Abstract
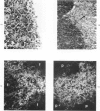
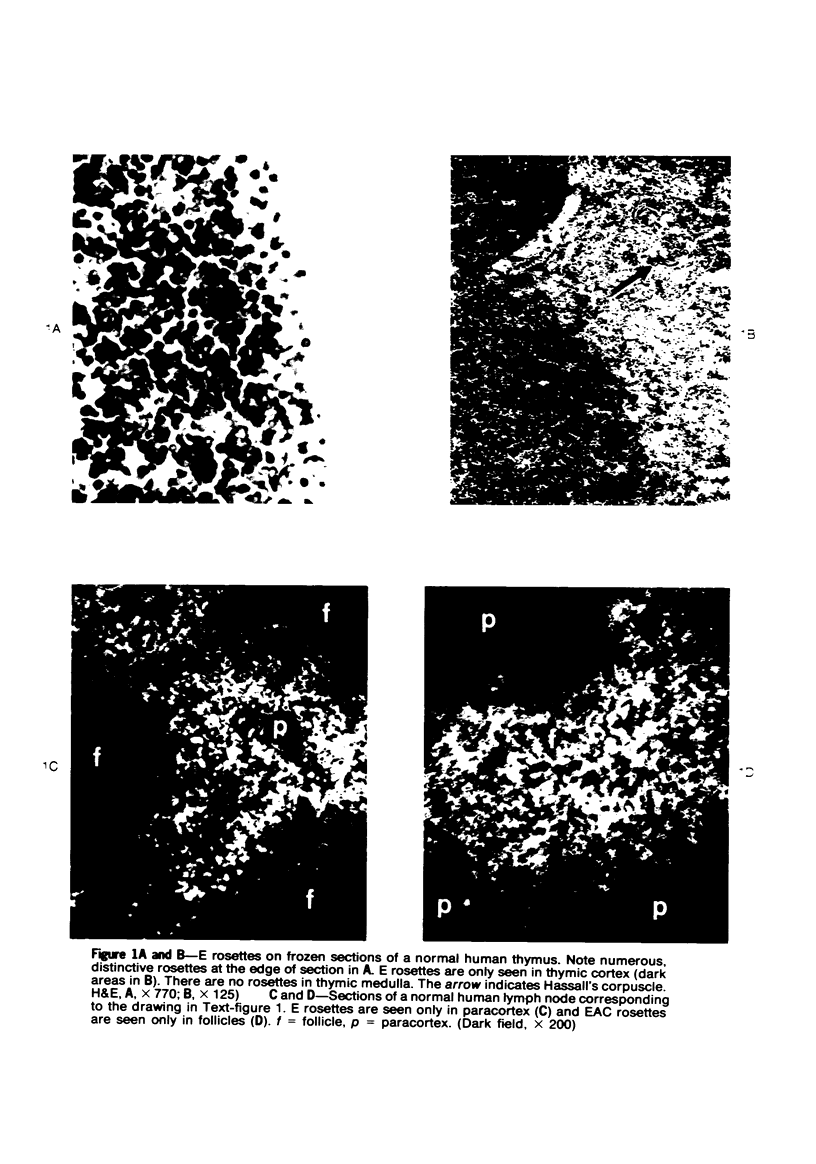
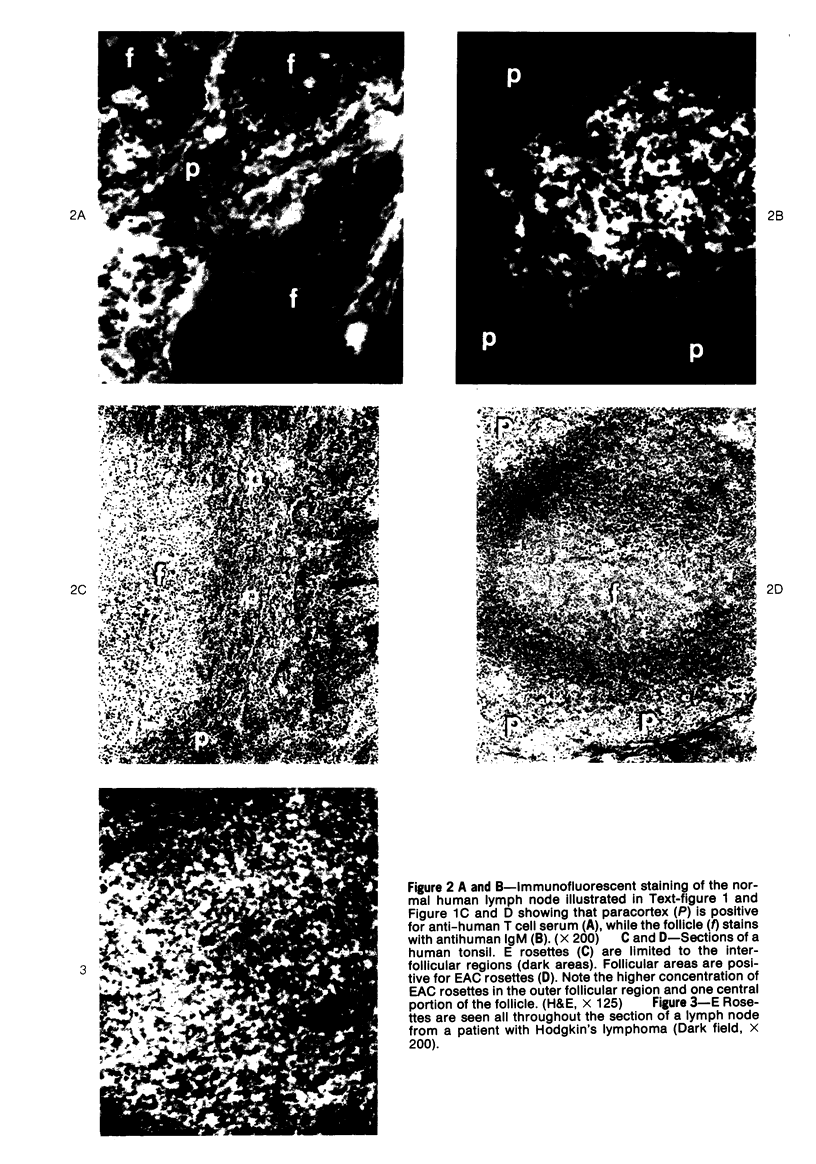
A technique for the formation of sheep erythrocyte (E) rosettes in frozen human tissue sections is reported. The labile nature of the receptor for E rosettes on lymphocytes requires the use of controlled conditions for tissue processing and the reaction with indicator cells. The distribution of E rosettes in sections of normal human thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleens was comparable to that of the T marker-positive cells identified by immunofluorescence with the specific anti-human T cell serum. There with no overlap with areas positive for 19S EAC and 7S EA rosettes. Erythrocytes treated with a sulfhydryl reagent, 2-aminoethylisothiuronium bromide (AET), and with neuraminidase formed better rosettes in sections than did untreated erythrocytes. E rosettes in tissue sections can determine changes in the distribution of T cells in different lymphoproliferative and infiltrating disorders.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chused T. M., Hardin J. A., Frank M. M., Green I. Identification of cells infiltrating the minor salivary glands in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudy A. L., Schmitt D., Viac J., Alario A., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J. Morphological, immunological and immunocytochemical identification of lymphocytes extracted from cutaneous infiltrates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):61–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson R. L., Hearing V. J., Dellon A. L., Frank M., Edelson E. K., Green I. Differentiation between B cells, T cells, and histiocytes in melanocytic lesions: primary and metastatic melanoma and halo and giant pigmented nevi. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Nov;4(4):557–568. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson R. L., Smith R. W., Frank M. M., Green I. Identification of subpopulations of mononuclear cells in cutaneous infiltrates. I. Differentiation between B cells, T cells, and histiocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Aug;61(2):82–89. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12675403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K. T cell control of antibody production. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:1–40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Douglas S. D., Fudenberg H. H. The IgG receptor: an immunological marker for the characterization of mononuclear cells. Immunology. 1969 Jul;17(1):7–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Polley M. J., Linscott W. D., Fudenberg H. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human monocytes: distinct receptor sites for the third component of complement and for immunoglobulin G. Science. 1968 Dec 13;162(3859):1281–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S., Shevach E. M., Frank M. M., Berard C. W., Green I. Nodular lymphoma--evidence for origin from follicular B lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 11;290(15):813–819. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404112901501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S., Shevach E. M., Sussman E. H., Frank M., Green I., Berard C. W. Membrane receptor sites for the identification of lymphoreticular cells in benign and malignant conditions. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1975 Mar;2:107–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Clark C. An improved rosetting assay for detection of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Andersson L. C. Antigen-binding T cells as helper cells. Separation of helper cells by immune rosette formation. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes N. F., Miki S. S., Peixinho Z. F. Combined detection of human T and B lymphocytes by rosette formation with sheep erythrocytes and zymosan-C3 complexes. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):531–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
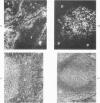
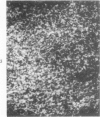
- Millard P. R., Rabin B. S., Whiteside T. L., Hubbard J. D. The effects of tissue processing on markers for T and B cells from solid tissues. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Mar;67(3):230–235. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.3.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelants G. E., Rydén A., Hägg L. B., Loor F. Active synthesis of immunoglobulin receptors for antigen by T lymphocytes. Nature. 1974 Jan 11;247(5436):106–108. doi: 10.1038/247106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silveira N. P., Mendes N. F., Tolnai M. E. Tissue localization of two populations of human lymphocytes distinguished by membrane receptors. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1456–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Enhanced binding of neuraminidase-treated sheep erythrocytes to human T lymphocytes. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Berardi R. S., Rabin B. S. Quantitation of human peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(6):731–738. doi: 10.1159/000231361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Rabin B. S. Surface immunoglobulin on activated human peripheral blood thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):762–771. doi: 10.1172/JCI108335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L. Reactivity of anti-human brain serum with human lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jan;86(1):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]