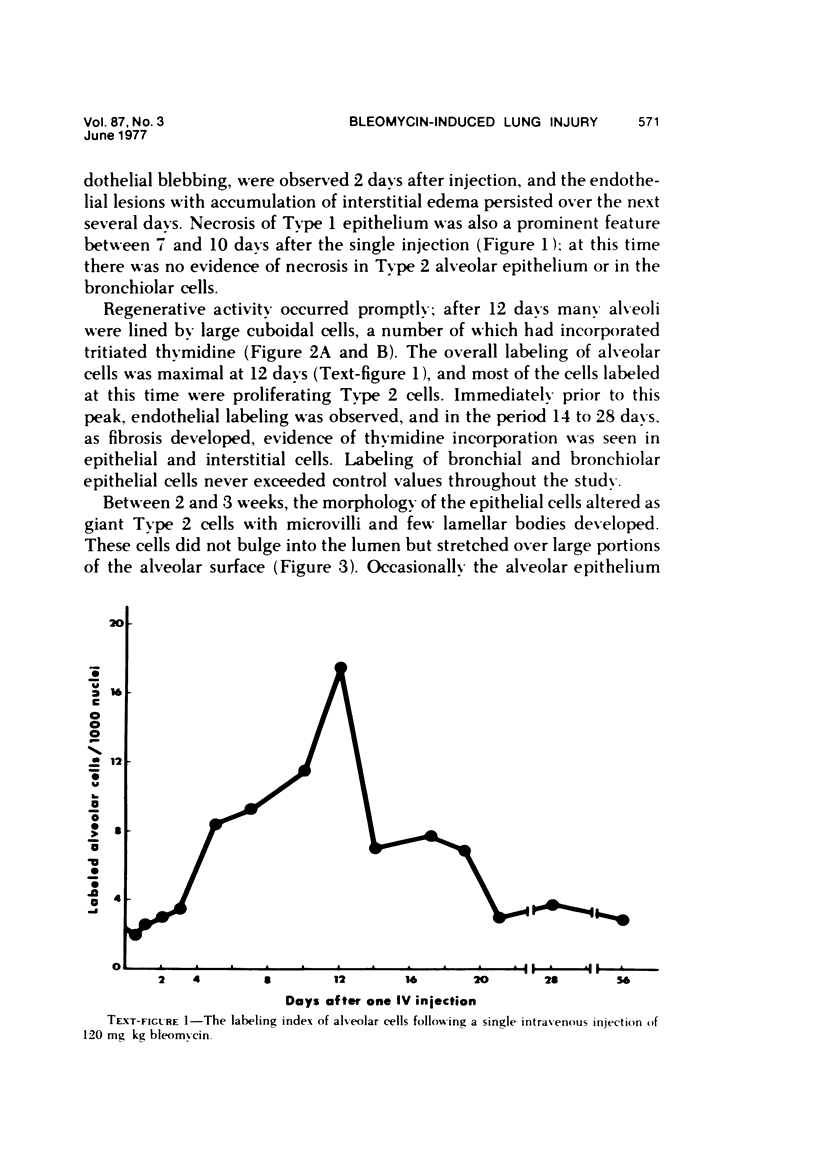
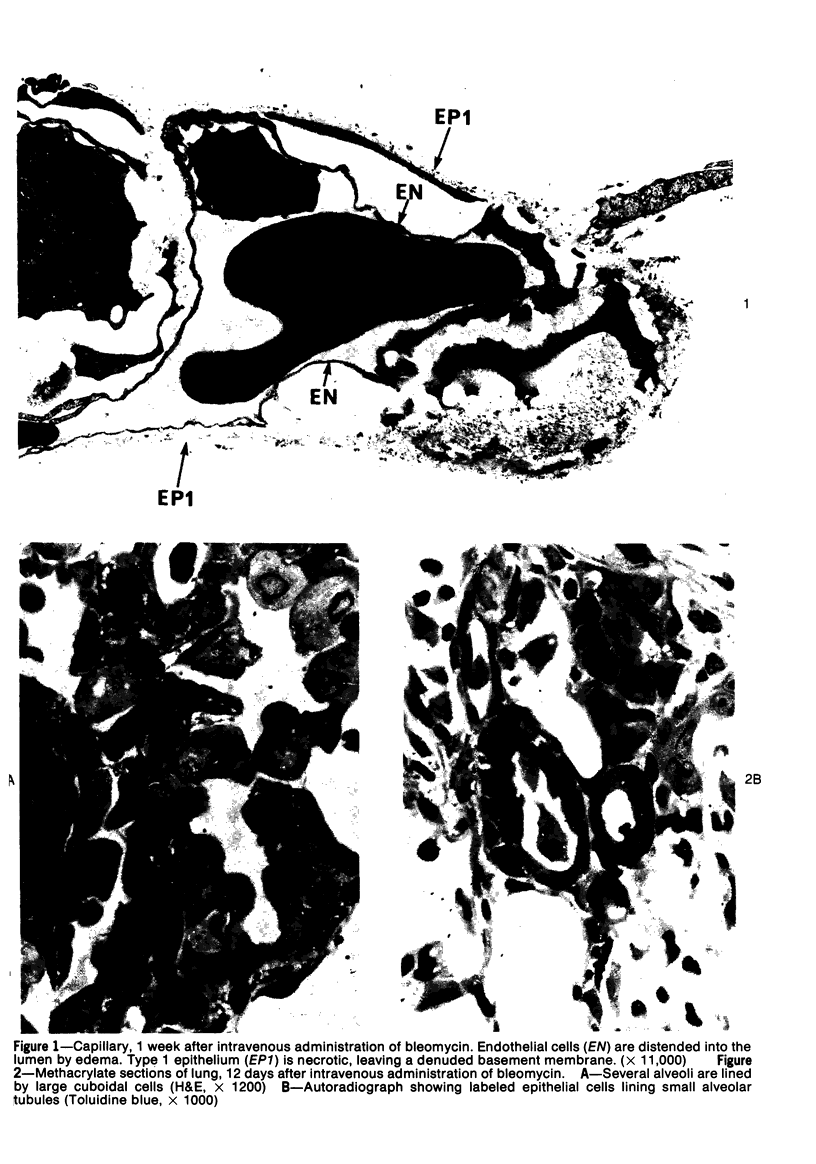
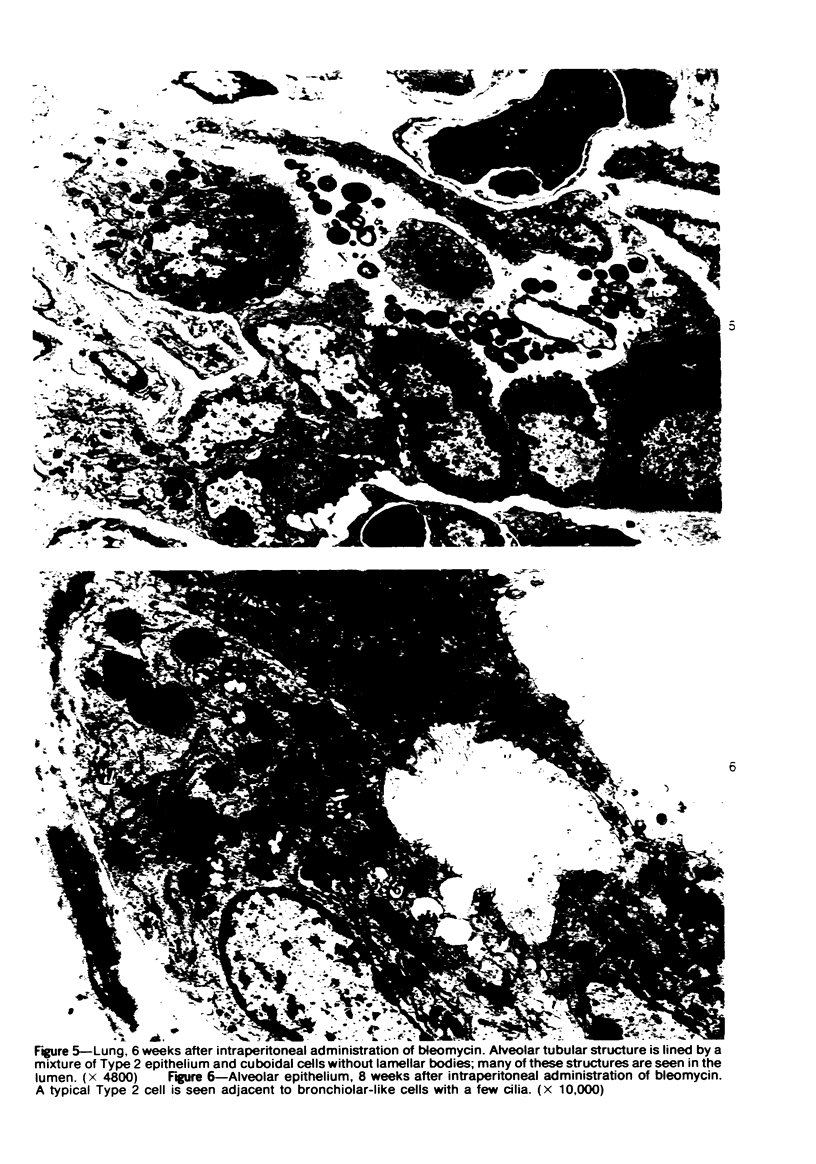
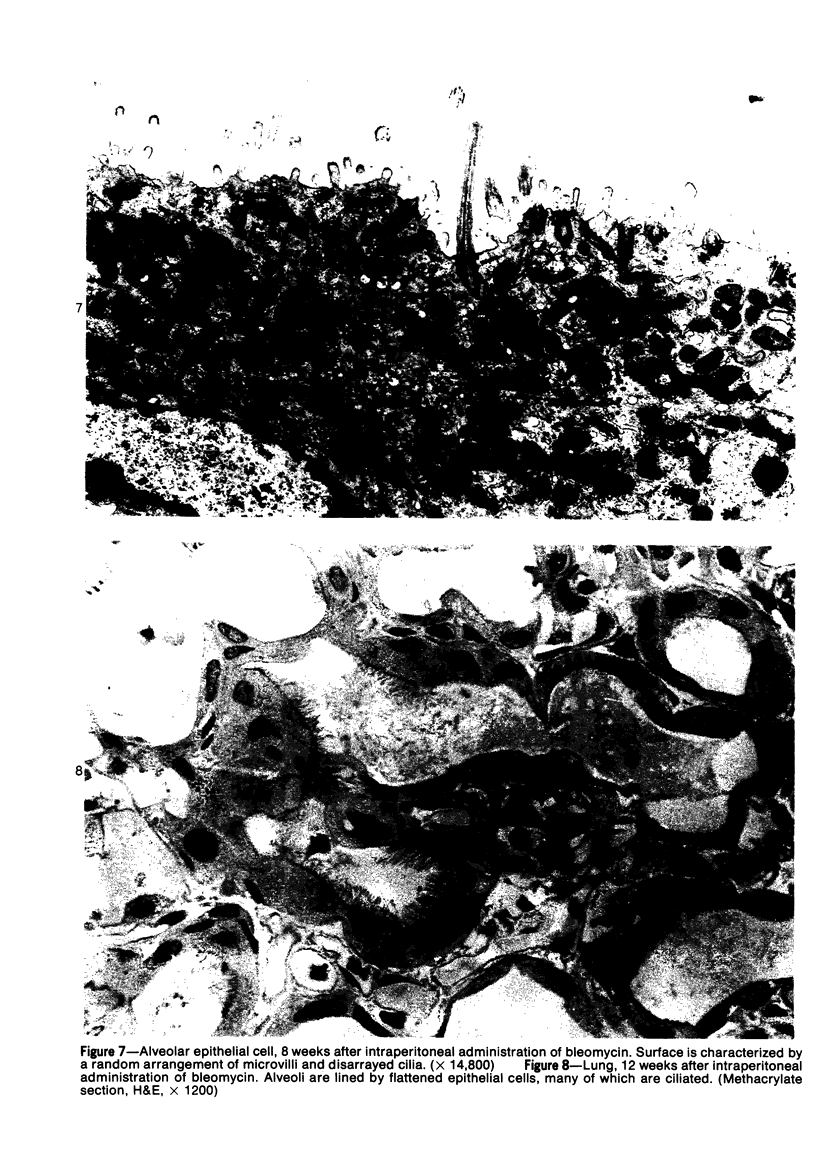
Abstract
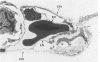
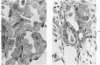
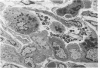
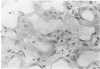
Bleomycin is known to induce diffuse pulmonary fibrosis and epithelial metaplasia. The reaction of the alveolar epithelium following a single intravenous or multiple intraperitoneal injections of bleomycin to mice is now examined in a combined morphologic and cytodynamic study. Necrosis of Type 1 cells was observed, followed by proliferation of Type 2 cells, a common reparative process. The proliferated cells transformed to a variety of epithelial forms, including ciliated cells and cells with morphologic features intermediate between alveolar and bronchiolar epithelium. No evidence of cell injury or increased cell division was found in the bronchial epithelium. It is concluded that the metaplastic ciliated epithelial cells are produced by an abnormal reparative process in the alveolar epithelium. The results suggest that, whereas the "resting" Type 2 cell is not vulnerable to bleomycin, in the postmitotic phase the drug may modify the synthetic mechanisms of cellular differentiation and thereby induce metaplasia.
Full text
PDF
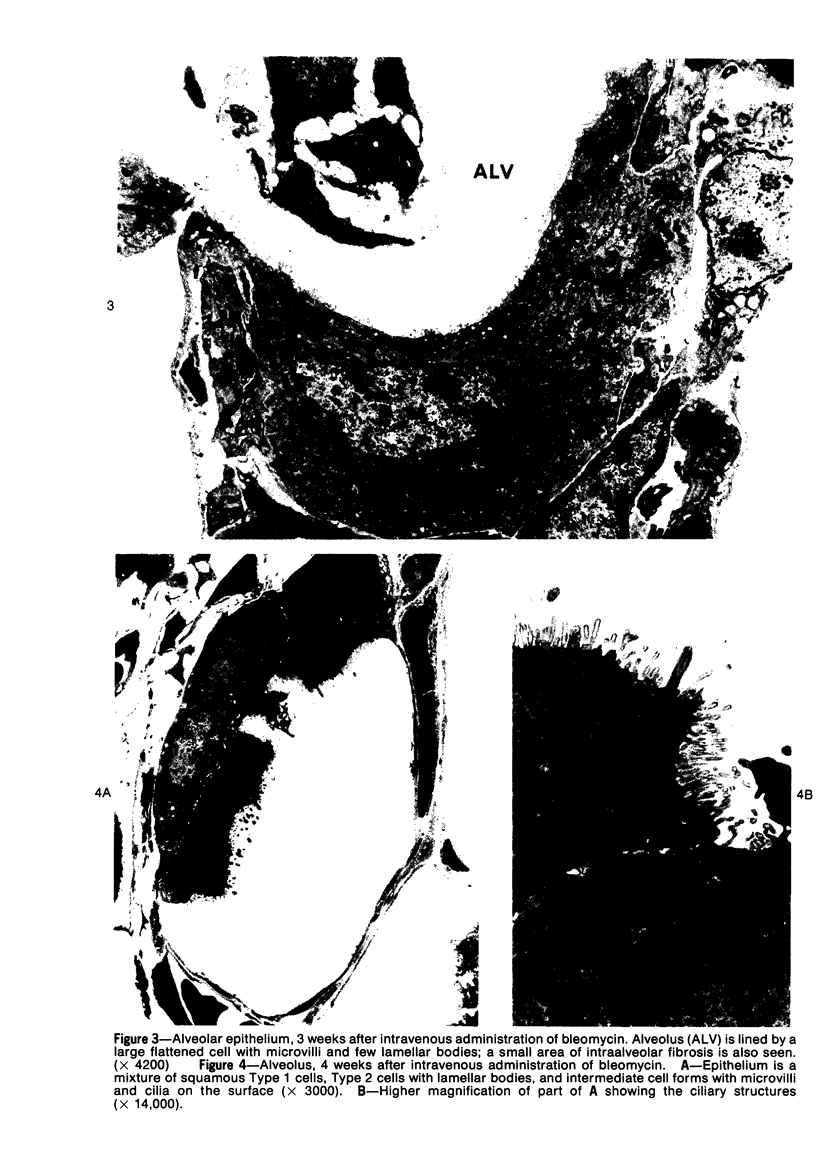







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Derivation of type 1 epithelium from type 2 cells in the developing rat lung. Lab Invest. 1975 Jun;32(6):736–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A., Thomas G., Wood M., Harris W. J. Histology and ultrastructure of metaplasia of alveolar epithelium following infection of mice and hamsters with influenza virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Apr;55(2):130–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. T. Hyperplaisa of the Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelium in Disease. Am J Pathol. 1943 Nov;19(6):901–911. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen O. P. The effect of bleomycin on rapidly proliferating epidermis. A comparative investigation using micro-flow fluorometry, H3Tdr incorporation and a stathmokinetic method (colcemid). Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1975 Dec 19;19(4):337–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02889377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal Z. M., Kohn K. W., Ewig R. A., Fornace A. J., Jr Single-strand scission and repair of DNA in mammalian cells by bleomycin. Cancer Res. 1976 Oct;36(10):3834–3838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen P. H., Clausen O. P., Iversen U. M., Rohrbach R. Some effects of bleomycin on the proliferation, maturation time and protein synthesis of hairless mouse epidermis. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1976 Jan;9(1):77–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1976.tb01255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOW F. N. The pulmonary alveolar epithelium of laboratory mammals and man. Anat Rec. 1953 Oct;117(2):241–263. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettesheim P., Szakal A. K. Morphogenesis of alveolar bronchiolization. Lab Invest. 1972 Feb;26(2):210–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Chemistry and mechanism of action of bleomycin. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Ishizuka M., Maeda K., Takeuchi T. Studies on bleomycin. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):891–895. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<891::aid-cncr2820200550>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuzumi G., Hyo Y., Hoshiya T., Yasuzumi F. Effects of bleomycin on human tongue carcinoma cells as revealed by electron microscopy. Cancer Res. 1976 Oct;36(10):3574–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]