Abstract
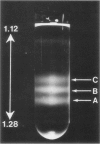
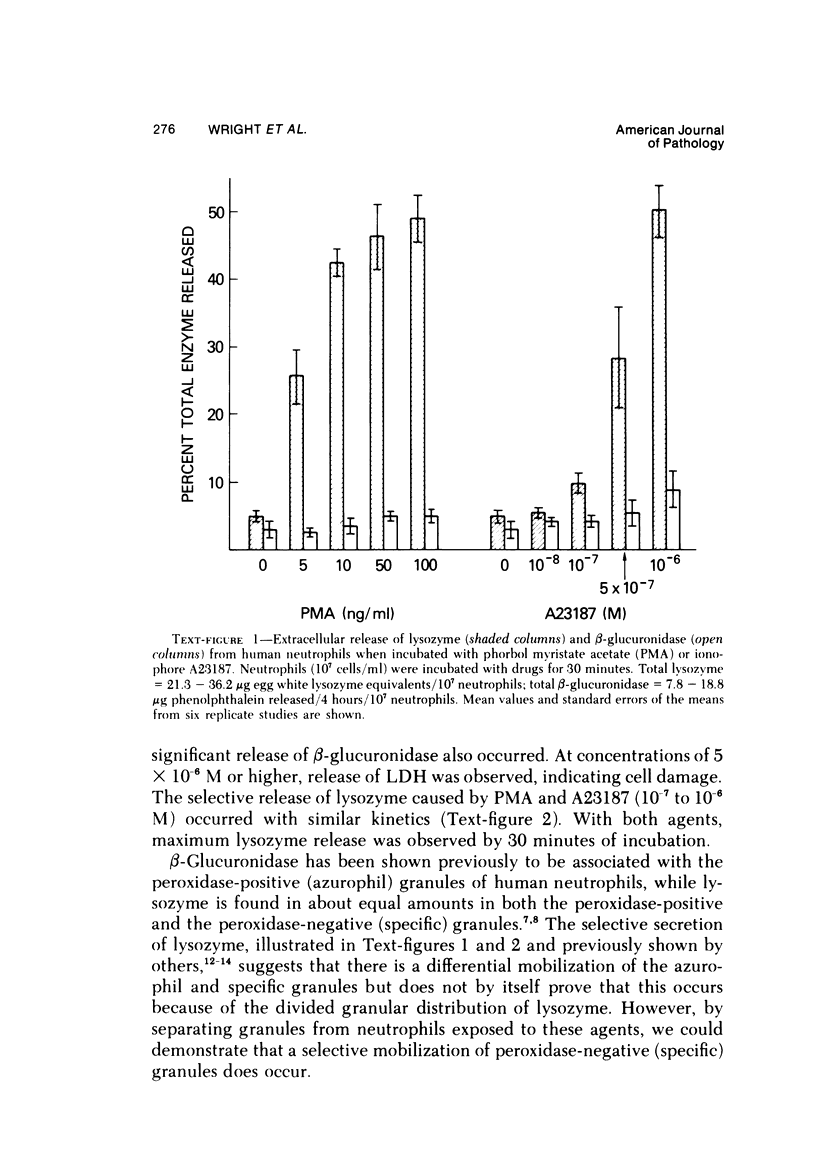
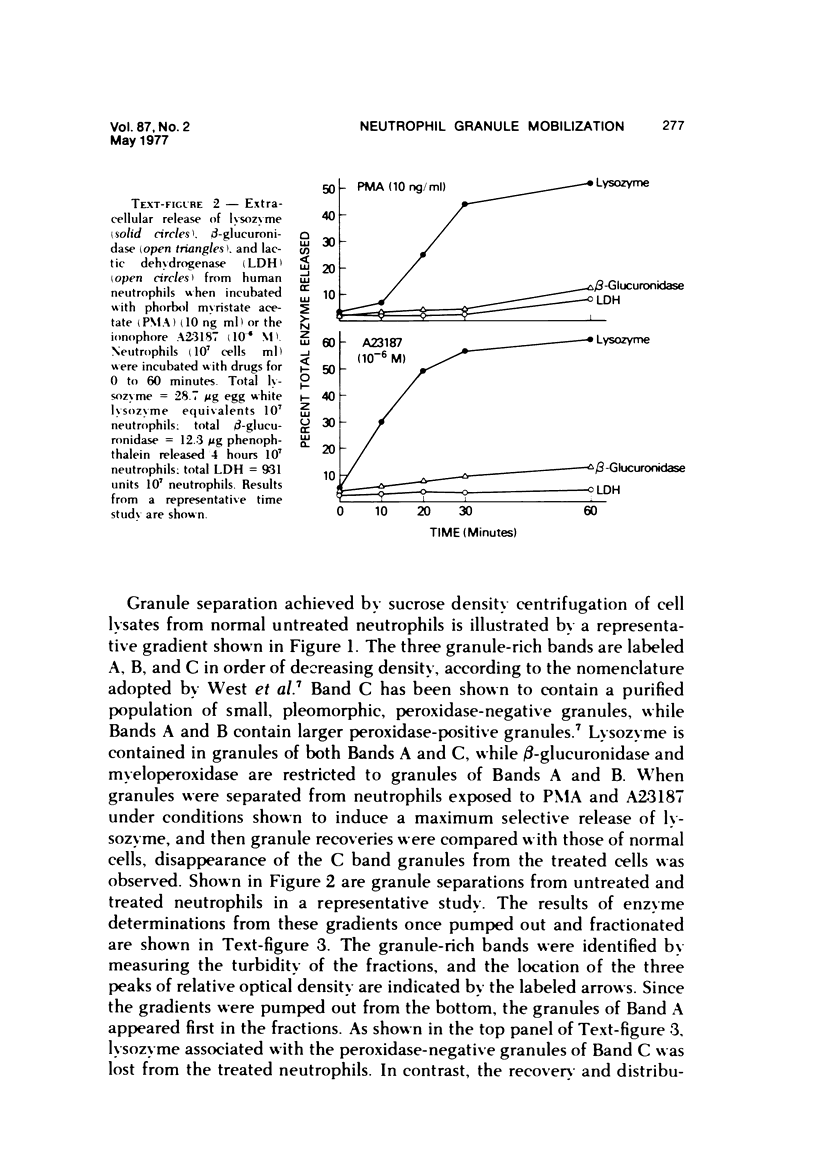
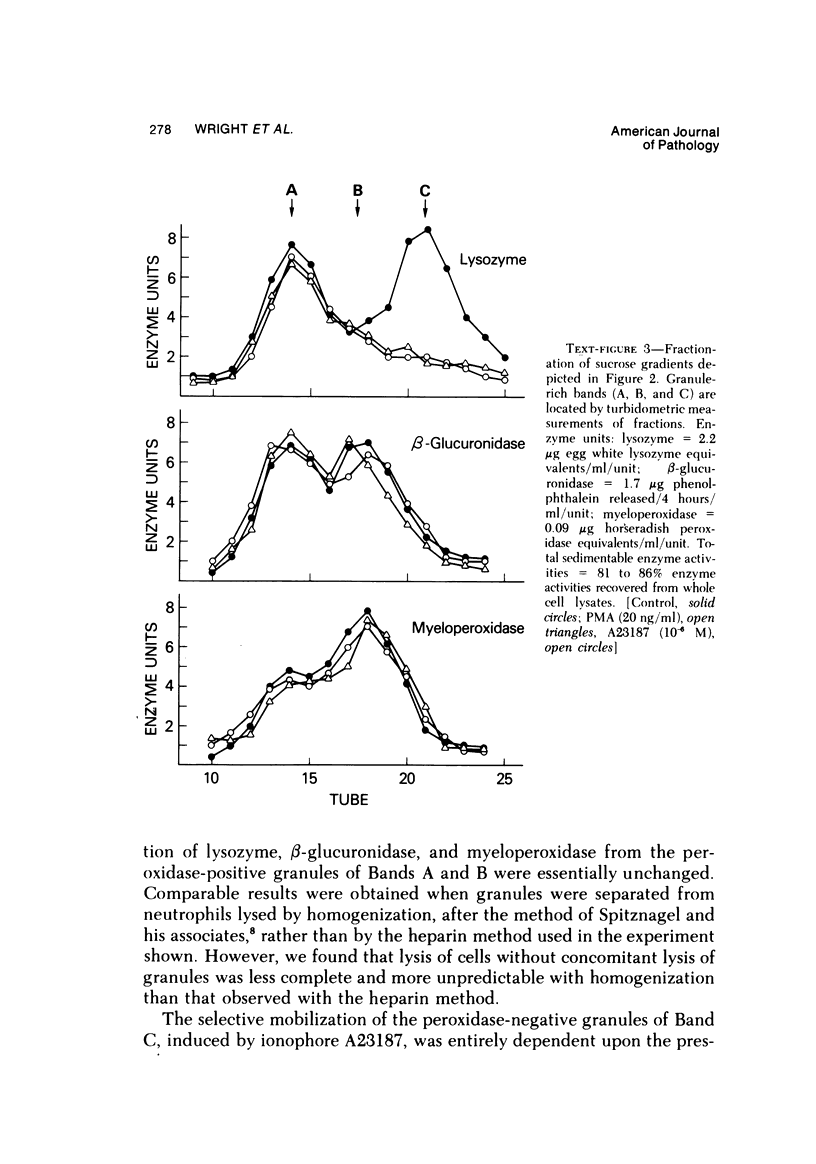
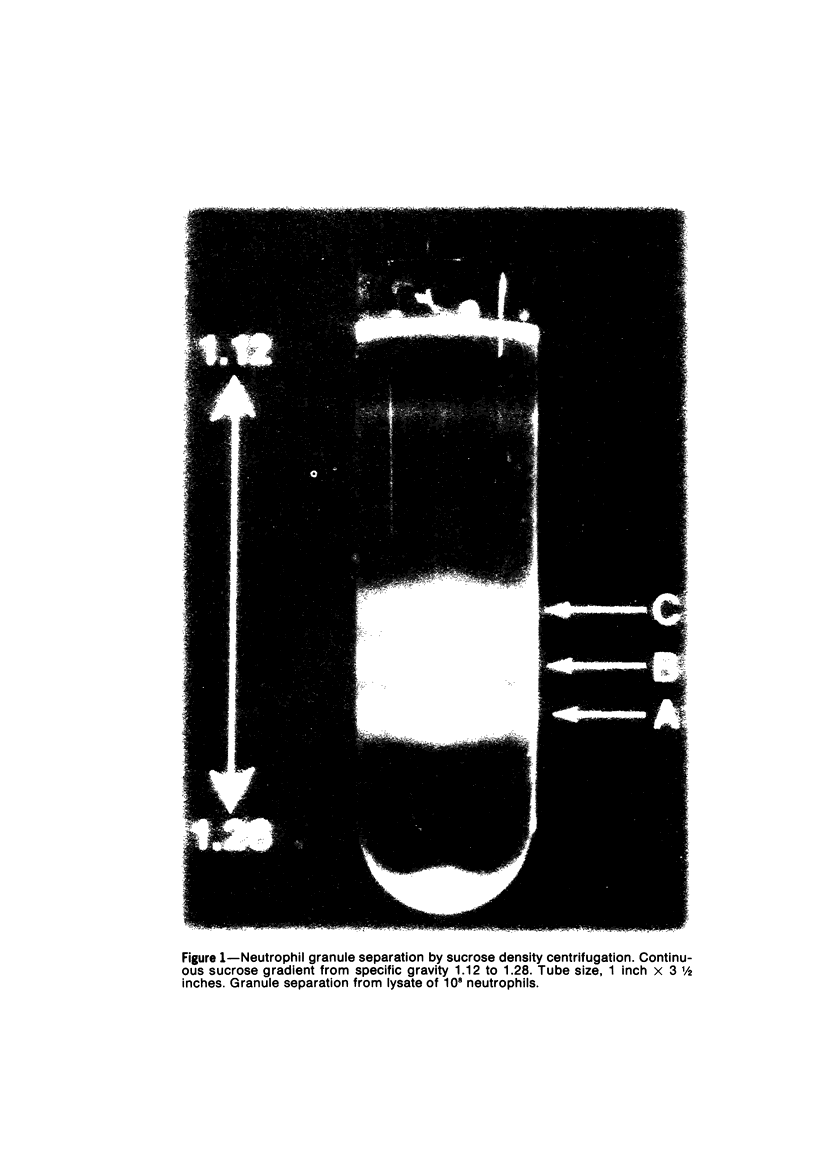
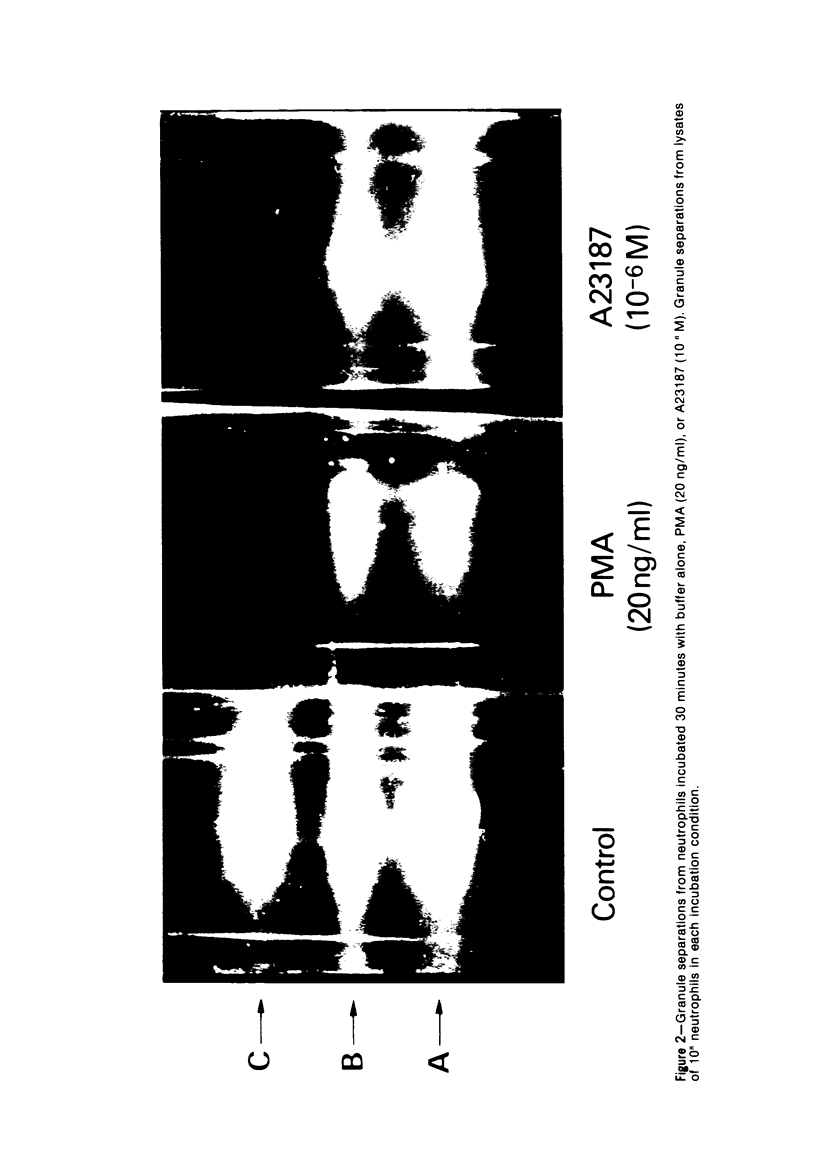
Phorbol myristate acetate (PMA, 2 to 100 ng/ml) and ionophore A23187 (10(-7) to 10(-6) M) cause human neutrophils to release up to 50% of the granule-associated enzyme lysozyme extracellularly without release of beta-glucuronidase or the cytoplasmic enzyme LDH. When azurophil and specific granules are separated from neutrophil lysates by sucrose density centrifugation, it is found that lysozyme release from neutrophils exposed to PMA or to A23187 reflects a selective disappearance of the small, peroxidase-negative (specific) granules from the cells. These studies demonstrate that neutrophils can mobilize the specific and azurophil granules independently. These studies also demonstrate that under certain conditions the specific granules of human neutrophils behave like the storage granules of secretory cells. Finally, these studies show that techniques of separating neutrophil granules according to their sedimentation characteristics successfully divide these granules into populations that are distinct not only by cytochemical and morphologic criteria but also according to their availability for mobilization and extracellular release. (APM J Pathol 87:273-284, 1977).
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. I. Histochemical staining of bone marrow smears. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):286–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. II. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy of bone marrow cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):299–317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Origin of granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Two types derived from opposite faces of the Golgi complex in developing granulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):277–301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F. Sequential degranulation of the two types of polymorphonuclear leukocyte granules during phagocytosis of microorganisms. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):249–264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Ullyot J. L., Farquhar M. G. The development of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes in human bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):907–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane D. E., Douglas W. W. Calcium-induced extrusion of secretory granules (exocytosis) in mast cells exposed to 48-80 or the ionophores A-23187 and X-537A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):408–412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eimerl S., Savion N., Heichal O., Selinger Z. Induction of enzyme secretion in rat pancreatic slices using the ionophore A-23187 and calcium. An experimental bypass of the hormone receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3991–3993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., White J. G., Holmes B. Specific degranulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1974 Mar 22;248(446):347–348. doi: 10.1038/248347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Hoffstein S. T., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Effects of phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):647–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffell M. S., Spitznagel J. K. Intracellular and extracellular degranulation of human polymorphonuclear azurophil and specific granules induced by immune complexes. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1241–1249. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1241-1249.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Dalldorf F. G., Leffell M. S., Folds J. D., Welsh I. R., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E. Character of azurophil and specific granules purified from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):774–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Costa J. L., Moss J., Kopin I. J. Mechanism of release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurones by the calcium ionophores X 537A and A 23187. Life Sci. 1974 May 1;14(9):1705–1719. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West B. C., Rosenthal A. S., Gelb N. A., Kimball H. R. Separation and characterization of human neutrophil granules. Am J Pathol. 1974 Oct;77(1):41–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel B. K., Horn R. G., Spicer S. S. Fine structural studies on the development of heterophil, eosinophil, and basophil granulocytes in rabbits. Lab Invest. 1967 Mar;16(3):349–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]