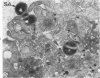
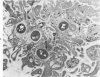
Abstract
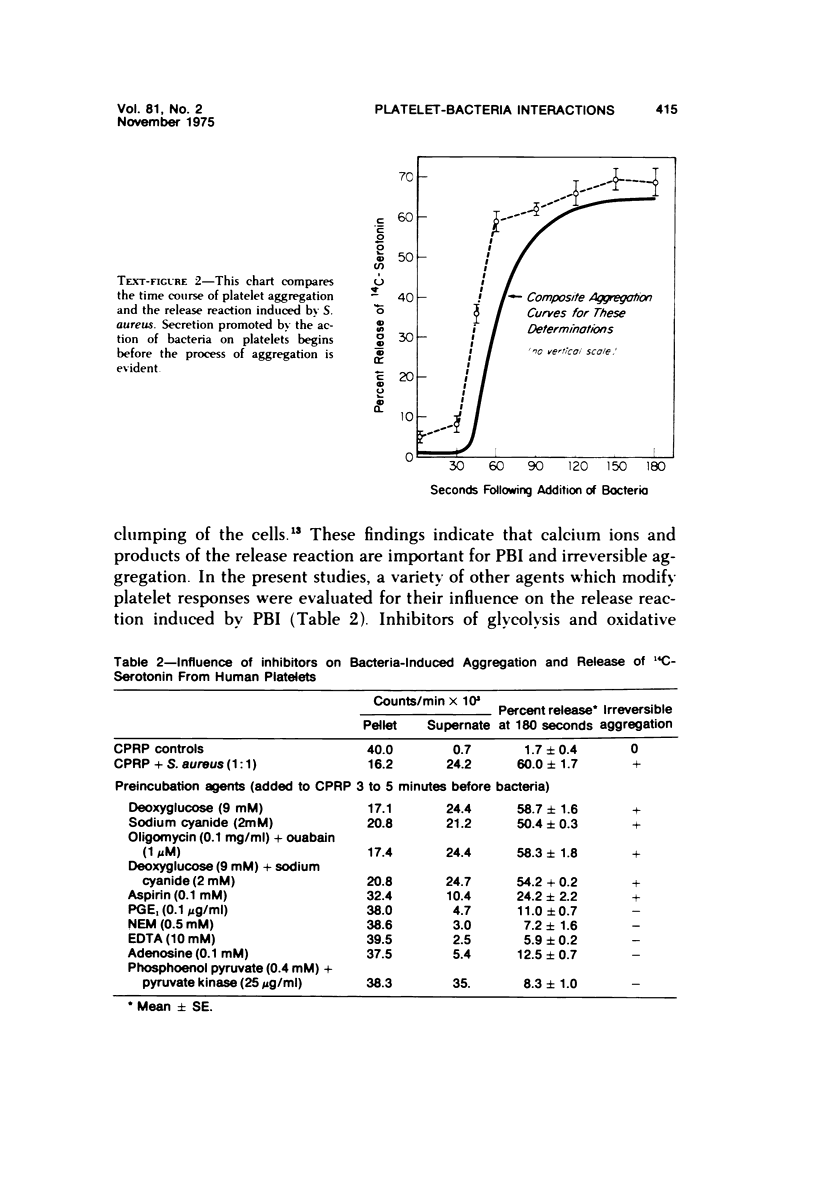
Release of 14C-serotonin from human platelets prelabeled with 14C-5-hydroxytryptamine was measured during platelet aggregation induced by Staphylococcus aureus. Platelet-bacteria interaction (PBI) was as potent a stimulus of the platelet release reaction as collagen, thrombin, or epinephrine. Inhibitors which blocked platelet aggregation also prevented the release reaction of PBI. Sequential measurements of release, when correlated with nephelometry of aggregation, showed close correlation between the onset of release and the onset of platelet shape change and early aggregation. Ultrastructural studies with polylysine, an agent capable of polymerizing platelet granule contents, revealed that granule components are secreted to the region of the bacteria trapped between platelets in the forming aggregates. Platelet peroxidase activity remained localized within the dense tubular system of the platelets.
Full text
PDF

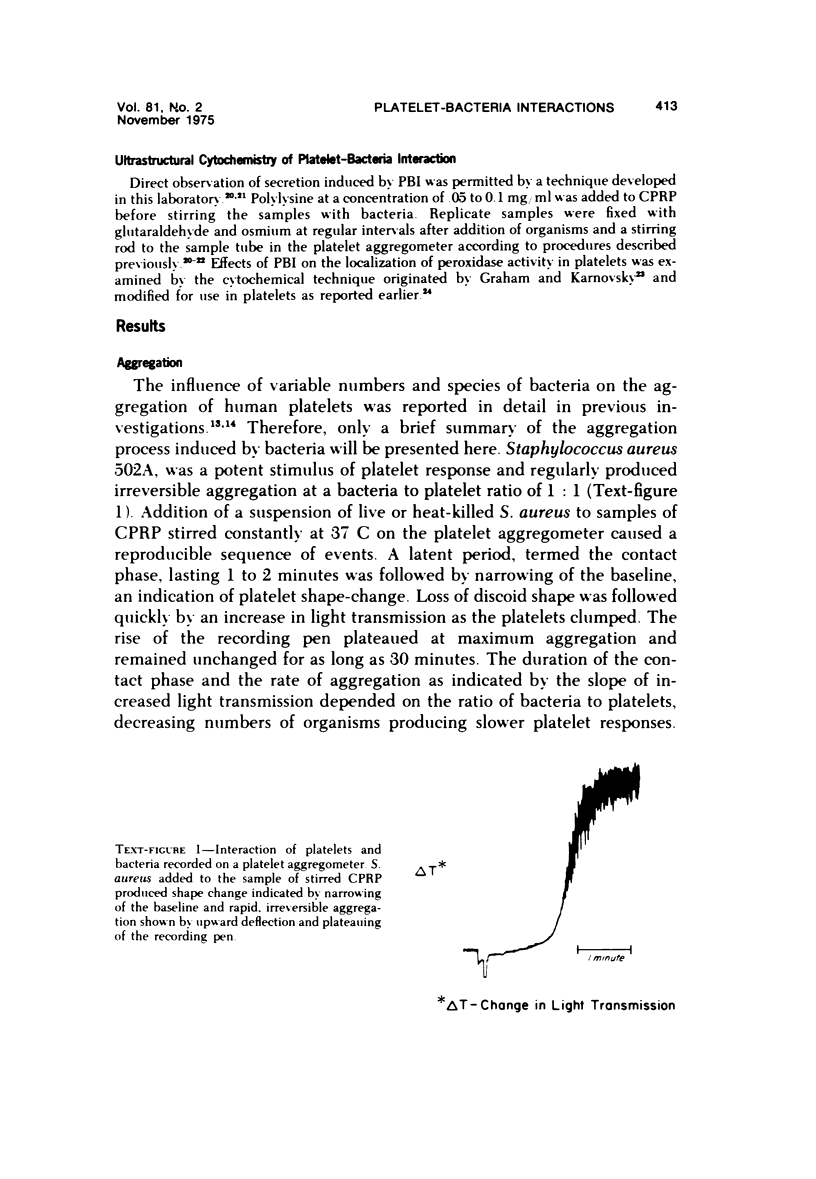
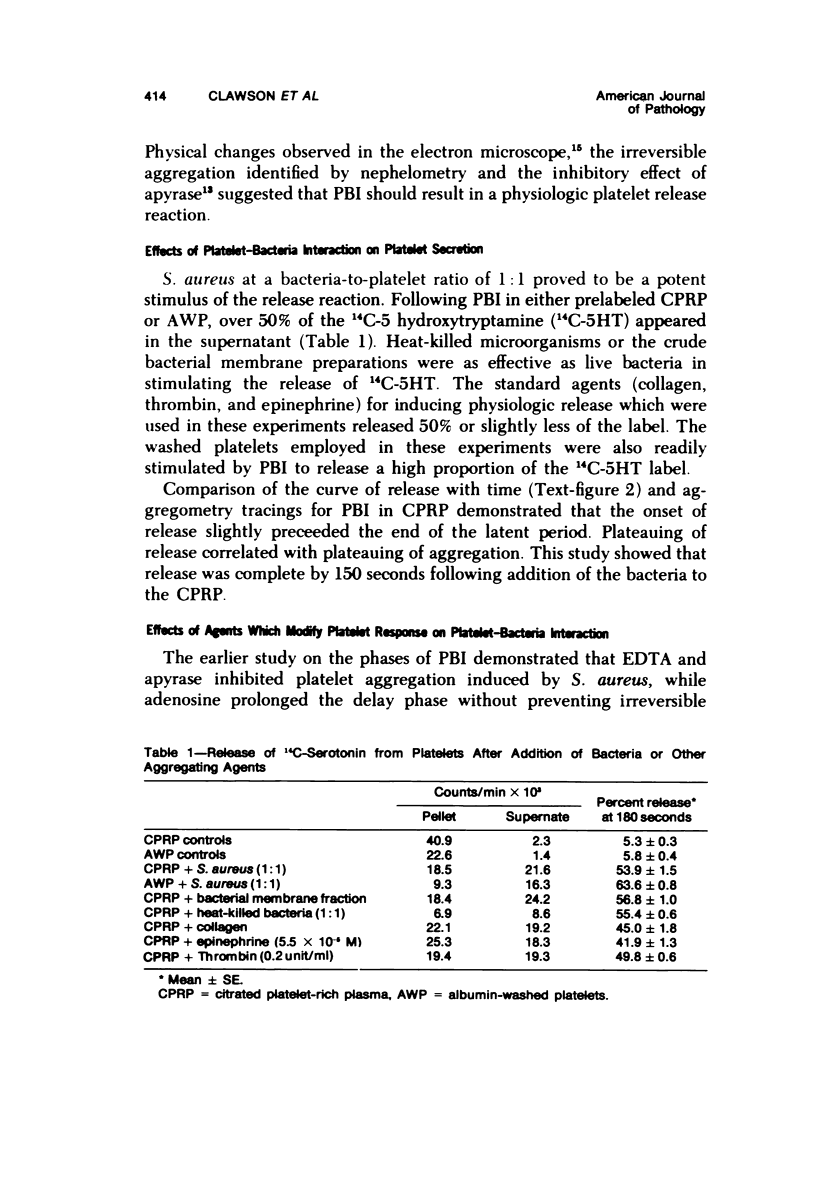





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clawson C. C. Platelet interaction with bacteria. 3. Ultrastructure. Am J Pathol. 1973 Mar;70(3):449–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. I. Reaction phases and effects of inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):367–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. II. Fate of the bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):381–397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Ferreira J. F. The blood platelet: electron microscopic studies. Int Rev Cytol. 1964;17:99–148. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day H. J., Holmsen H. Concepts of the blood platelet release reaction. Ser Haematol. 1971;4(1):3–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES A., TONKS R. S. Intravascular platelet clumping in rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:379–390. doi: 10.1002/path.1700840212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerushalmy Z., Zucker M. B. Some effects of fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) on blood platelets. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen L., Hovig T., Rowsell H. C., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation and vascular injury in swine and rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1970 Nov;61(2):161–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Packham M. A. Factors influencing platelet function: adhesion, release, and aggregation. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Jun;22(2):97–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEHBENS W. E., FLOREY H. W. The behavior of intravenously injected particles observed in chambers in rabbits' ears. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1960 Jul;45:252–264. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1960.sp001470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Ingerman C., Kocsis J. J., Silver M. J. Formation of prostaglandins during the aggregation of human blood platelets. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):965–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI107262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aken W. G., Vreeken J. Accumulaon of macromolecular particles in the reticuloendothelial system (RES) mediated by platelet aggregation and disaggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Dec 31;22(3):496–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N. Albumin density gradient separation and washing of platelets and the study of platelet coagulant activities. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):205–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Effects of cationic polypeptides on thrombasthenic and afibrinogenemic blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):447–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Electron microscopic studies of platelet secretion. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1974;2(0):49–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Exocytosis of secretory organelles from blood platelets incubated with cationic polypeptides. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):41–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Identification of platelet secretion in the electron microscope. Ser Haematol. 1973;6(3):429–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Interaction of membrane systems in blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):295–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H., Estensen R. D. Investigation of the release reaction in platelets exposed to phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 May;75(2):301–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]