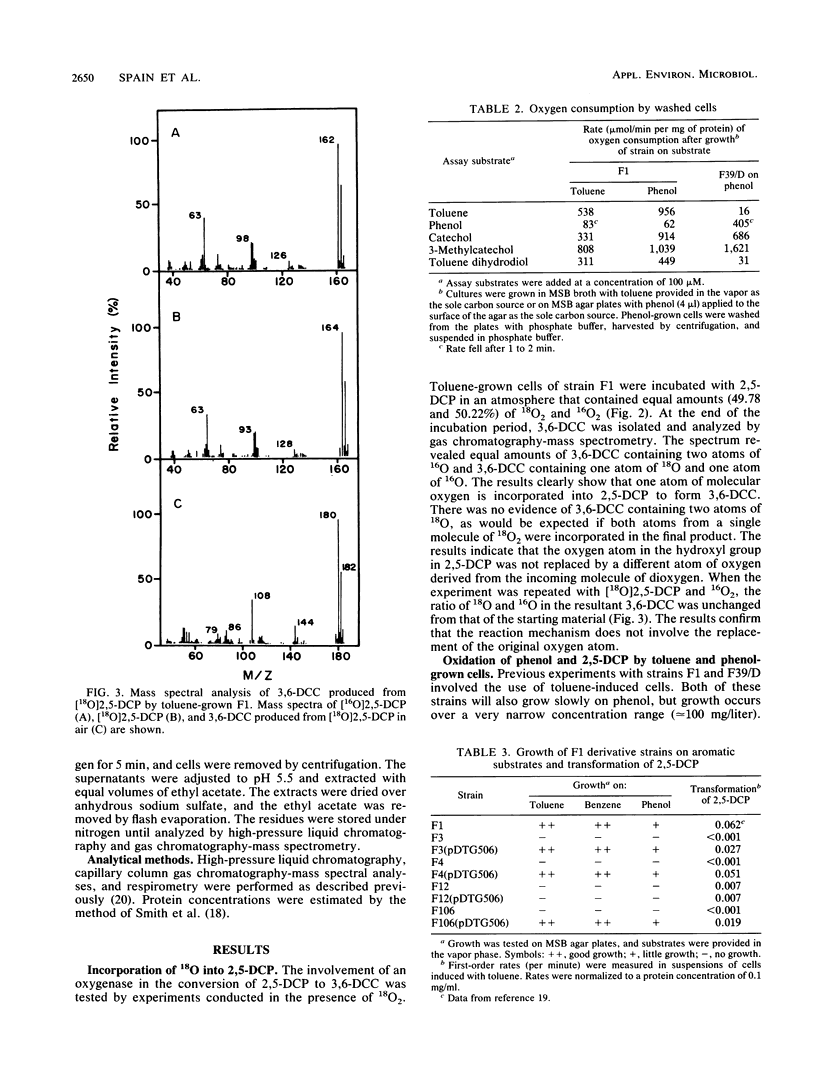
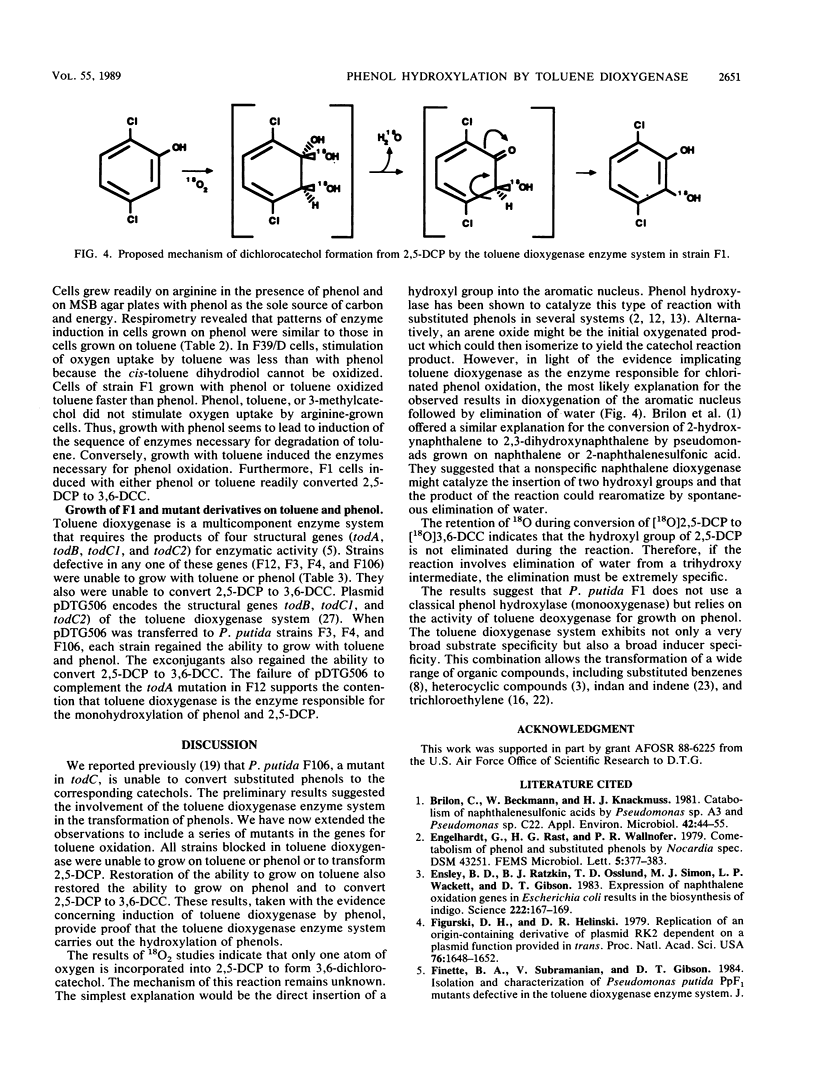
Abstract
Pseudomonas putida F1 contains a multicomponent enzyme system, toluene dioxygenase, that converts toluene and a variety of substituted benzenes to cis-dihydrodiols by the addition of one molecule of molecular oxygen. Toluene-grown cells of P. putida F1 also catalyze the monohydroxylation of phenols to the corresponding catechols by an unknown mechanism. Respirometric studies with washed cells revealed similar enzyme induction patterns in cells grown on toluene or phenol. Induction of toluene dioxygenase and subsequent enzymes for catechol oxidation allowed growth on phenol. Tests with specific mutants of P. putida F1 indicated that the ability to hydroxylate phenols was only expressed in cells that contained an active toluene dioxygenase enzyme system. 18O2 experiments indicated that the overall reaction involved the incorporation of only one atom of oxygen in the catechol, which suggests either a monooxygenase mechanism or a dioxygenase reaction with subsequent specific elimination of water.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Knackmuss H. J. Catabolism of Naphthalenesulfonic Acids by Pseudomonas sp. A3 and Pseudomonas sp. C22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.44-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Ratzkin B. J., Osslund T. D., Simon M. J., Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Expression of naphthalene oxidation genes in Escherichia coli results in the biosynthesis of indigo. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.6353574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Hensley M., Yoshioka H., Mabry T. J. Formation of (+)-cis-2,3-dihydroxy-1-methylcyclohexa-4,6-diene from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1626–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. I. Enzymatic formation of catechol from benzene. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2653–2662. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O., Nozaki M. Nature and mechanisms of oxygenases. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):389–396. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knackmuss H. J., Hellwig M. Utilization and cooxidation of chlorinated phenols by Pseudomonas sp. B 13. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00689343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobal V. M., Gibson D. T., Davis R. E., Garza A. X-ray determination of the absolute stereochemistry of the initial oxidation product formed from toluene by Pseudomonas puida 39-D. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jun 27;95(13):4420–4421. doi: 10.1021/ja00794a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Pritchard P. H. Trichloroethylene metabolism by microorganisms that degrade aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):604–606. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.604-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Gibson D. T. Oxidation of substituted phenols by Pseudomonas putida F1 and Pseudomonas sp. strain JS6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1399–1404. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1399-1404.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Kwart L. D., Gibson D. T. Benzylic monooxygenation catalyzed by toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1360–1367. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Gibson D. T., Liu T. N. Toluene dioxygenase: a multicomponent enzyme system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziffer H., Jerina D. M., Gibson D. T., Kobal V. M. Absolute stereochemistry of the (+)-cis-1,2-dihydroxy-3-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene produced from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jun 13;95(12):4048–4049. doi: 10.1021/ja00793a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., McCombie W. R., Gibson D. T., Finette B. A. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1: genetic organization of the tod operon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1498–1503. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1498-1503.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



