Abstract
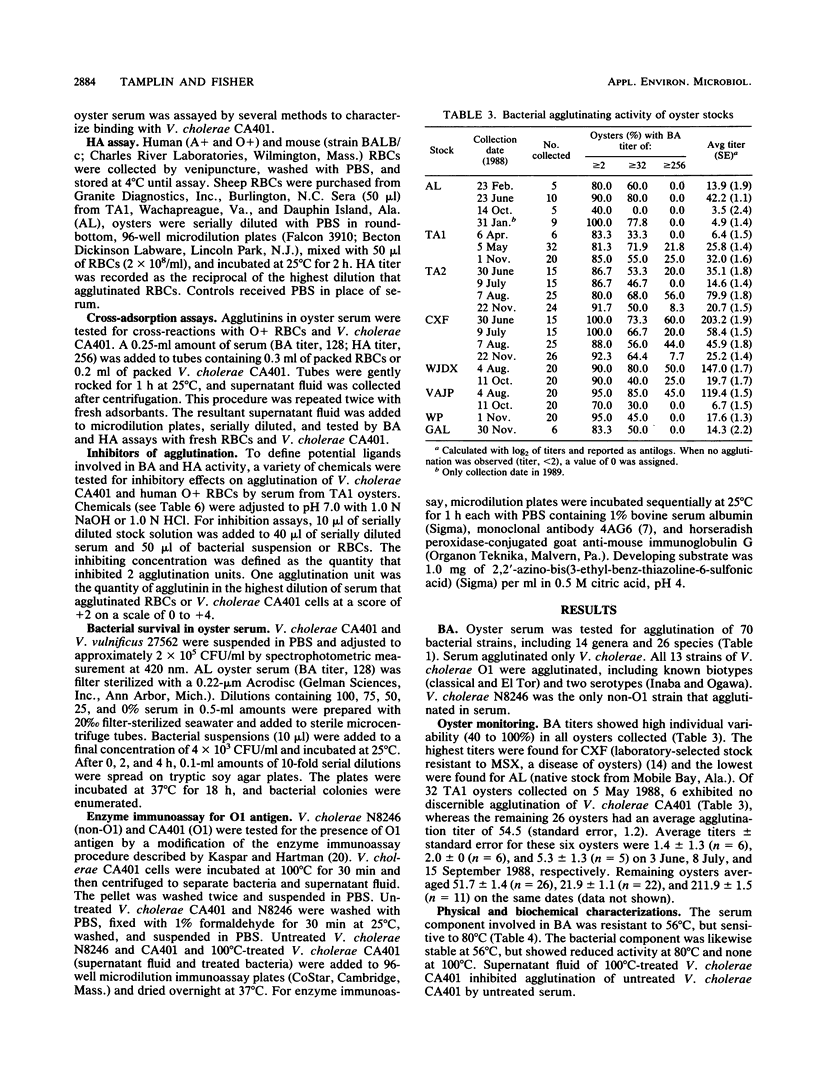
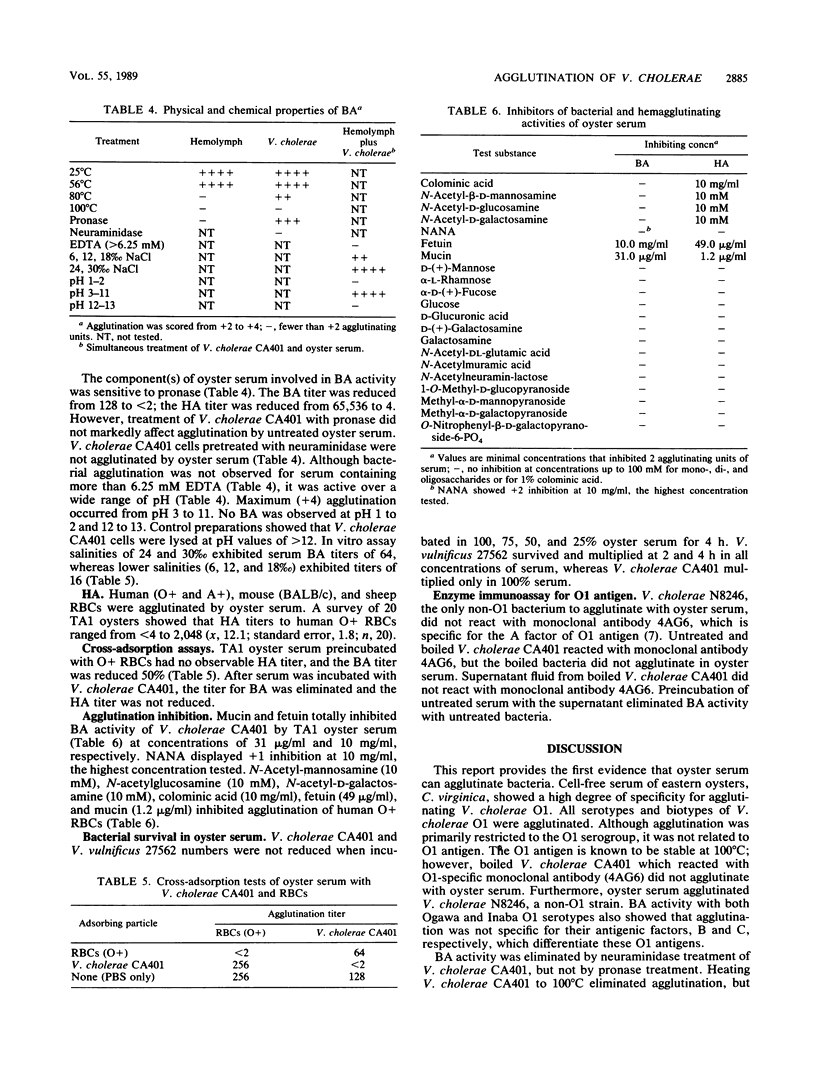
Cell-free hemolymph (serum) of the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, agglutinated Vibrio cholerae, including all O1 serovars and biovars. Seventy-nine other strains of bacteria, including 14 genera and 26 species, were not agglutinated. The A, B, and C factors of O1 antigen were not involved in agglutination. Bacterial agglutinating (BA) activity was demonstrated for oysters inhabiting different environments of the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf coasts. Oyster serum BA titers showed high individual variation. The serum component(s) involved in BA was inhibited by 80 degrees C heat, pronase, EDTA, mucin, and fetuin treatments. N-Acetylneuraminic acid (10 mg/ml) weakly inhibited BA activity. Ligands of V. cholerae were sensitive to neuraminidase and resistant to 80 degrees C and pronase. High salinities (24 and 30%) enhanced BA. Cross-adsorption tests with V. cholerae and human O+ erythrocytes indicated that BA and hemagglutinating activities may involve different serum components. These results imply that the ecology of V. cholerae in C. virginica is influenced by agglutinating activity of oyster serum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD W. C., SHAPLEIGH E. Antigenic relations of blood group antigens as suggested by tests with lectins. J Immunol. 1954 Oct;73(4):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldo B. A., Sawyer W. H., Stick R. V., Uhlenbruck G. Purification and characterization of a galactan-reactive agglutinin from the clam Tridacna maxima (Röding) and a study of its combining site. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):467–477. doi: 10.1042/bj1750467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Tamplin M. L., Huq A., Colwell R. R. Enumeration of Vibrio cholerae O1 in Bangladesh waters by fluorescent-antibody direct viable count. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2862–2865. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2862-2865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. C. Functional morphology and biochemistry of molluscan phagocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975;266:343–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb35116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. E., Haskin H. H. Infection and mortality patterns in strains of oysters Crassostrea virginica selected for resistance to the parasite Haplosporidium nelsoni (MSX). J Parasitol. 1987 Apr;73(2):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Rodrick G. E. Isolation of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 from the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):559–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.559-560.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Powers C., Bryant R. G., Abbott S. L. Current perspectives on the epidemiology and pathogenesis of clinically significant Vibrio spp. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jul;1(3):245–267. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.3.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar C. W., Hartman P. A. Production and specificity of monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;63(4):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klontz K. C., Tauxe R. V., Cook W. L., Riley W. H., Wachsmuth I. K. Cholera after the consumption of raw oysters. A case report. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):846–848. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. F., Flemming C. Hemagglutinins from oyster hemolymph. Can J Zool. 1967 Nov;45(6 Suppl):1225–1234. doi: 10.1139/z67-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. J., Drasar B. S., Feachem R. G. Response of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae 01 to physico-chemical stresses in aquatic environments. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Dec;93(3):475–495. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Warner R. A., Cleland D. R. Distribution of Vibrio vulnificus and other lactose-fermenting vibrios in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):985–998. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.985-998.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauley G. B., Krassner S. M., Chapman F. A. Bacterial clearance in the California sea hare, Aplysia californica. J Invertebr Pathol. 1971 Sep;18(2):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(71)90150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R. W., Jangi M. S., Colwell R. R. Influence of salinity and organic nutrient concentration on survival and growth of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1080-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R., Jangi S., Colwell R. R. Effects of temperature and salinity on Vibrio cholerae growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1047–1058. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1047-1058.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Colwell R. R. Effects of microcosm salinity and organic substrate concentration on production of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):297–301. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.297-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M., Rodrick G. E., Blake N. J., Cuba T. Isolation and characterization of Vibrio vulnificus from two Florida estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1466–1470. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1466-1470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp M. R. Defense mechanisms of mollusks. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Feb;7(2):173–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp M. R. Hemagglutinin in the blood of the oyster Crassostrea virginica. J Invertebr Pathol. 1966 Dec;8(4):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(66)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



