Abstract
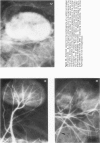
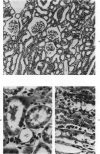
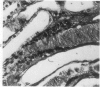
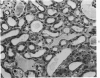
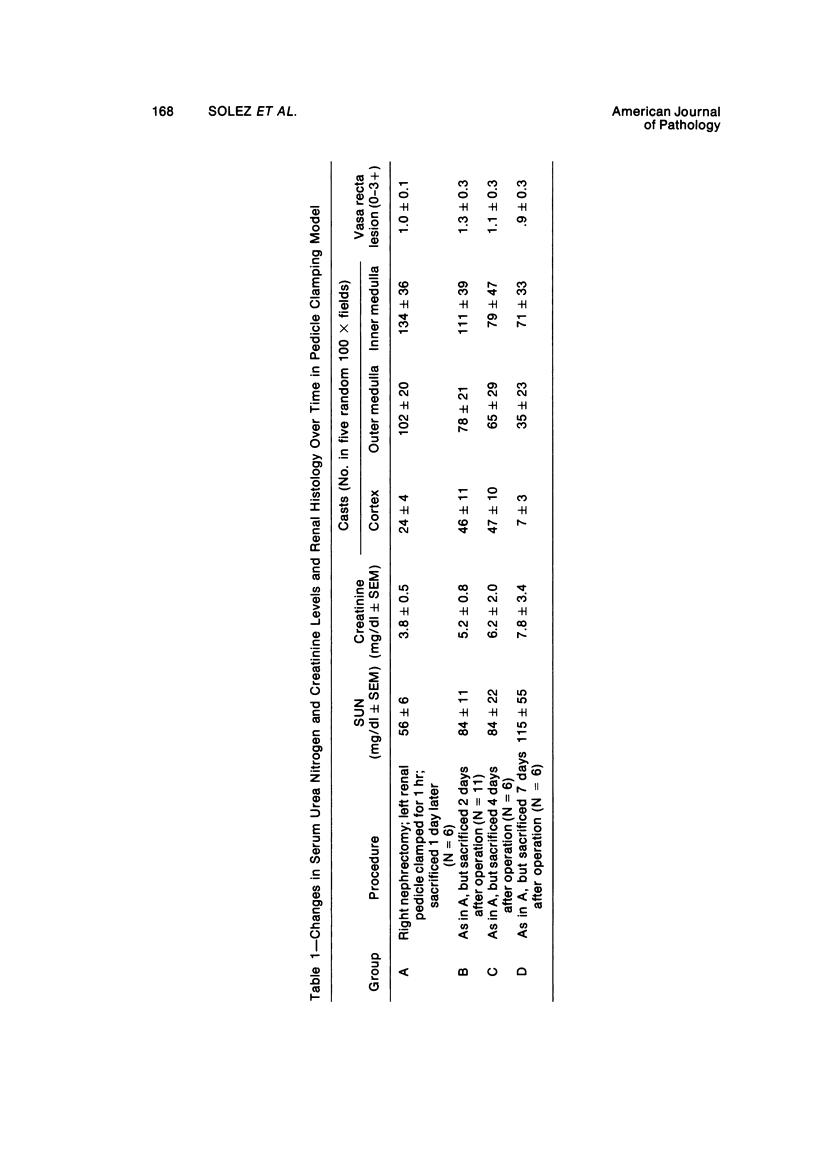
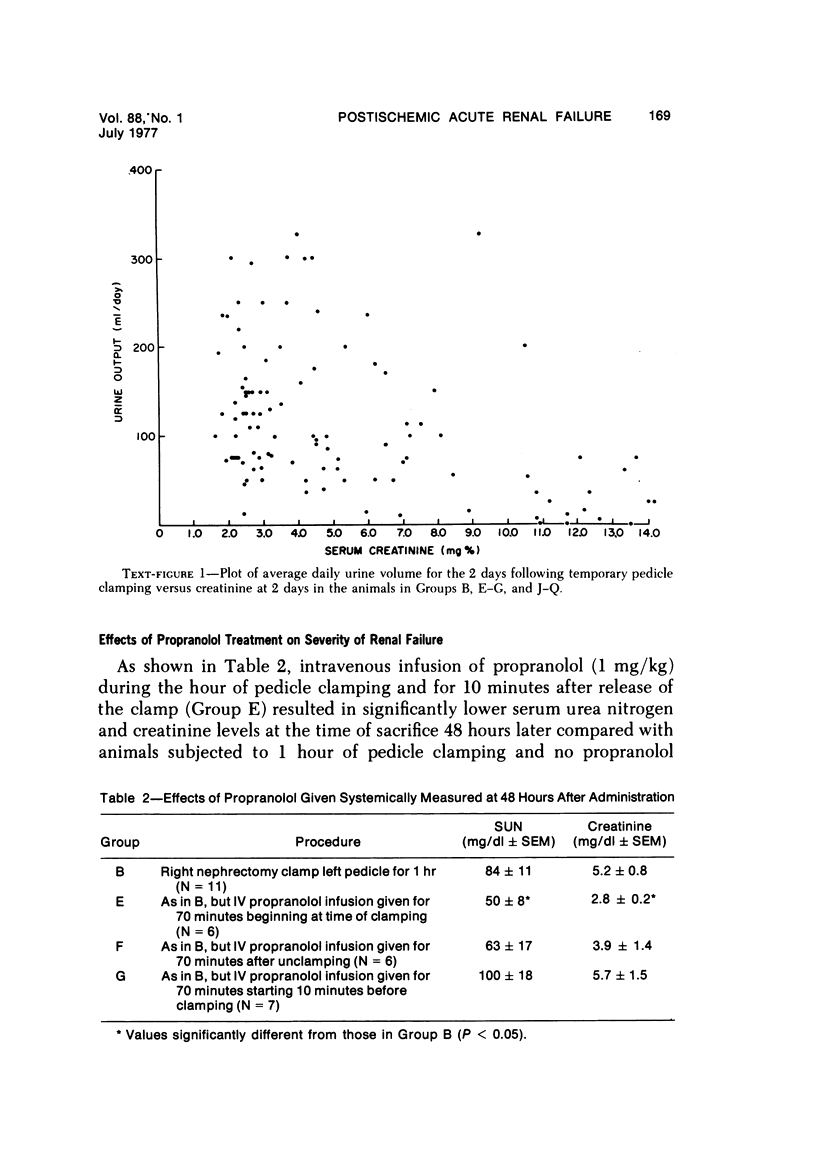
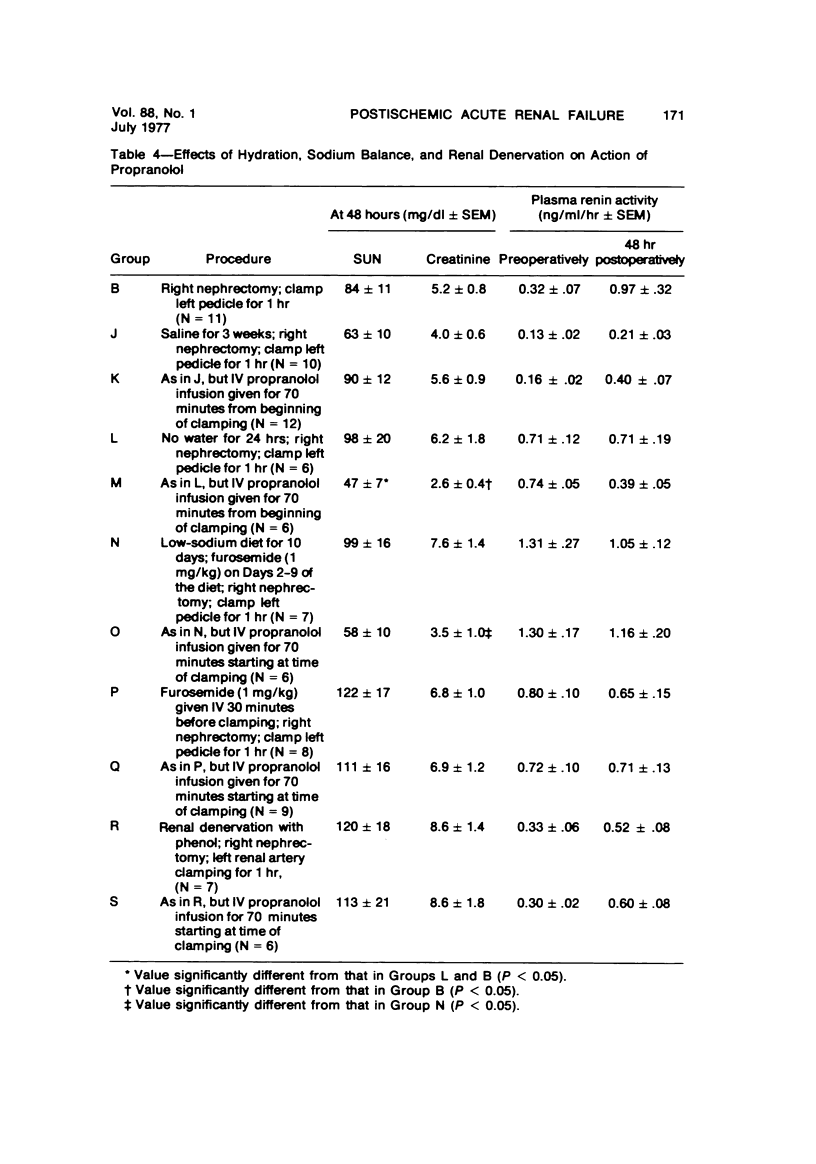
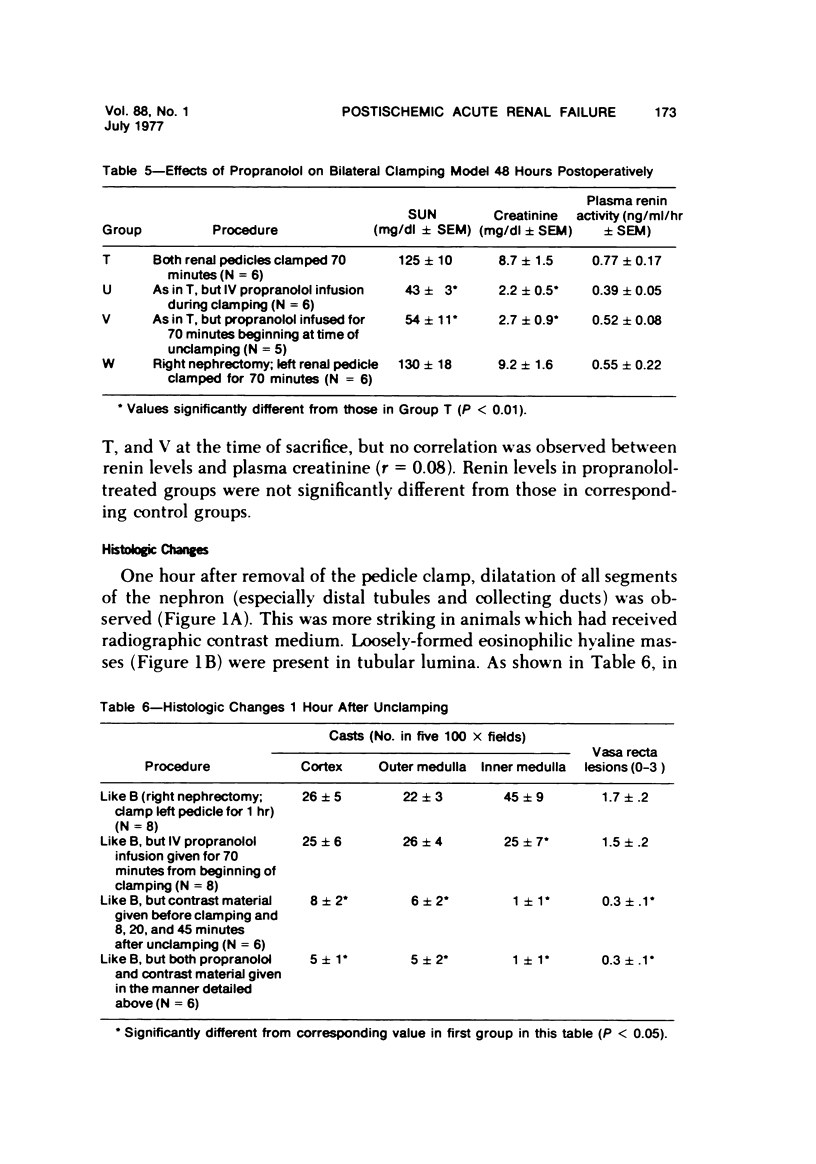
Acute renal failure caused in the rabbit by clamping one renal pedicle for 1 hour and removing the opposite kidney produced a histologic picture very similar to that observed in “hypotensive” acute renal failure in man. Intravenous infusion of propranolol, a drug which prevents renin release, at 1 mg/kg for 70 minutes beginning at time of pedicle clamping resulted in significantly lower serum creatinine in this model (2.8 ± 0.2 mg% at 48 hours with propranolol versus 5.2 ± 0.8 mg% without). Renin stimulation by dehydration or feeding a low-salt diet enhanced the difference between treated and untreated groups (2.6 ± 0.4 mg% with propranolol versus 6.2 ± 1.8 mg% without, after dehydration; 3.5 ± 1.0 mg% with propranolol versus 7.6 ± 1.4 mg% without, after low-salt diet).Suppression of renin production by saline feeding eliminated propranolol's beneficial effect (5.6 ± 0.9 mg% with propranolol versus 4.0 ± 0.6 mg% without). In rabbits with a normal food and water intake, renal denervation using phenol also eliminated propranolol's effect (creatinine 8.6 ± 1.4 mg% with propranolol versus 8.6 ± 1.8 mg% without). In rabbits with intact kidneys, flow probe recording of renal blood flow showed a significantly higher blood flow immediately after unclamping in the propranolol-treated animals, and renal angiograms showed less vasoconstriction in this group after unclamping. In this model of acute renal failure, renal vasoconstriction plays an important role following the initial ischemic insult. Propranolol lessens the severity of this vasoconstriction and the resulting acute renal failure. Its probable action is interference with neurogenically stimulated renin release.
Full text
PDF

















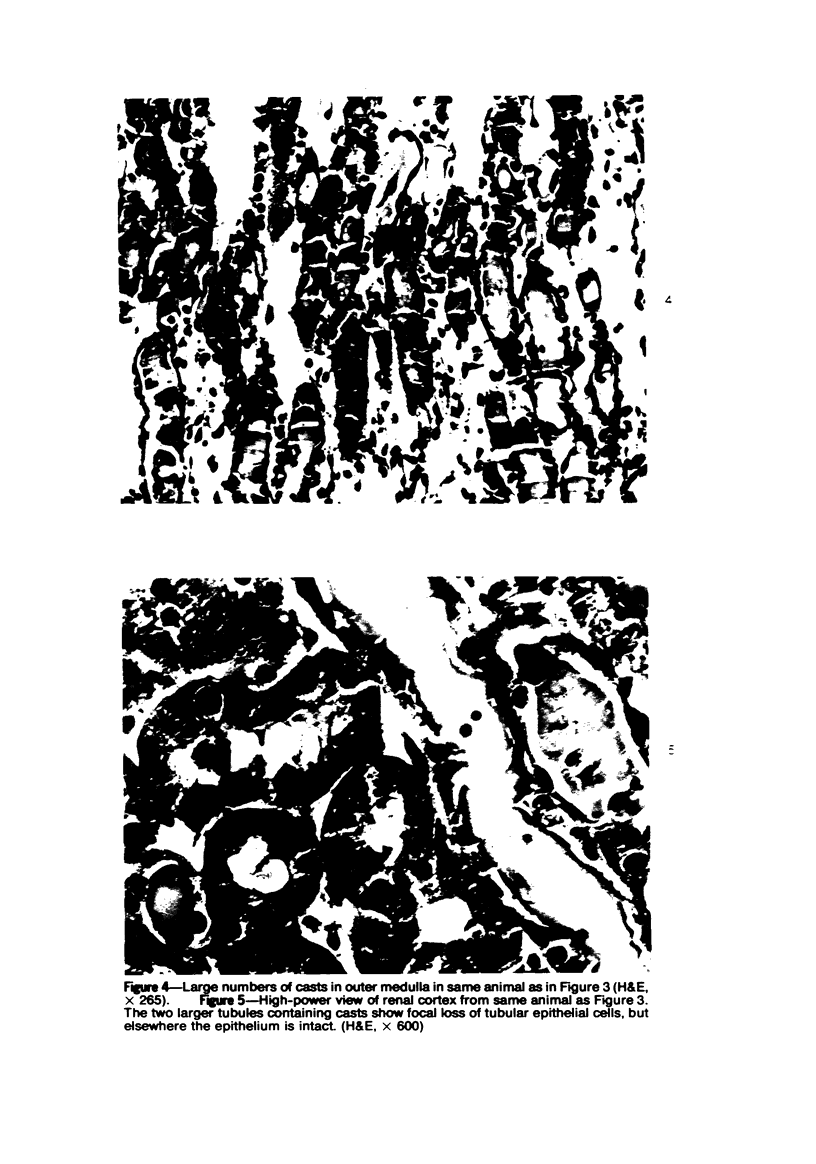
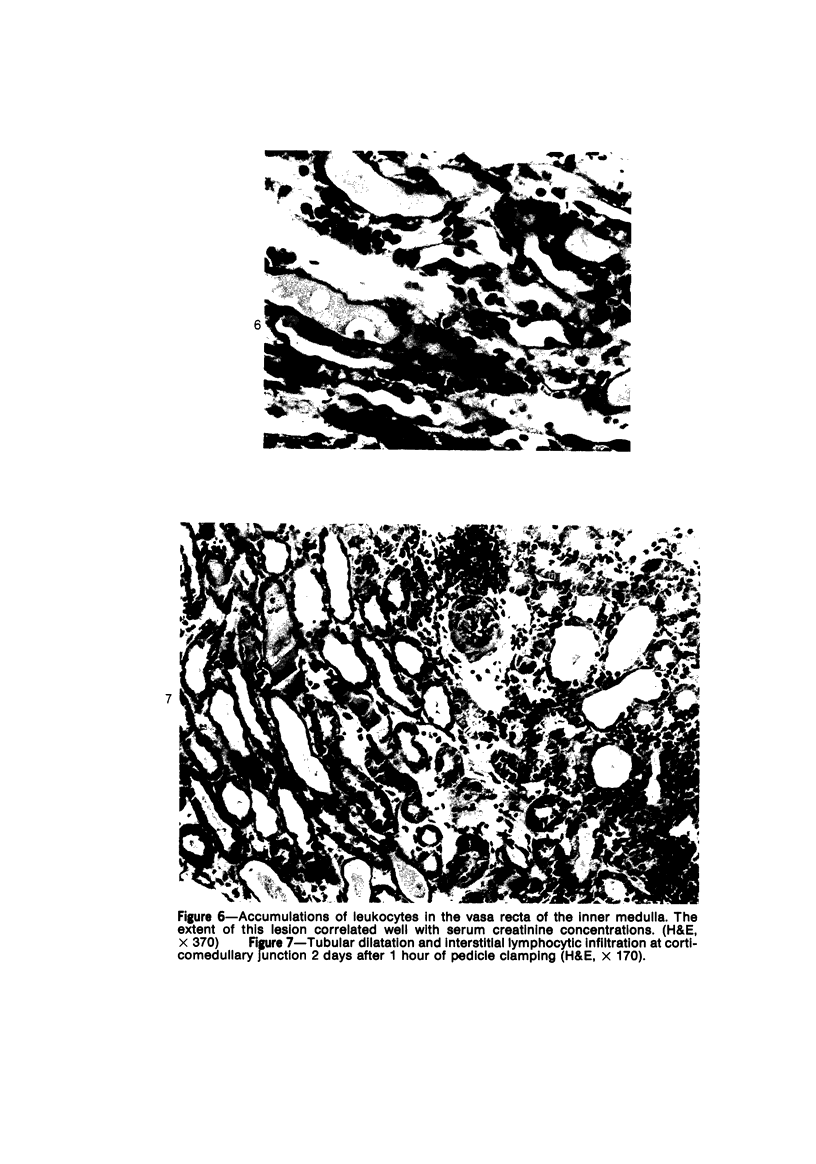
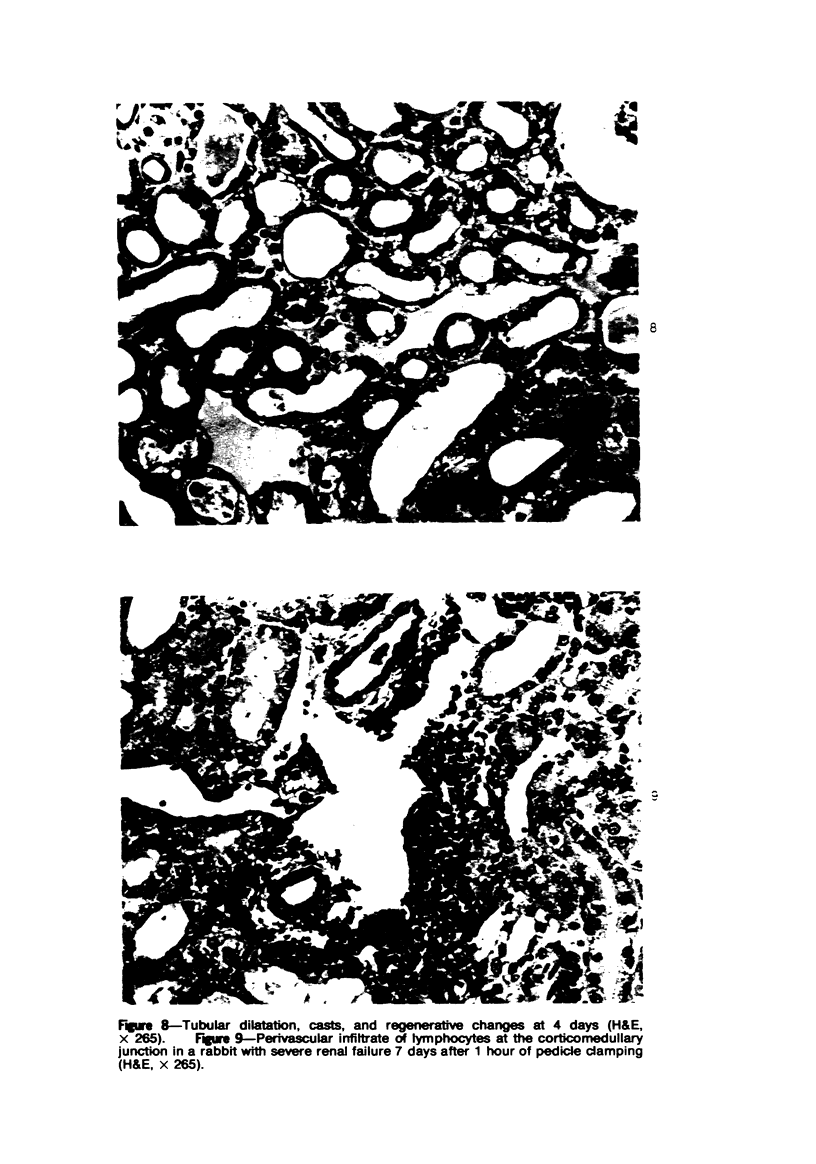
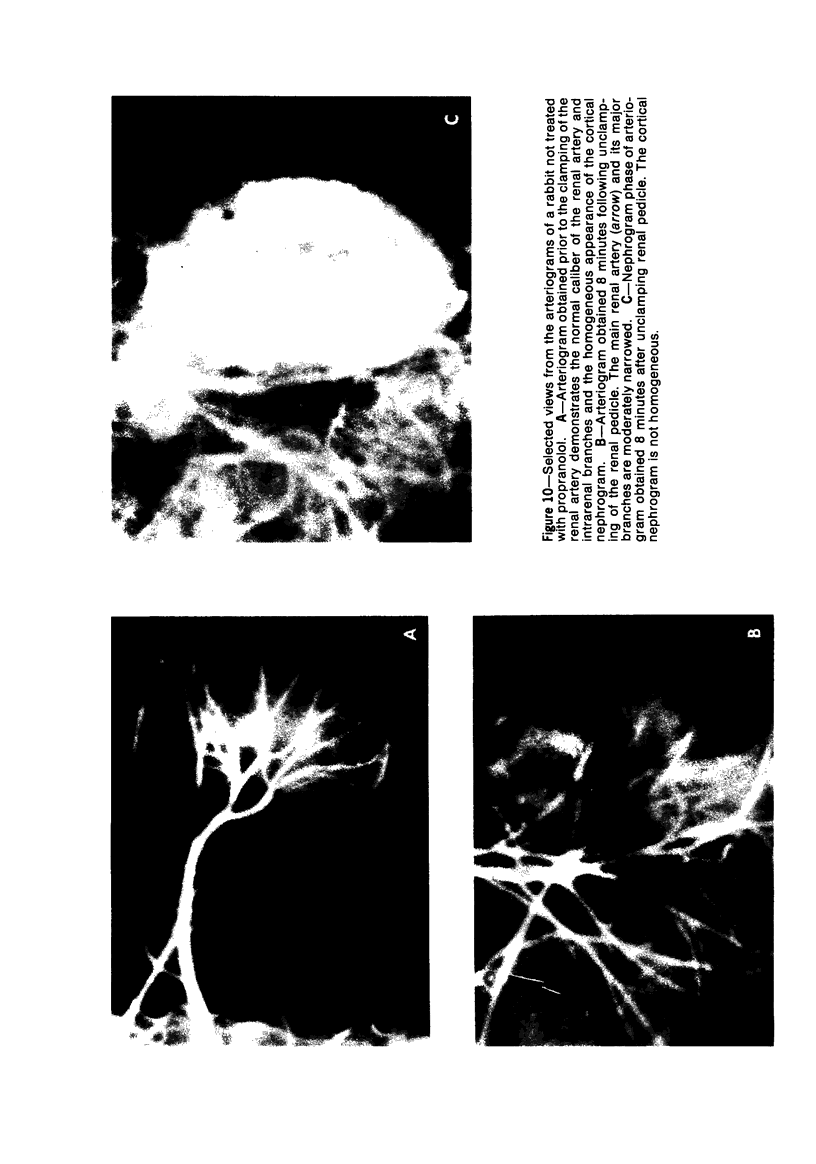
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey R. R., Natale R., Turnbull D. I., Linton A. L. Protective effect of frusemide in acute tubular necrosis and acute renal failure. Clin Sci. 1973 Jul;45(1):1–17. doi: 10.1042/cs0450001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrière S. Effect of norepinephrine, isoproterenol, and adrenergic blockers upon the intrarenal distribution of blood flow. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;47(2):199–208. doi: 10.1139/y69-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., McDonald F. D., Flamenbaum W., Dammin G. J., Oken D. E. Maintenance of renal function in salt loaded rats despite severe tubular necrosis induced by HgCl 2 . Nephron. 1971;8(3):205–220. doi: 10.1159/000179922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEKETE A., TARABA I., VISY M. SPLANCHNICOTOMY AFFORDS PROTECTION AGAINST ACUTE RENAL FAILURE IN DOGS. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1965;26:245–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn W. F., Arendshorst W. J., Gottschalk C. W. Pathogenesis of oliguria in acute renal failure. Circ Res. 1975 Jun;36(6):675–681. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.6.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamenbaum W. Pathophysiology of acute renal failure. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Jun;131(6):911–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G. J., Warltier D. C., Hardman H. F. Effect of propranolol and nitroglycerin on hemoglobin--oxygen affinity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;36(1):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg N. K., Epstein M., Rosen S. M., Basch R. I., Oken D. E., Merrill J. P. Acute oliguric renal failure in man: evidence for preferential renal cortical ischemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 Nov;47(6):455–474. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196811000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaina A., Solomon S., Eliahou H. E. Reduction in severity of acute renal failure in rats by beta-adrenergic blockade. Lancet. 1975 Jul 26;2(7926):157–159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Singer B. Effect of propranolol and theophylline on renin release caused by furosemide in the cat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;23(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Singer B. Specificity of blockade of renal renin release by propranolol in the cat. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Oct;47(4):331–343. doi: 10.1042/cs0470331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellstrand C. M., Casali R. E., Simmons R. L., Shideman J. R., Buselmeier T. J., Najarian J. S. Etiology and prognosis in acute post-transplant renal failure. Am J Med. 1976 Aug;61(2):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp R., Hollenberg N. K., Busch G. J., Abrams H. L. Prolonged unilateral acute renal failure induced by intra-arterial norepinephrine infusion in the dog. Invest Radiol. 1972 May-Jun;7(3):164–173. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197205000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J. Editorial: Non-beta-blocking actions of propranolol. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 6;293(19):988–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511062931909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. The essential action of propranolol in hypertension. Am J Med. 1976 May 31;60(6):837–852. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90904-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH W. H., FINGERHUT B., MILLER H. AUTOMATED AND MANUAL DIRECT METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF BLOOD UREA. Clin Chem. 1965 Jun;11:624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald F. D., Thiel G., Wilson D. R., DiBona G. F., Oken D. E. The prevention of acute renal failure in the rat by long-term saline loading: a possible role of the renin-angiotensin axis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):610–614. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken D. E. Role of prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Lancet. 1975 Jun 14;1(7920):1319–1322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen S. T., Skjoldborg H. The fine structure of the renal glomerulus in acute anuria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;70(2):205–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb01283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen T. S. Ultrastructure of the renal tubules in acute renal insufficiency. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(2):203–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Keeton T. K., Campbell W. B., Harper D. C. Evidence for a renal alpha-adrenergic receptor inhibiting renin release. Circ Res. 1976 May;38(5):338–346. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.5.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Jorgensen J. An easy radioimmunological microassay of renin activity, concentration and substrate in human and animal plasma and tissues based on angiotensin I trapping by antibody. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;39(5):816–825. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-5-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. A., MacDonald D. M., Pachnis B., Ganong W. F. Studies concerning the mechanism of suppression of renin secretion by clonidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):713–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K., Kramer E. C., Fox J. A., Heptinstall R. H. Medullary plasma flow and intravascular leukocyte accumulation in acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1974 Jul;6(1):24–37. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S., Boyd G. W. Andrenergic stimulation of renin secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):290–296. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. A., Thronell I. R., Graham R. M., Stokes G. S. Beta-adrenoreceptor blockade in the conscious rabbit: effects on plasma renin activity and blood pressure. Life Sci. 1975 Sep 15;17(6):959–967. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Yoon M. S., Freedman A. D. Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. R., Growdon J. H., Shahani B. T. Beta-adrenergic mechanisms in action tremor. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 6;293(19):950–953. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511062931902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanchetti A., Stella A., Leonetti G., Morganti A., Terzoli L. Control of renin release: a review of experimental evidence and clinical implications. Am J Cardiol. 1976 Mar 31;37(4):675–691. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(76)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]