Abstract
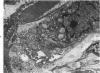
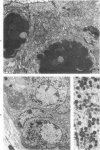
Thirty-three male Sprague-Dawley rats were fed a carcinogenic (0.064% 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene, 3'-Me-DAB) ground meal normal diet. After 12 weeks the ground meal diet was replaced with a normal pellet diet, and the 30 surviving animals were divided into three equal groups. One group was sacrificed at the twelfth week and the other groups 4 and 8 weeks later. Control animals were also run. Based on previous studies which used "tumor-promoting" diets and 3'-Me-DAB, we expected a less than 100% incidence of predominantly hepatocellular carcinomas. However, we found mucin-producing cholangiocarcinomas in all 30 animals and, in addition, a small hepatocellular component in 3 of the animals. By electron microscopy the intestinal mucosal features of microvillous border cells, goblet cells, and endocrine-like cells were found. We suggest that the tumors produced as described here provide a good animal model of mucin-producing cholangiocarcinomas.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert L. I., Zak F. G., Werthamer S., Bochetto J. F. Cholangiocarcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of five cases with ultrastructural observations. Hum Pathol. 1974 Nov;5(6):709–728. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBER E. Similarities in the sequence of early histological changes induced in the liver of the rat by ethionine, 2-acetylamino-fluorene, and 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 1956 Feb;16(2):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIRMINGER H. I., MULAY A. S. Histochemical and morphologic differentiation of induced tumors of the liver in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1952 Aug;13(1):19–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber E. Carcinogenesis--cellular evolution as a unifying thread: Presidential address. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2537–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb S. A morphological and histochemical study of carcinogenesis of the liver in rats fed 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 1973 May;33(5):1119–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma M. H., Webber A. J. Fine structure of liver tumors induced in the rat by 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 1966 May;26(5):935–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A. Carcinogenesis by chemicals: an overview--G. H. A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res. 1970 Mar;30(3):559–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Minase T., Onhoe T. Demonstration of glucose 6-phosphatase activity in the oval cells of rat liver and the significance of the oval cells in azo dye carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3379–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON H. L., BORSOS-NACHTNEBEL E. Study of liver tumor development and histologic changes in other organs in rats fed azo dye 3-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 1951 Jun;11(6):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVOBODA D. J. FINE STRUCTURE OF HEPATOMAS INDUCED IN RATS WITH P-DIMETHYLAMINOAZOBENZENE. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Aug;33:315–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda D., Higginson J. A comparison of ultrastructural changes in rat liver due to chemical carcinogens. Cancer Res. 1968 Sep;28(9):1703–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao K., Nakano M. Cholangiofibrosis induced by short-term feeding of 3'-methyl-4-(dimethylamino)azobenzene: an electron microscopic observation. Gan. 1974 Jun;65(3):249–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welbourn R. B., Pearse A. G., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Joffe S. N. The APUD cells of the alimentary tract in health and disease. Med Clin North Am. 1974 Nov;58(6):1359–1374. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]