Abstract
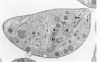
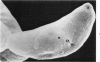
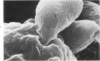
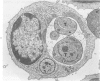
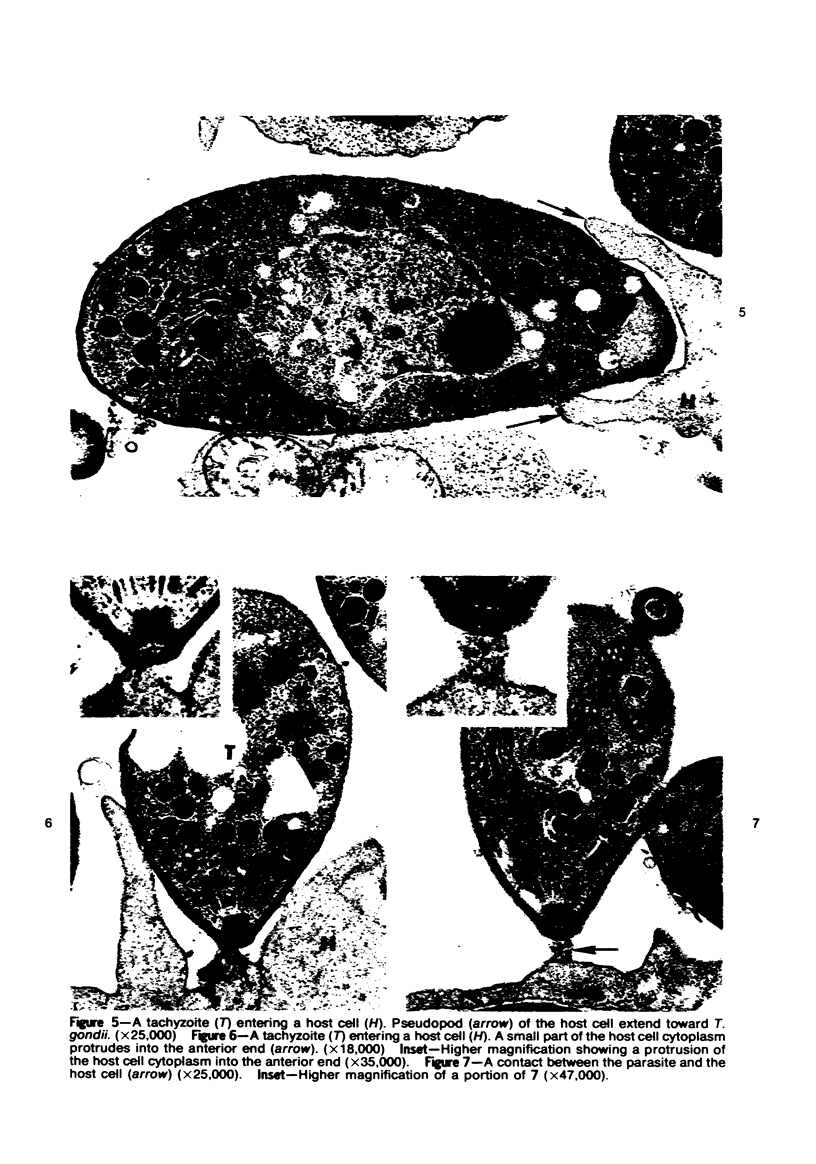
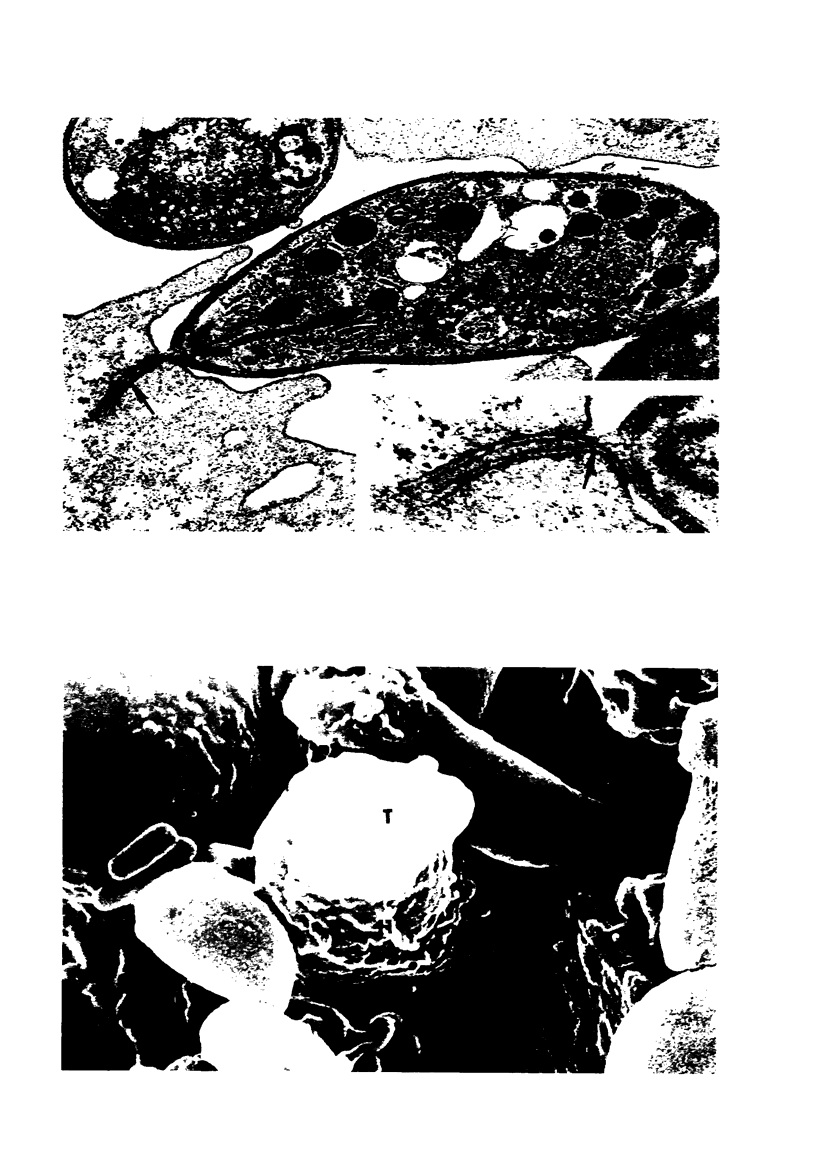
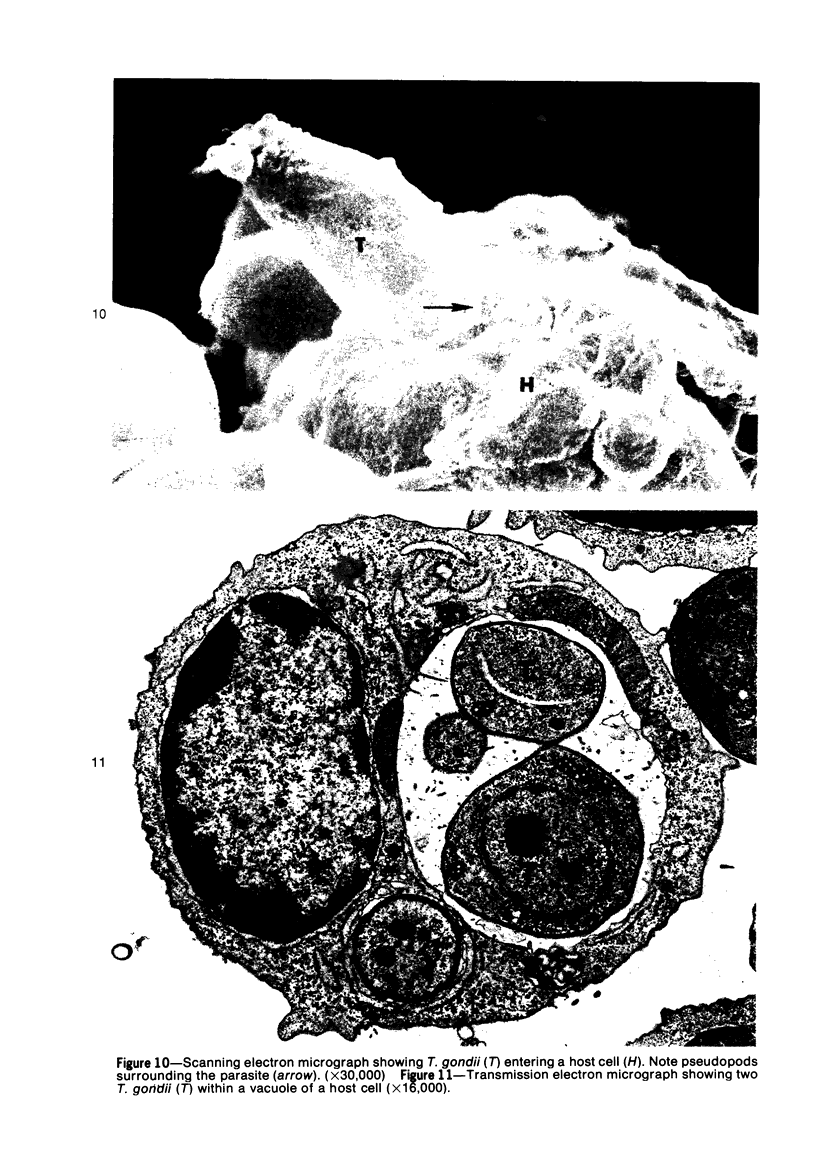
Entry by tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii, the causative agent of toxoplasmosis, into peritoneal cells was investigated with transmission and scanning electron microscopy. The process of entry is initiated by the parasite contacting the host cell with its anterior end, creating a small depression in the plasmalemma of the host cell. Occasionally, a small portion of the host cell cytoplasm protrudes and contaccts the anterior end of the parasite. A cylindrical structure (35 nm in diameter) extends from the pellicle of the parasite to the host cell. Such structures appear to assist host cell entry by T. gondii. As the entry process progresses, pseudopods of the host cell surround theparasite and finally T gondii becomes intracellular, being located in a vacuole separated from the host cell cytoplasm by a unit membrane. (Am J. Pathol 87:285-296, 1977).
Full text
PDF





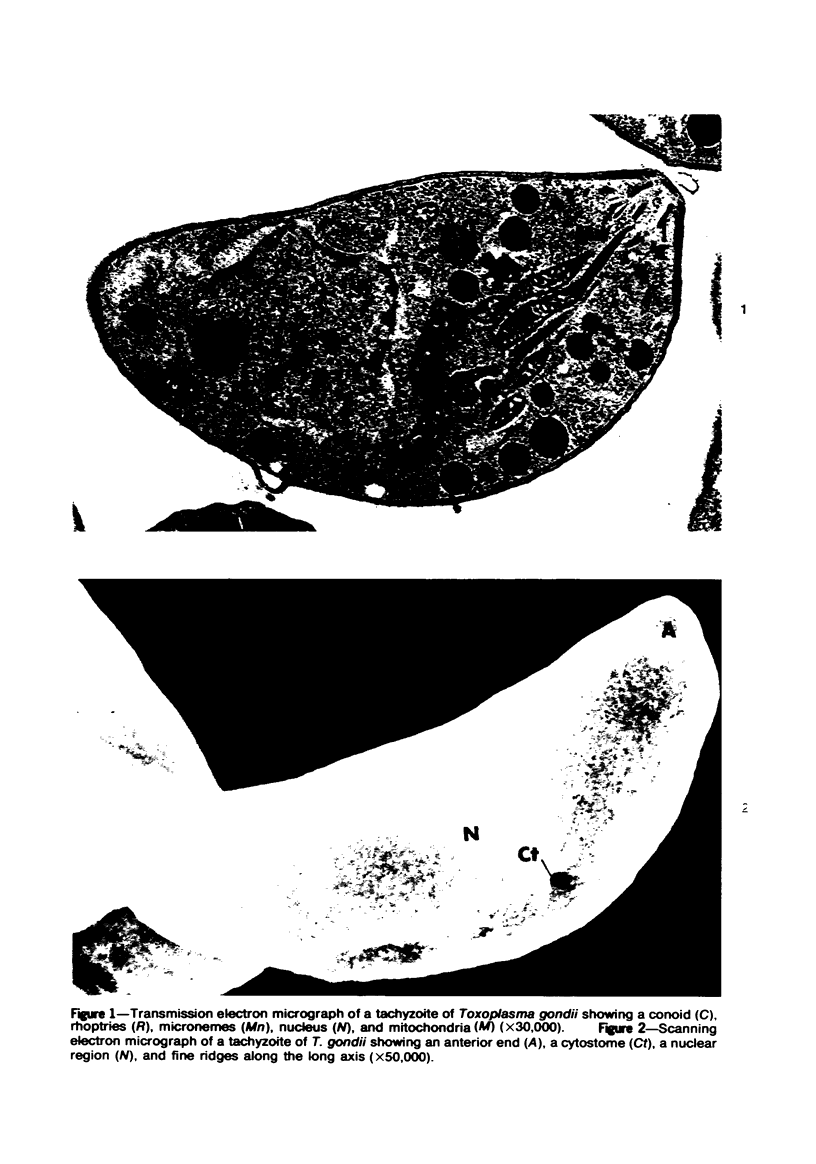
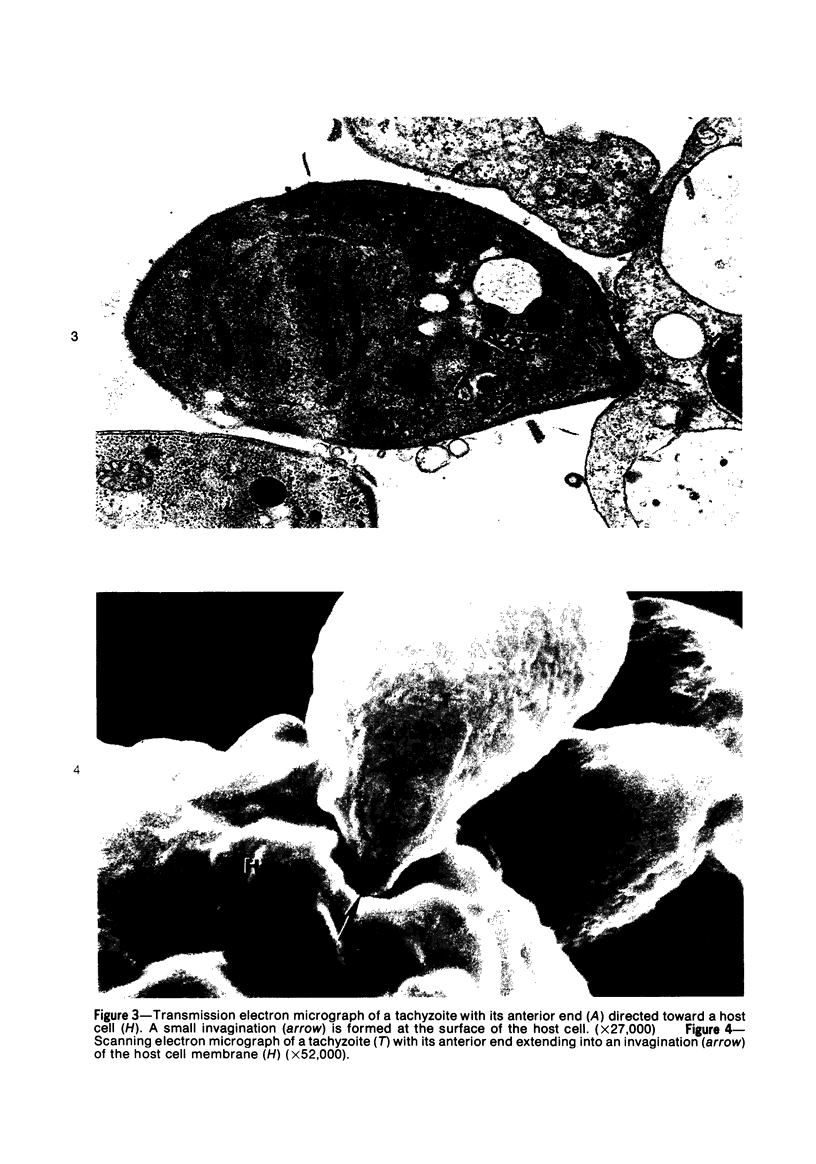

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannister L. H., Butcher G. A., Dennis E. D., Mitchell G. H. Structure and invasive behaviour of Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites in vitro. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):483–491. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000047247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommer W., Heunert H. H., Milthaler B. Kinematographische Studien über die Eigenbewegung von Toxoplasma gondii. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1969 Dec;20(4):450–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Yeh S., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. I. Mechanism of entry and intracellular fate of the parasite. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1157–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Scanning electron microscopy of Toxoplasma gondii. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladda R., Aikawa M., Sprinz H. Penetration of erythrocytes by merozoites of mammalian and avian malarial parasites. J Parasitol. 1969 Jun;55(3):633–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Carlberg K., Norrby R. Interactions between Toxoplasma gondii and its host cells: function of the penetration-enhancing factor of toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):853–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.853-861.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Endocytosis. Semin Hematol. 1970 Apr;7(2):161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Hammond D. M., Speer C. A. Ultrastructural study of the intra- and extracellular sporozoites of Eimeria callospermophili. J Parasitol. 1970 Oct;56(5):907–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtyseck E. Electron microscope observations concerning the penetration of a host cell by Eimeria ferrisi in vivo. Z Parasitenkd. 1975;46(1):91–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00383672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Garnham P. C., Shiroishi T. The fine structure of the sporozoite of Lankesteria culicis. J Protozool. 1971 Feb;18(1):98–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Melton M. L. The fine structure and reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1968 Apr;54(2):209–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]