Abstract
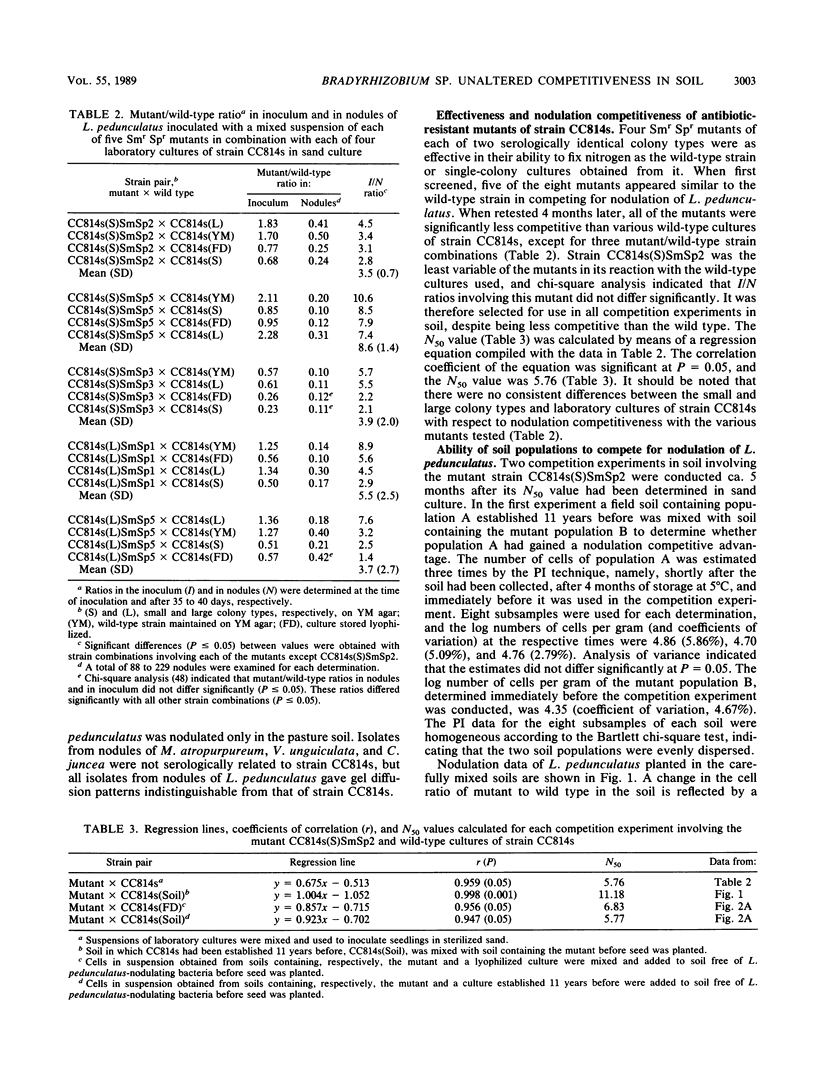
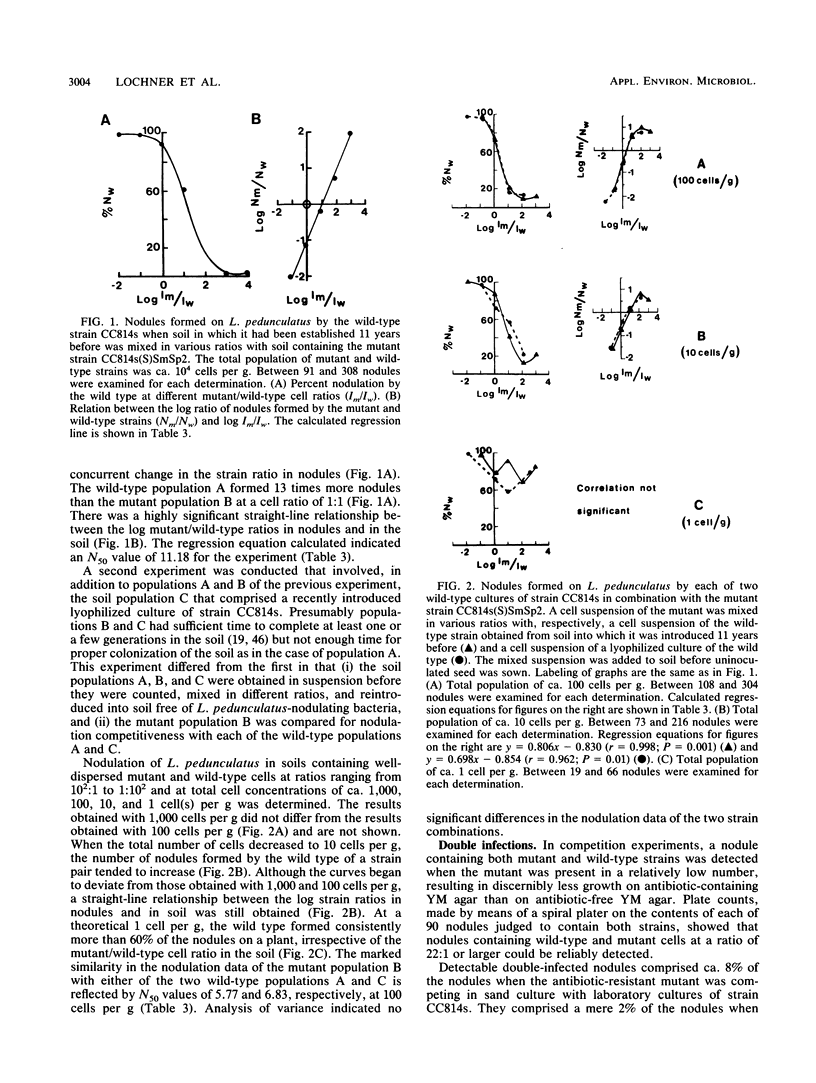
A Bradyrhizobium sp. (Lotus) strain that formed a soil population that was highly competitive for nodulation of Lotus pedunculatus 11 years after its introduction into a field soil and a culture of the same strain stored lyophilized were compared with an antibiotic-resistant mutant in respect of their nodulation competitiveness. The mutant was less competitive than the wild-type strain it was isolated from and had to be present at a cell ratio of 5.76:1 in mixed inoculum in sand culture to form 50% of the nodules on L. pedunculatus (50% nodulation value, 5.76). The 50% nodulation values for a soil population of the mutant mixed with soil populations of the lyophilized and field soil strain were, respectively, 6.83 and 5.77, indicating that the field soil strain was not significantly different from the lyophilized strain in nodulation competitiveness. A 50% nodulation value of 11.18 obtained when soil containing a recently established mutant population was mixed with the field soil containing the population established 11 years before, indicating that the plant infection technique underestimated cell numbers of the field soil population by 100%. Nodulation competitiveness was unaffected by the size of the strain populations in the range of 100 to 1,000 cells per g of soil; at 10 cells per g a significant correlation between strain ratios in nodules and in soil was still evident. The results indicated that apparently superior nodulation competitiveness of a well-established soil population relative to that of a subsequently introduced strain may not necessarily reflect the intrinsic competitive abilites of the strain(s) involved. The soil strain did not differ from laboratory-maintained cultures in antigenic properties, effectiveness, or whole cell protein electrophoresis profiles.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amarger N., Lobreau J. P. Quantitative study of nodulation competitiveness in Rhizobium strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):583–588. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.583-588.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Mills K. K., Crist D. K., Evans W. R., Bauer W. D. Effects of culture age on symbiotic infectivity of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):443–451. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.443-451.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Nonspecific staining: its control in immunofluorescence examination of soil. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1012–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. J., Dughri M. H. Population Size and Distribution of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii in Relation to Total Soil Bacteria and Soil Depth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):959–964. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.959-964.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel B., Cleyet-Marel J. C., Normand P., Bardin R. Stability of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Inoculants after Introduction into Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2636–2642. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2636-2642.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDMAN W. F. IMMUNE DIFFUSION ANALYSIS OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SOLUBLE ANTIGENS OF TWO STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM MELILOTI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:782–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.782-794.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demezas D. H., Bottomley P. J. Autecology in Rhizospheres and Nodulating Behavior of Indigenous Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1014–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1014-1019.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling D. N., Broughton W. J. Competition for nodulation of legumes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:131–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson J. K., Bezdicek D. F., Brockman F. J., Li S. W. Enumeration of Tn5 mutant bacteria in soil by using a most- probable-number-DNA hybridization procedure and antibiotic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.446-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamicker B. J., Brill W. J. Methods To Alter the Recovery and Nodule Location of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Inoculant Strains on Field-Grown Soybeans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1737–1742. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1737-1742.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley M. T., Bohlool B. B. Release of Rhizobium spp. from Tropical Soils and Recovery for Immunofluorescence Enumeration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):241–248. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.241-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishinevsky B., Bar-Joseph M. Rhizobium strain identification in Arachis hypogaea nodules by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Can J Microbiol. 1978 Dec;24(12):1537–1543. doi: 10.1139/m78-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B., Dowdle S., Sadowsky M. J. Competition of Rhizobium japonicum Strains in Early Stages of Soybean Nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):870–873. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.870-873.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B. Influence of Environmental Factors on Interstrain Competition in Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1128–1133. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1128-1133.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B. Suppression of nodule development of one side of a split-root system of soybeans caused by prior inoculation of the other side. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):125–130. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis J. N., Barbour W. M., Miller T. B., Israel D. W., Elkan G. H. Characterization of a Mannitol-Utilizing, Nitrogen-Fixing Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 Derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):81–85. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.81-85.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Yamaguchi M. Fractionation and Estimation of Particle-Attached and Unattached Bradyrhizobium japonicum Strains in Soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):911–914. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.911-914.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert F. M., Schmidt E. L. Population Changes and Persistence of Rhizobium phaseoli in Soil and Rhizospheres. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.550-556.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Gibson A. H., Dudman W. F., Watson J. M. Evidence for genetic exchange and recombination of Rhizobium symbiotic plasmids in a soil population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2942–2947. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2942-2947.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rensburg H. J., Strijdom B. W. Competitive Abilities of Rhizobium meliloti Strains Considered to Have Potential as Inoculants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):98–106. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.98-106.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rensburg H. J., Strijdom B. W. Effectiveness of Rhizobium strains used in inoculants after their introduction into soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.127-131.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



