Abstract
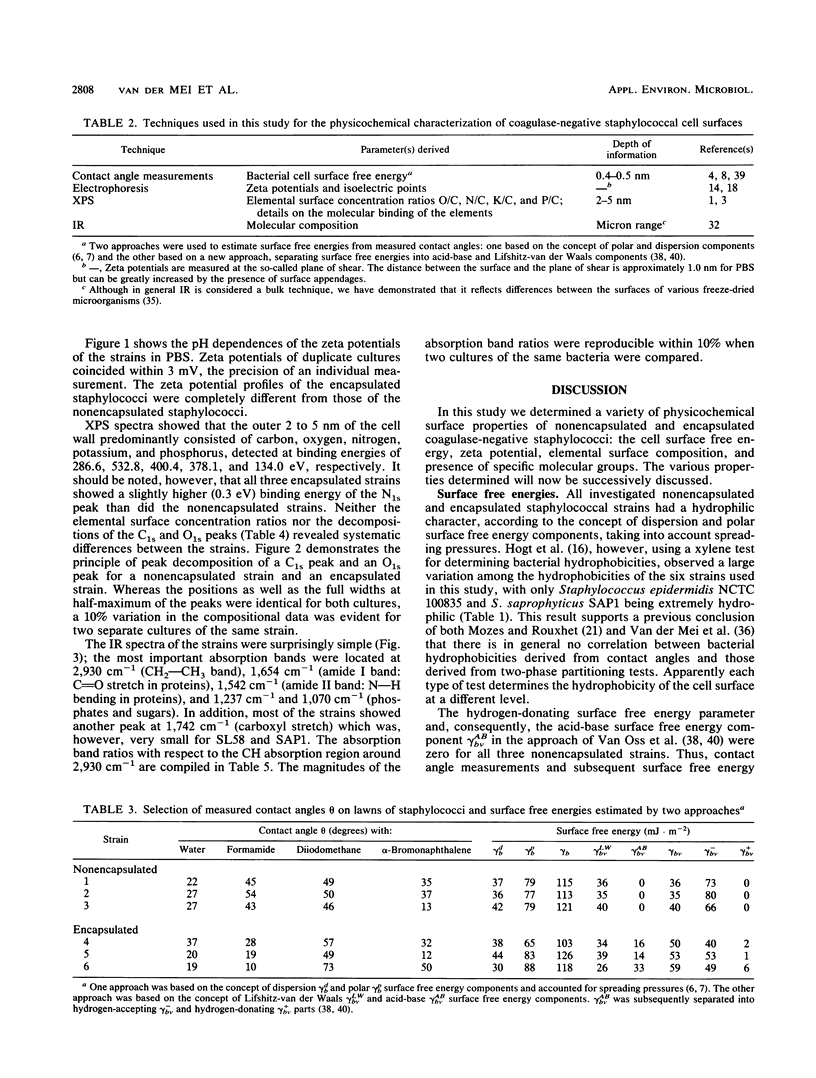
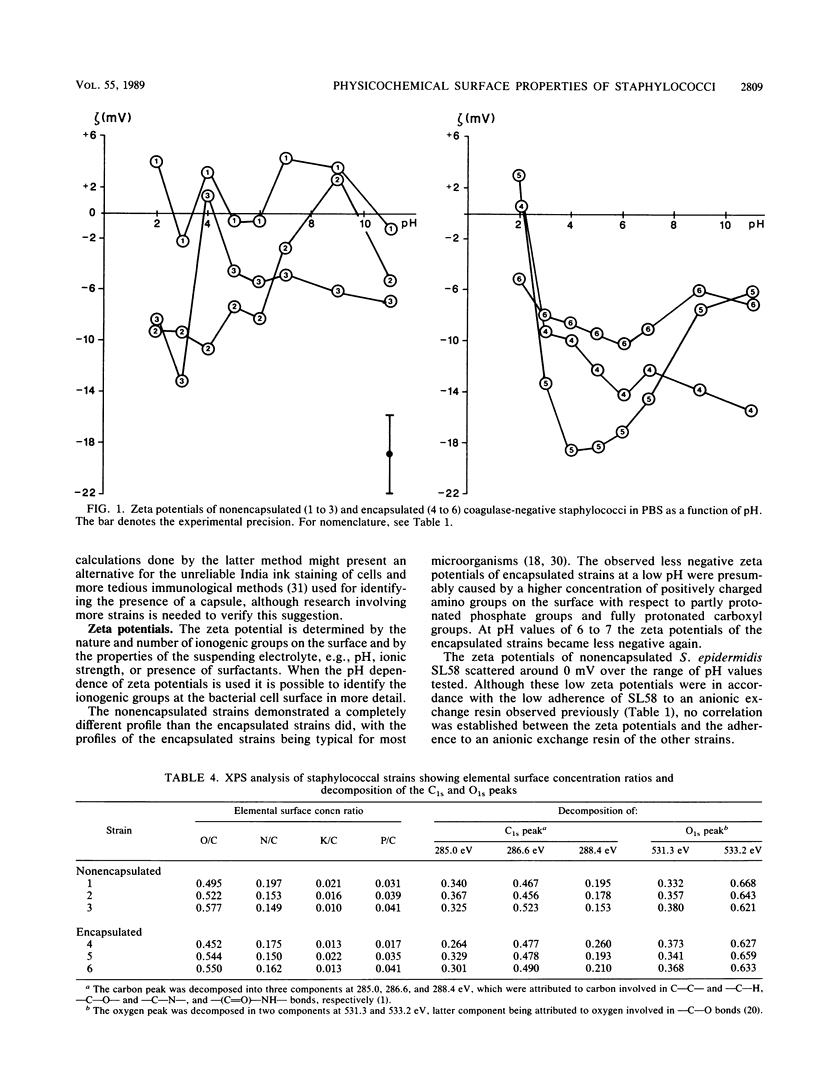
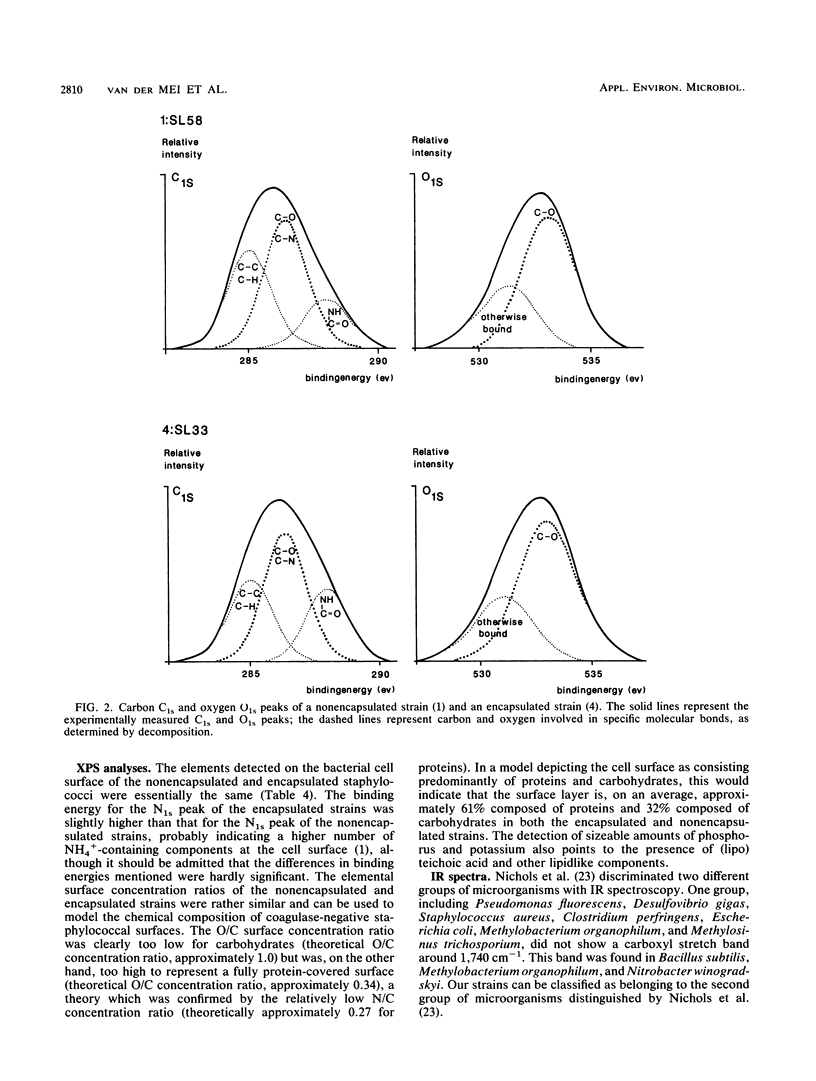
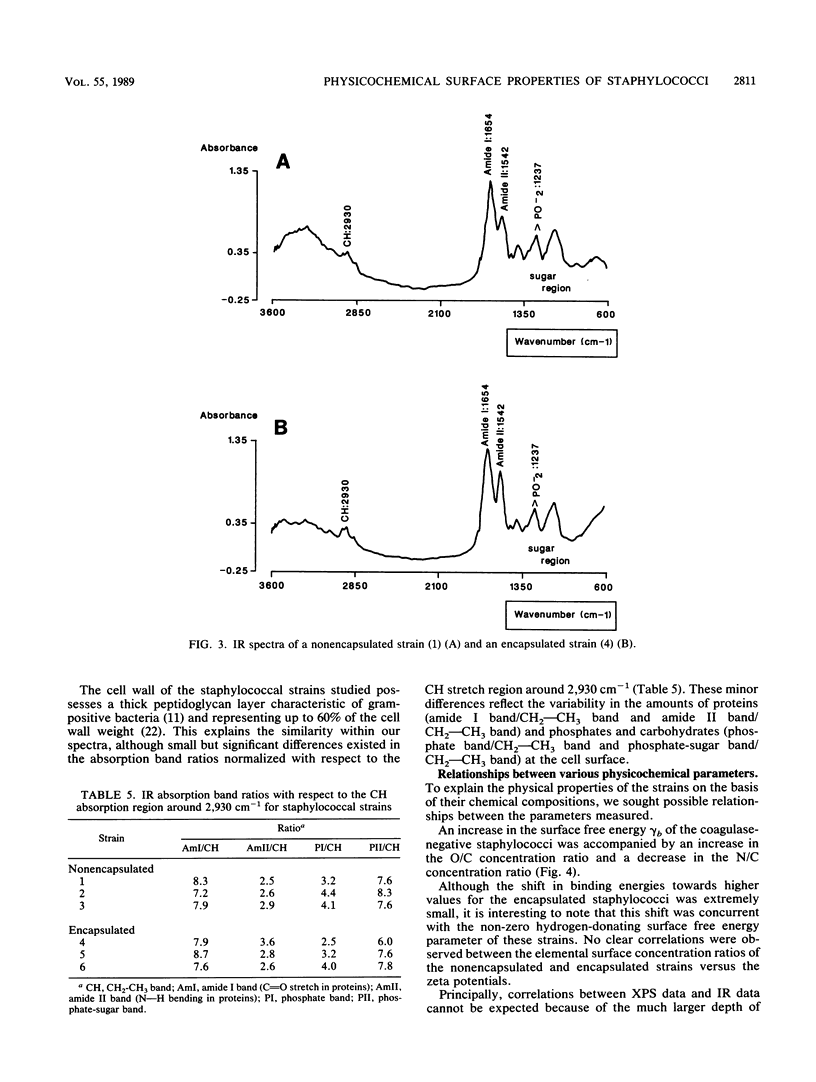
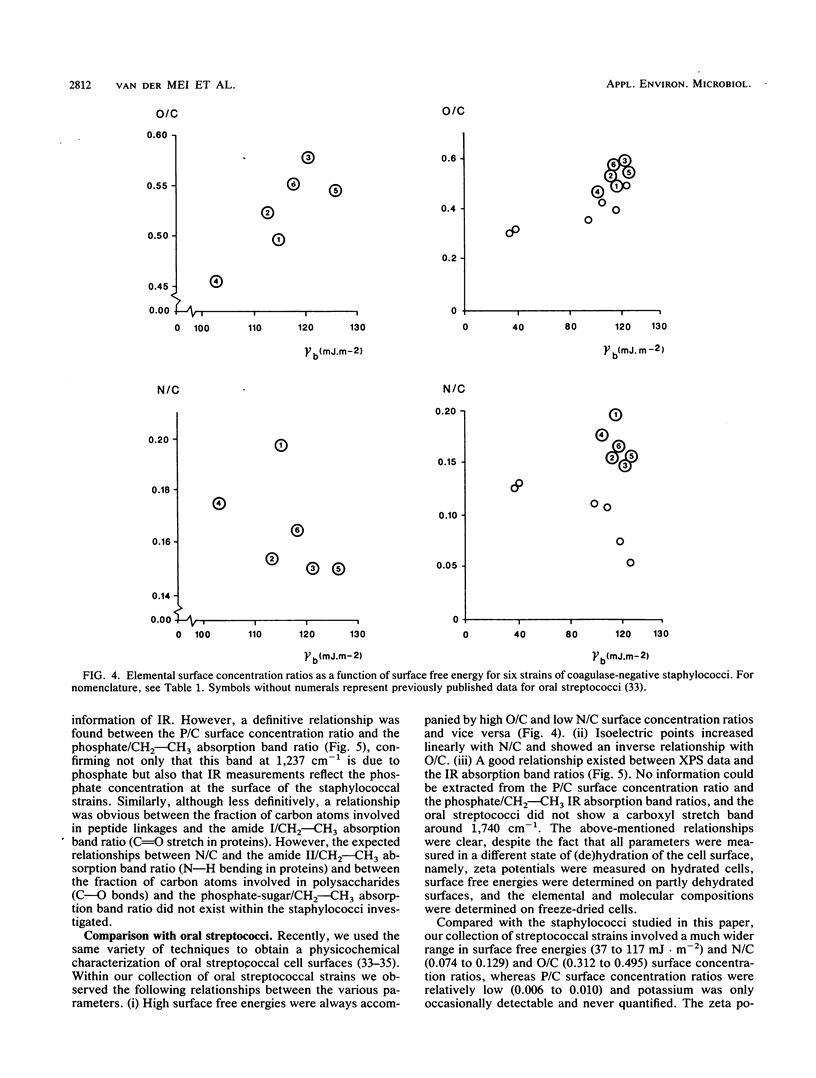
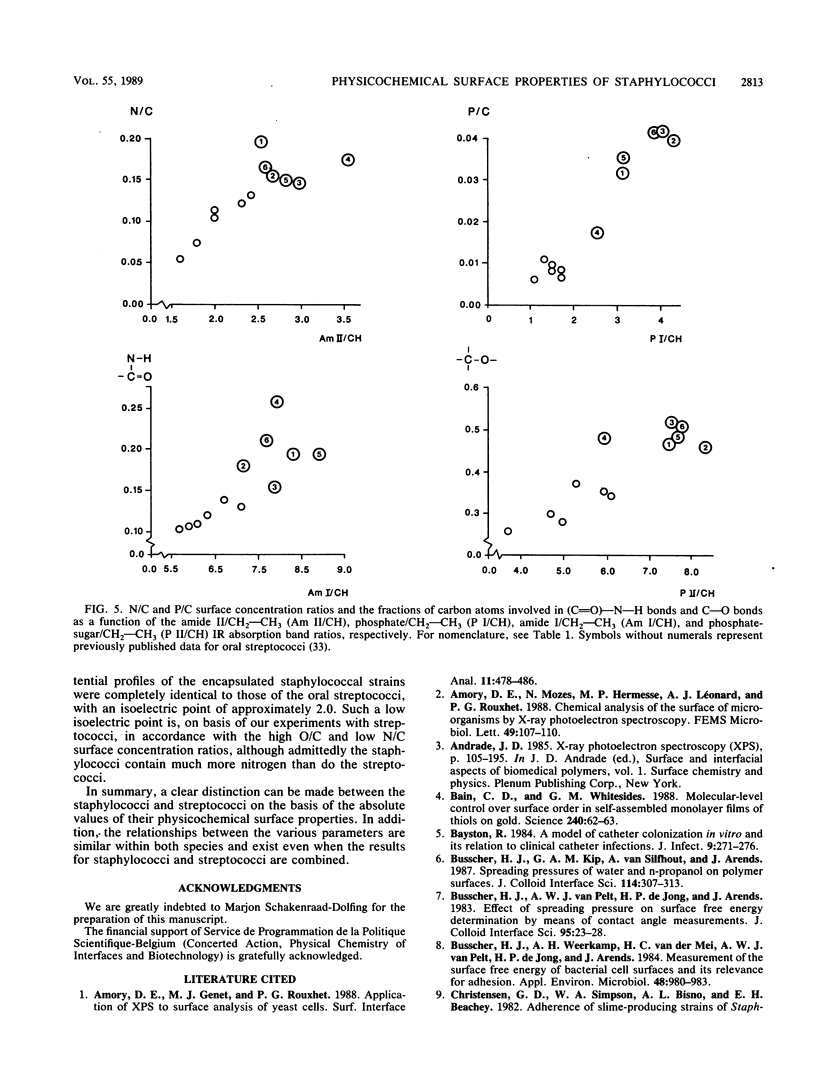
Cell surfaces of three nonencapsulated and three encapsulated coagulase-negative staphylococci were characterized by their surface free energies, zeta potentials, and elemental and molecular compositions. Surface free energies were calculated from contact angle measurements with various liquids. All six strains showed a high surface free energy (103 to 126 mJ.m-2), estimated from the concept of polar and dispersion components. However, the hydrogen-donating surface free energy parameter was zero for all nonencapsulated strains. The zeta potential profile measured as a function of pH in phosphate-buffered saline for the nonencapsulated strains was completely different from that of the encapsulated strains. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was used to determine the elements (O, C, N, P, and K) in the outer 2 to 5 nm of the freeze-dried cell surface and showed that the hydrophilic character of the staphylococci was related to oxygen (O/C ratio, approximately 0.52)- and phosphorus (P/C ratio, approximately 0.03)-containing groups. Both the elemental and molecular characterizations (done by infrared spectroscopy) pointed to the presence of polysaccharides and polypeptides on the cell surface of the nonencapsulated and encapsulated strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain C. D., Whitesides G. M. Molecular-Level Control over Surface Order in Self-Assembled Monolayer Films of Thiols on Gold. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):62–63. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4848.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayston R. A model of catheter colonisation in vitro and its relationship to clinical catheter infections. J Infect. 1984 Nov;9(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)90596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Experimental foreign body infections in mice challenged with slime-producing Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):407–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.407-410.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., Feijen J. Adhesion of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus to a hydrophobic biomaterial. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2485–2491. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., Hulstaert C. E., Feijen J. Cell surface characteristics of coagulase-negative staphylococci and their adherence to fluorinated poly(ethylenepropylene). Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.294-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., de Vries J. A., Feijen J. Adhesion of coagulase-negative staphylococci to biomaterials. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2959–2968. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagi S., Miyake Y., Inagaki K., Tsuru H., Suginaka H. Hydrophobic interaction in Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis adherence to various denture base resin materials. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):11–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.11-14.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozes N., Léonard A. J., Rouxhet P. G. On the relations between the elemental surface composition of yeasts and bacteria and their charge and hydrophobicity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 22;945(2):324–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann D., Barnickel G., Bradaczek H., Labischinski H., Giesbrecht P. Infrared spectroscopy, a tool for probing bacterial peptidoglycan. Potentialities of infrared spectroscopy for cell wall analytical studies and rejection of models based on crystalline chitin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(3):505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols P. D., Henson J. M., Guckert J. B., Nivens D. E., White D. C. Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopic methods for microbial ecology: analysis of bacteria, bacteria-polymer mixtures and biofilms. J Microbiol Methods. 1985;4:79–94. doi: 10.1016/0167-7012(85)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Glantz P. O., Krasse B. Surface potential and adherence of oral streptococci to solid surfaces. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jul;84(4):240–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. II. Scanning electron microscopy of naturally infected intravenous catheters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schakenraad J. M., Busscher H. J., Wildevuur C. R., Arends J. Thermodynamic aspects of cell spreading on solid substrata. Cell Biophys. 1988 Aug;13(1):75–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02797367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. A., Moore N. F. Measurement of surface charge of baculovirus polyhedra. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):598–602. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.598-602.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Yamashita N., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Isolation and characterization of a capsular polysaccharide adhesin from Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):713–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Contact angles and phagocytosis of non-opsonized bacteria. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Sep;12(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. Electrophoretic mobility and hydrophobicity as a measured to predict the initial steps of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1898–1901. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1898-1901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Mei H. C., Léonard A. J., Weerkamp A. H., Rouxhet P. G., Busscher H. J. Surface properties of Streptococcus salivarius HB and nonfibrillar mutants: measurement of zeta potential and elemental composition with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2462–2466. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2462-2466.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Mei H. C., Noordmans J., Busscher H. J. Molecular surface characterization of oral streptococci by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 27;991(3):395–398. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



