Abstract
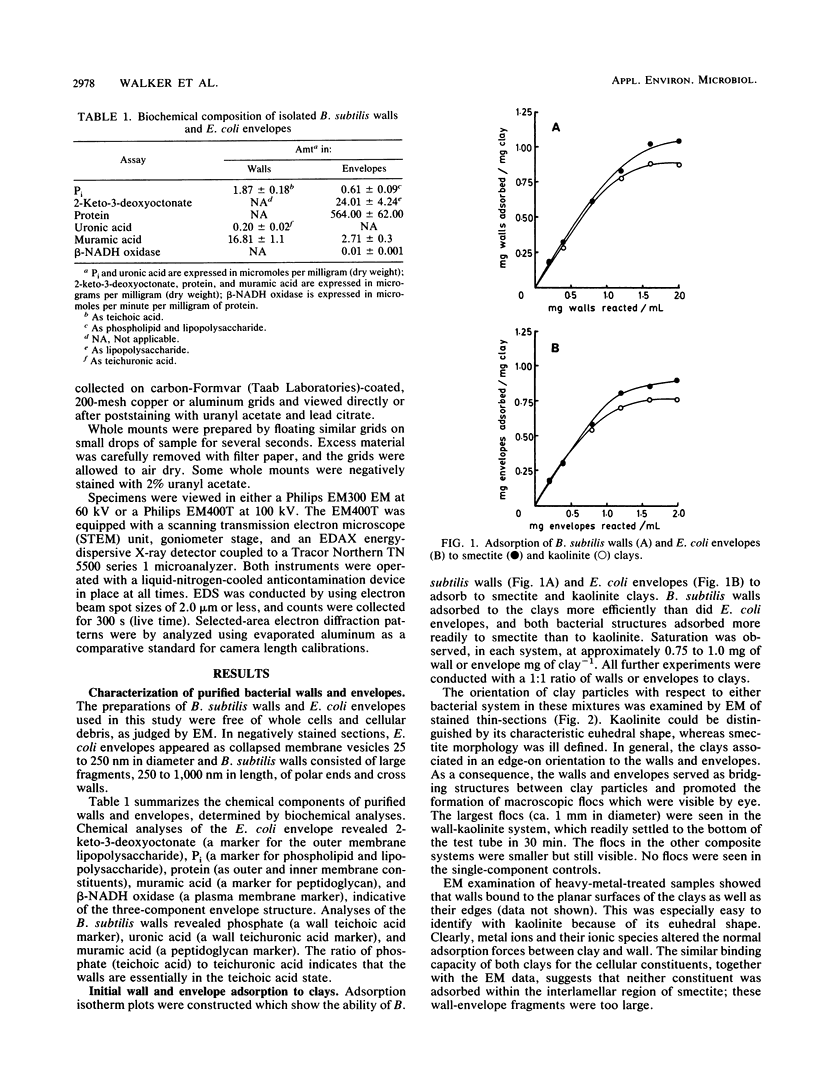
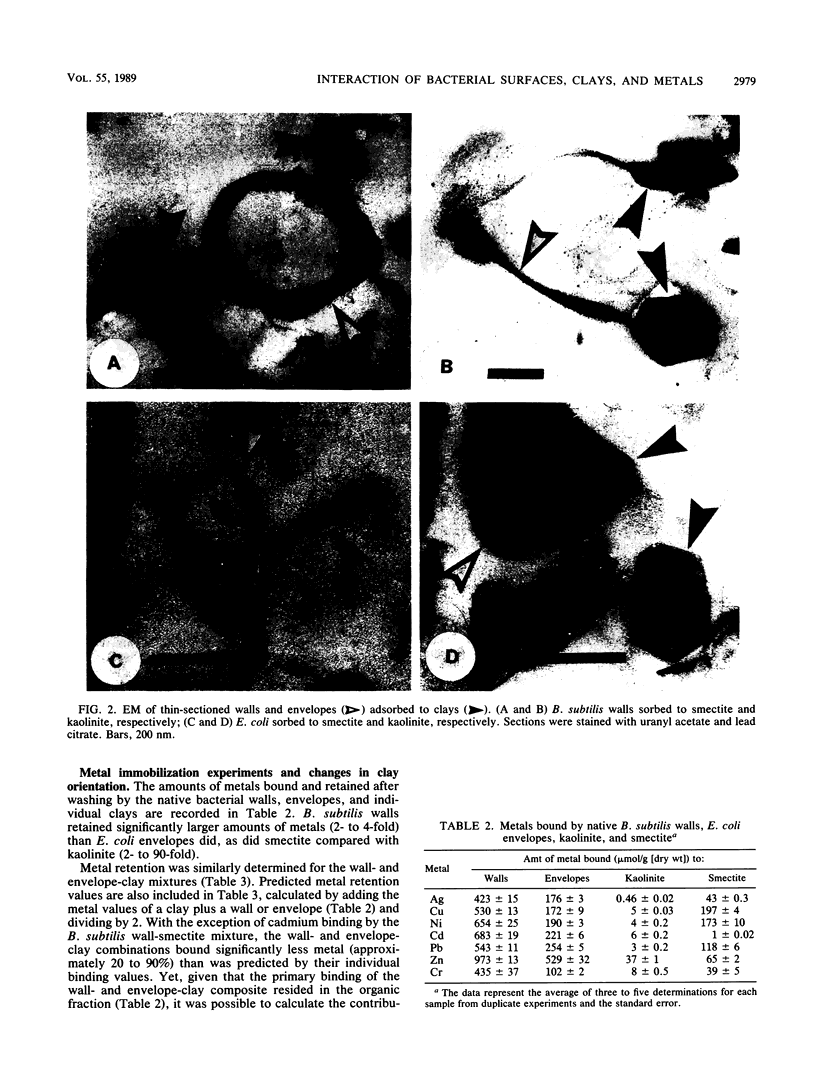
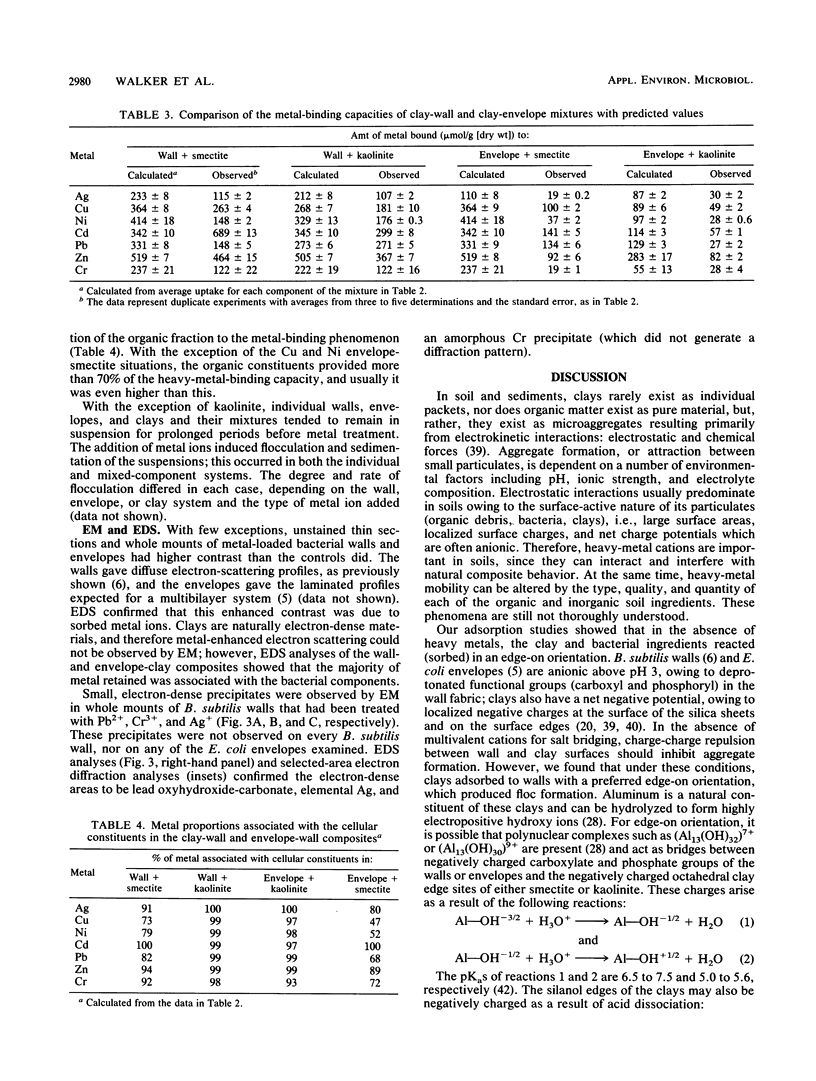
Isolated Escherichia coli K-12 cell envelopes or Bacillus subtilis 168 cell walls were reacted with smectite or kaolinite clay in distilled deionized water (pH 6.0); unbound envelopes or walls were separated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation, and the extent of adsorption was calculated. At saturation, both clays adsorbed approximately 1.0 mg (dry weight) of envelopes or walls per mg (dry weight) of clay. Clays showed a preference for edge-on orientation with both walls and envelopes, which was indicative of an aluminum polynuclear bridging mechanism between the wall or envelope surface and the clay edge. The addition of heavy metals increased the incidence of planar surface orientations, which suggested that multivalent metal cation bridging was coming into play and was of increasing importance. The metal-binding capacity of isolated envelopes, walls, clays, and envelope-clay or wall-clay mixtures was determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy after exposure to aqueous 5.0 mM Ag+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, and Cr3+ nitrate salt solutions at pHs determined by the buffering capacity of wall, envelope, clay, or composite system. The order of metal uptake was walls greater than envelopes greater than smectite clay greater than kaolinite clay for the individual components, and walls plus smectite greater than walls plus kaolinite greater than envelopes plus smectite greater than envelopes plus kaolinite for the mixtures. On a dry-weight basis, the envelope-clay and wall-clay mixtures bound 20 to 90% less metal than equal amounts of the individual components did.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

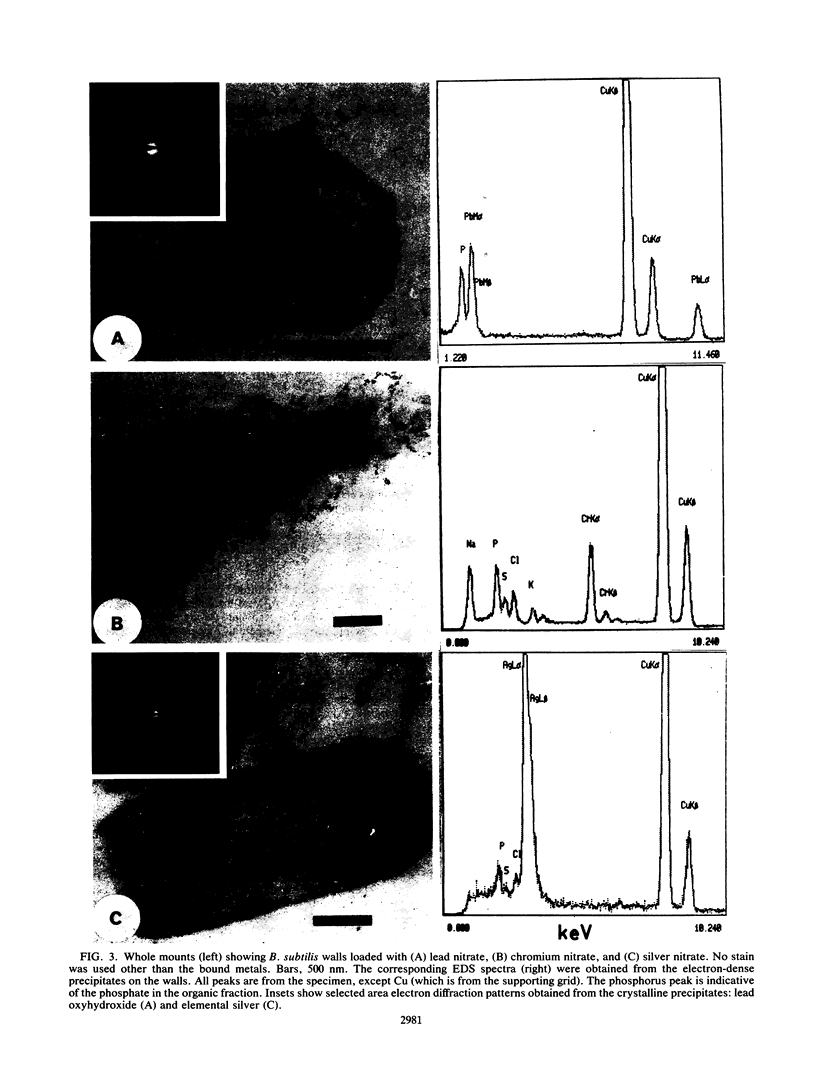



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich H., Stotzky G. Environmental factors that influence the toxicity of heavy metal and gaseous pollutants to microorganisms. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1980;8(2):99–145. doi: 10.3109/10408418009081123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Koval S. F. Binding of metals to cell envelopes of Escherichia coli K-12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):325–335. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.325-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):876–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.876-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W. Structure and plasticity at various organization levels in the bacterial cell. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):513–521. doi: 10.1139/m88-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J. Physicochemical roles of soluble metal cations in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K-12. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jul;32(7):594–601. doi: 10.1139/m86-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe W. S. The environmental crisis: quantifying geosphere interactions. Science. 1981 Jul 3;213(4503):105–110. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4503.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauner B., Höltje J. V., Schwarz U. The composition of the murein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10088–10095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzija O. A simple method for the quantitative determination of muramic acid. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Hattori R. The physical environment in soil microbiology: an attempt to extend principles of microbiology to soil microoganisms. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1976 May;4(4):423–461. doi: 10.3109/10408417609102305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle B. D., Beveridge T. J. Metal binding by the peptidoglycan sacculus of Escherichia coli K-12. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Feb;30(2):204–211. doi: 10.1139/m84-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle B., Beveridge T. J. Binding of metallic ions to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):749–752. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.749-752.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOKRASCH L. C. Analysis of hexose phosphates and sugar mixtures with the anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld E. M., Beveridge T. J., Doyle R. J. Discontinuity of charge on cell wall poles of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Sep;31(9):875–877. doi: 10.1139/m85-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld E. M., Beveridge T. J., Koch A. L., Doyle R. J. Asymmetric distribution of charge on the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1167–1171. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1167-1171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]