Abstract
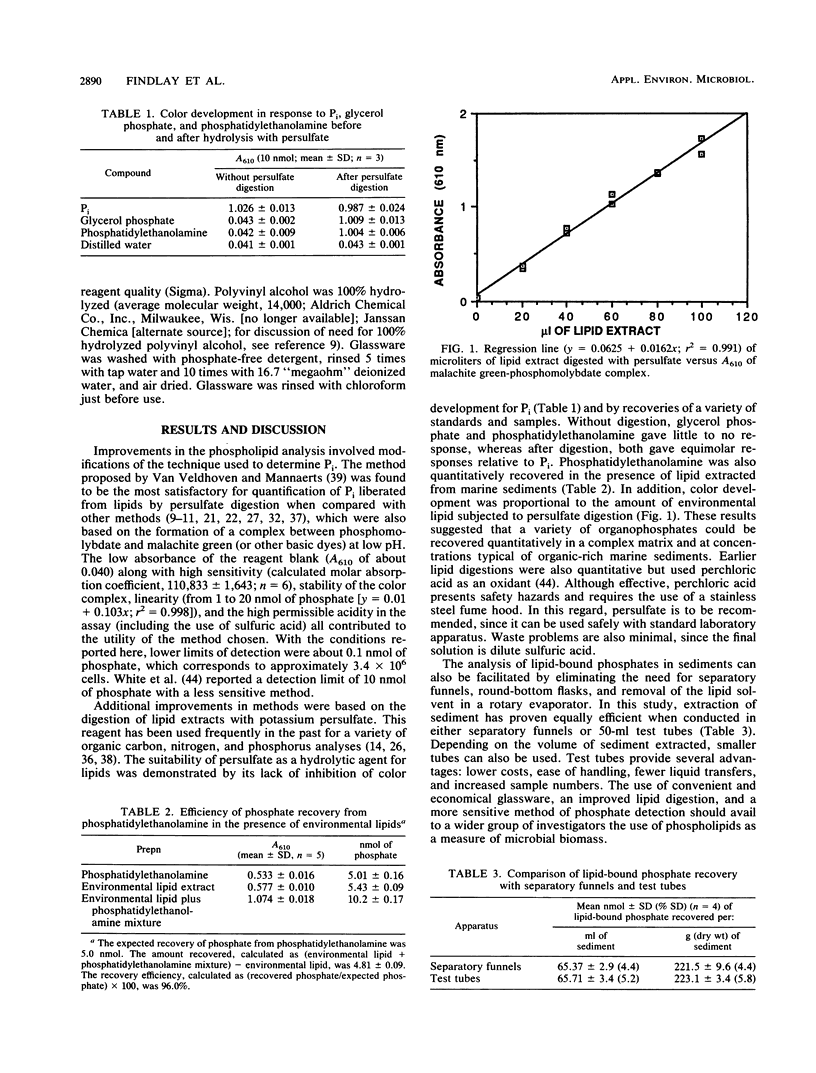
Improvements in the analysis of lipid-bound phosphates resulted in a simplified and sensitive method for determining microbial biomass in sediments. Sensitivity was enhanced over previous methods by use of a dye, malachite green, which when complexed with phosphomolybdate at low pH has a high extinction coefficient (at 610 nm). The use of a persulfate oxidation technique to liberate phosphate from lipids increased the simplicity and safety of the method relative to the traditional perchloric acid digestions. The modified method was both accurate (yielding quantitative recoveries of cells added to sediments) and precise (coefficient of variation of less than 5% for cells and sediments). A comparison with an epifluorescence technique indicated that the analysis of lipid-bound phosphate was more rapid and less tedious and could be successfully applied to a wider variety of sediment types. An estimate of the lipid-bound phosphate-to-carbon conversion factor based on a diverse enrichment culture from sediments suggested that previous factors for pure cultures may have been too low.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Kelleher P. A. Biosynthesis of retinal phospholipids by base exchange reactions. Exp Eye Res. 1981 Jun;32(6):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(81)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken L. R., Olsen R. A. Buoyant densities and dry-matter contents of microorganisms: conversion of a measured biovolume into biomass. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1188–1195. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1188-1195.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken L. R. Separation and purification of bacteria from soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1482–1487. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1482-1487.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott T. L., Kaplan L. A. Bacterial biomass, metabolic state, and activity in stream sediments: relation to environmental variables and multiple assay comparisons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):508–522. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.508-522.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratbak G. Bacterial biovolume and biomass estimations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1488–1493. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1488-1493.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. G., Karl D. W. Inorganic phosphate assay with malachite green: an improvement and evaluation. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1982 Dec;7(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chifflet S., Torriglia A., Chiesa R., Tolosa S. A method for the determination of inorganic phosphate in the presence of labile organic phosphate and high concentrations of protein: application to lens ATPases. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jan;168(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concustell E., Cortés M., Ferragut A., Gener J. Inorganic phosphorus measurement: an improved method. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Dec 15;81(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federle T. W., Hullar M. A., Livingston R. J., Meeter D. A., White D. C. Spatial distribution of biochemical parameters indicating biomass and community composition of microbial assemblies in estuarine mud flat sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.58-63.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Derr J. E. Assay of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the 0.1-5 nanomole range. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M. Dehalogenation in marine sediments containing natural sources of halophenols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3079–3085. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3079-3085.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Fuhrman J. A. Relationships between Biovolume and Biomass of Naturally Derived Marine Bacterioplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1298–1303. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1298-1303.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagna P. A. Sampling design and enumeration statistics for bacteria extracted from marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1366–1372. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1366-1372.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty D. J., Boon P. I., Hansen J. A., Hunt W. G., Poiner I. R., Pollard P. C., Skyring G. W., White D. C. Microbial biomass and productivity in seagrass beds. Geomicrobiol J. 1985;4(1):21–51. doi: 10.1080/01490458509385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moslen M. T., Kanz M. F., Ferguson A. E. A stable colorimetric assay to measure toxin elevation of inorganic phosphate in bile. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):405–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T. Carbon and nitrogen content of natural planktonic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.28-32.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schallenberg M., Kalff J., Rasmussen J. B. Solutions to problems in enumerating sediment bacteria by direct counts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1214–1219. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1214-1219.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatton J. B., Ward C., Williams A., Weinhouse S. A microcolorimetric assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90657-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Veldhoven P. P., Mannaerts G. P. Inorganic and organic phosphate measurements in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90649-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


