Abstract
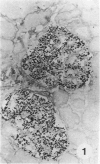
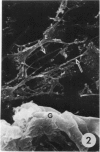
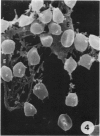
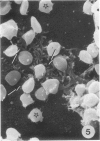
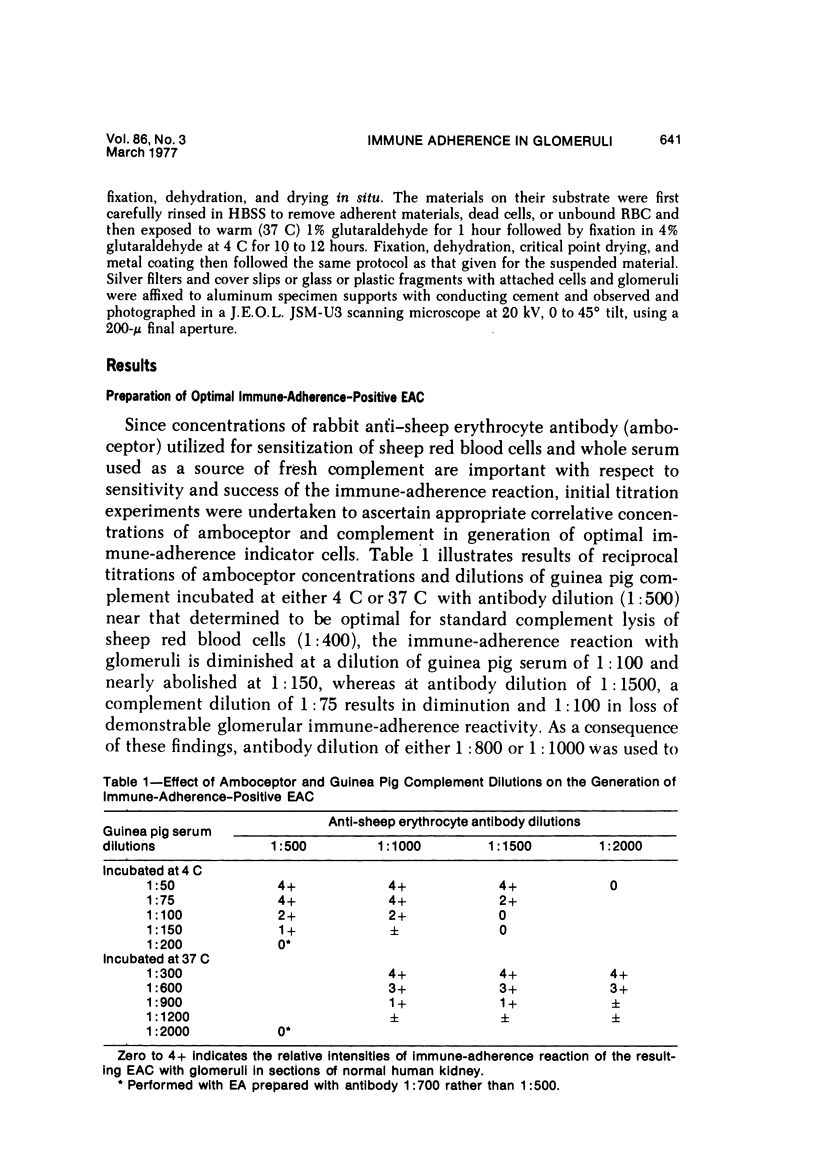
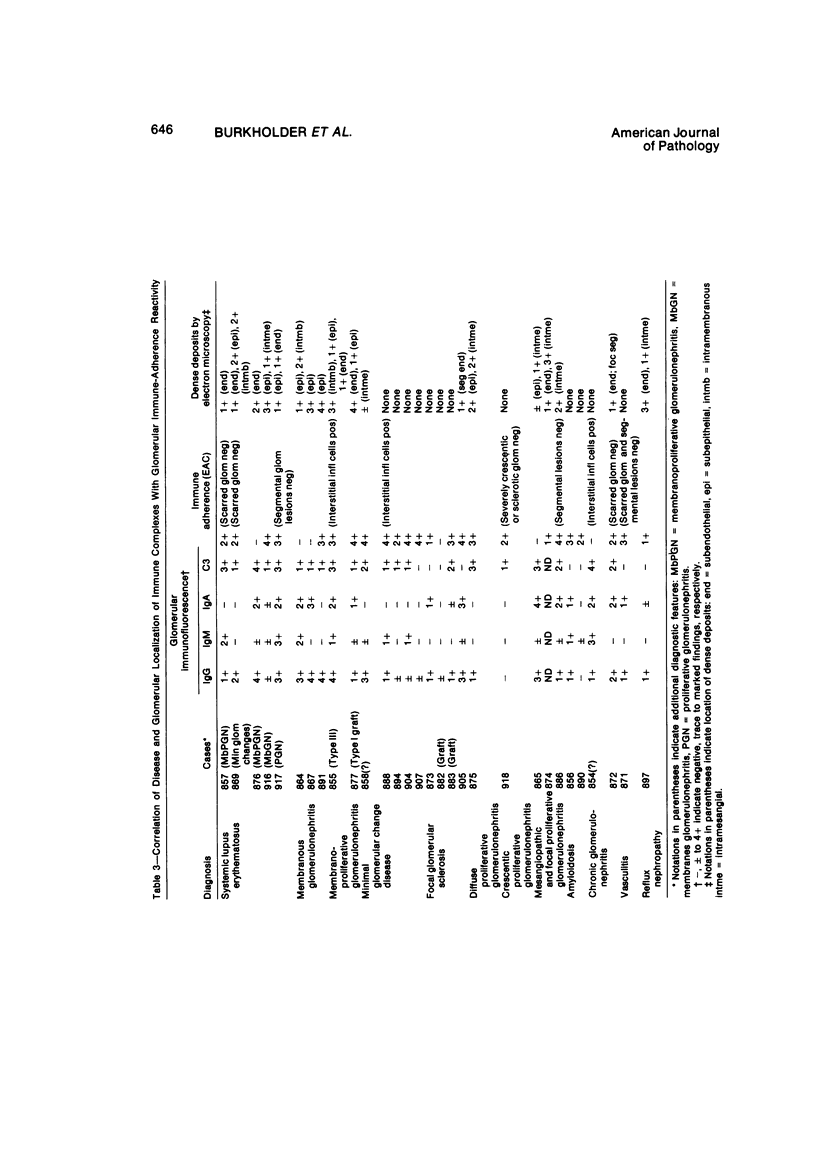
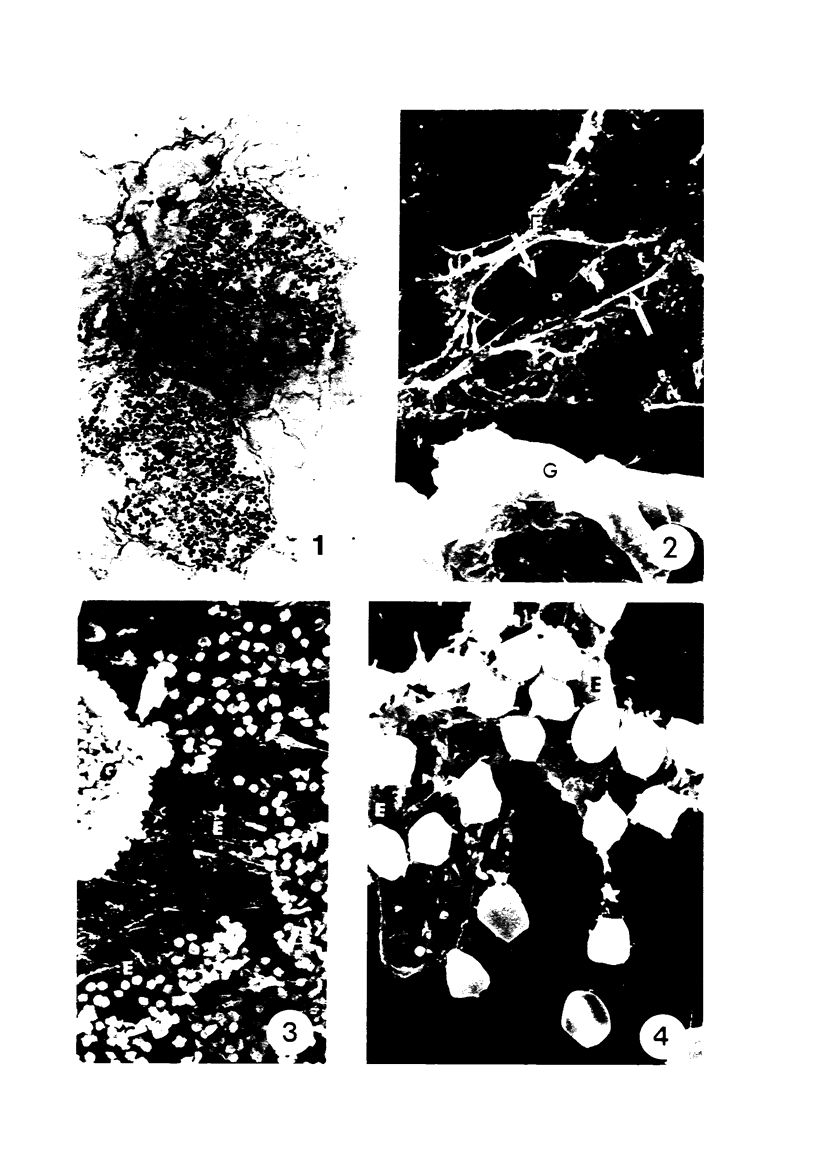
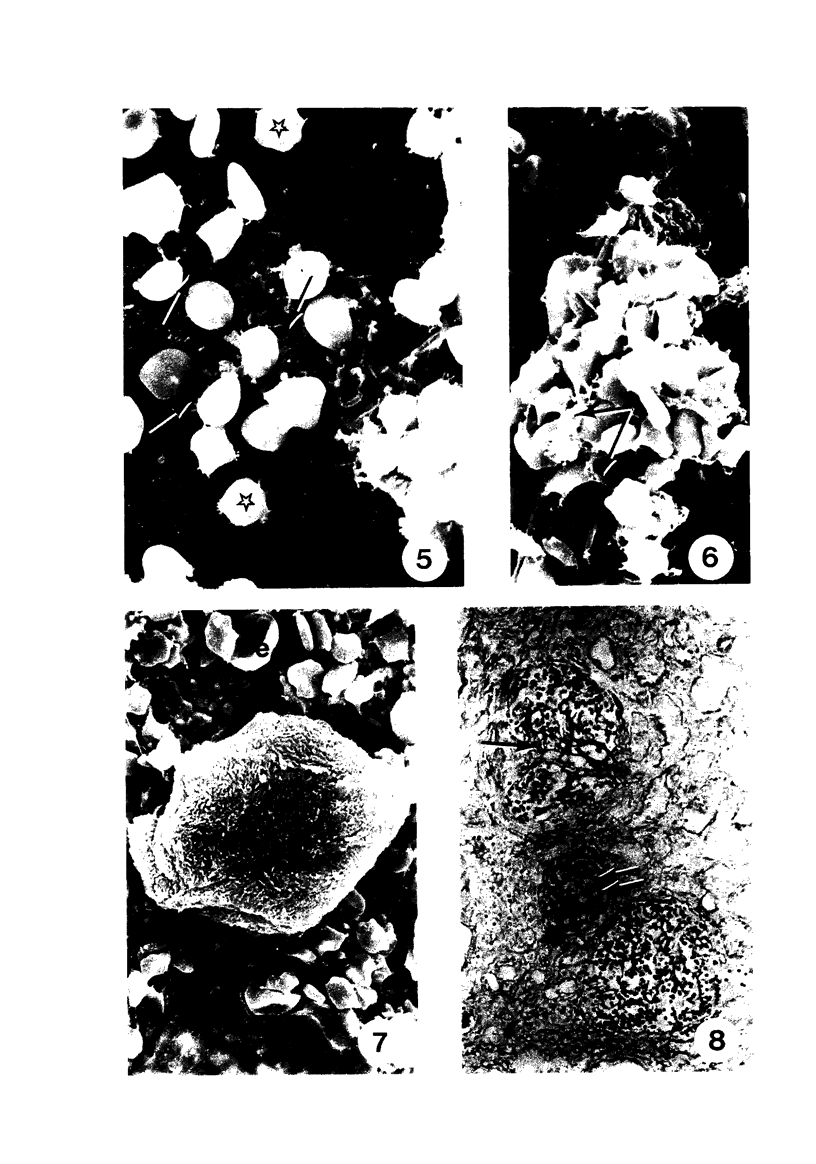
Several very recent reports have indicated the presence of receptor sites for the third component of complement in human but not other vertebrate renal glomeruli. The present study constitutes a demonstration that the glomerular capillary epithelial cell bears this receptor, detectable with either EAC complexes (EAC1423b) or fluores ceinated zymosan-C3 (ZC3b) complexes, Fresh, unfixed frozen sections of normal or diseased human kidneys, mechanically isolated human glomeruli, dissociated glomerular cells, and glomeruli and golmerular cells maintained in tissue culture were examined with various EAC complexes or ZC3b and examined by phase light microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, or transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Clearly, by scanning electron microscopy it was determined that glomerular capillary epithelial cells bind the immune-adherence EAC indicator cells. Because glomeruli or glomerular epithelial cells did not bind E, EA, EACI, EAC14, or EAC142 but did bind EAC1423b or ZC3b, it is concluded that C3b (activated bound fragment of the third component of complement) is responsible for the immune-adherence reaction in glomeruli. Preliminary examination of diseased renal biopsies indicates that sclerotic glomeruli, focal segmental sclerotic or proliferative glomerular capillary lesions, and proliferative epithelial crescents are immune-adherence negative. Furthermore, a clear or consistent inverse relationship between glomerular capillary deposits of C3 which presumably might block epithelial C3 receptor sites, and immune-adherence reactivity with EAC in vitro was not as evident in this study as reported previously by other investigators. Nevertheless, it is still attractive to conceive that glomerular C3 receptor sites might be responsible for binding of antigen-antibody-complement complexes and formation of immune-complex deposits, at least on the epimembranous (subepithelial) surface of glomerular capillary walls. Inability to demonstrate this immune-adherence phenomenon in glomeruli of other vertebrate animals suggests among other things that more investigation is necessary before ascribing a unique or universal significance to the C3 receptors identified in human glomeruli.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa M. A scanning electron microscopy of the glomerulus of normal and nephrotic rats. Lab Invest. 1970 Nov;23(5):489–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B. Contractile activity of human glomeruli in culture. Nephron. 1969;6(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000179708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R. Immune adherence by the fourth component of complement. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):396–398. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Frank M. M., Green I. A receptor for the third component of complement in the human renal glomerulus. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):1029–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Shin M. L., Nagle R. B., Green I., Frank M. M. The glomerular complement receptor in immunologically mediated renal glomerular injury. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 1;295(1):10–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607012950103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN P. G., BURKHOLDER P. M. Studies on the antigenic properties of complement. II. Analysis of specific agglutinins against certain components of guinea pig complement fixed on sensitized sheep erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:107–117. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN P. G. Studies on immune hemolysis: preparation of a stable and highly reactive complex of sensitized erythrocytes and the first component of complement (EAC'1): inactivation of cell-fixed C'1 by some complement reagents. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:77–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. The role of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody in the pathogenesis of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):989–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J. D., EVELAND W. C., SMITH C. W. Superiority of fluorescein isothiocyanate (Riggs) for fluorescent-antibody technic with a modification of its application. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer C. J., Lindeman J. A modified method for tissue localization of cells bearing a complement receptor. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Nov;9(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON R. A., Jr The immune-adherence phenomenon; a hypothetical role of erythrocytes in defence against bacteria and viruses. Proc R Soc Med. 1956 Jan;49(1):55–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIOKA K., LINSCOTT W. D. COMPONENTS OF GUINEA PIG COMPLEMENT. I. SEPARATION OF A SERUM FRACTION ESSENTIAL FOR IMMUNE HEMOLYSIS AND IMMUNE ADHERENCE. J Exp Med. 1963 Nov 1;118:767–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.5.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Polley M. J., Rabellino E. M., Grey H. M. Two different complement receptors on human lymphocytes. One specific for C3b and one specific for C3b inactivator-cleaved C3b. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):798–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A. T., Gabay Y. E., Lagrue G. Analysis of glomerular complement receptors in various types of glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Jul;6(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]