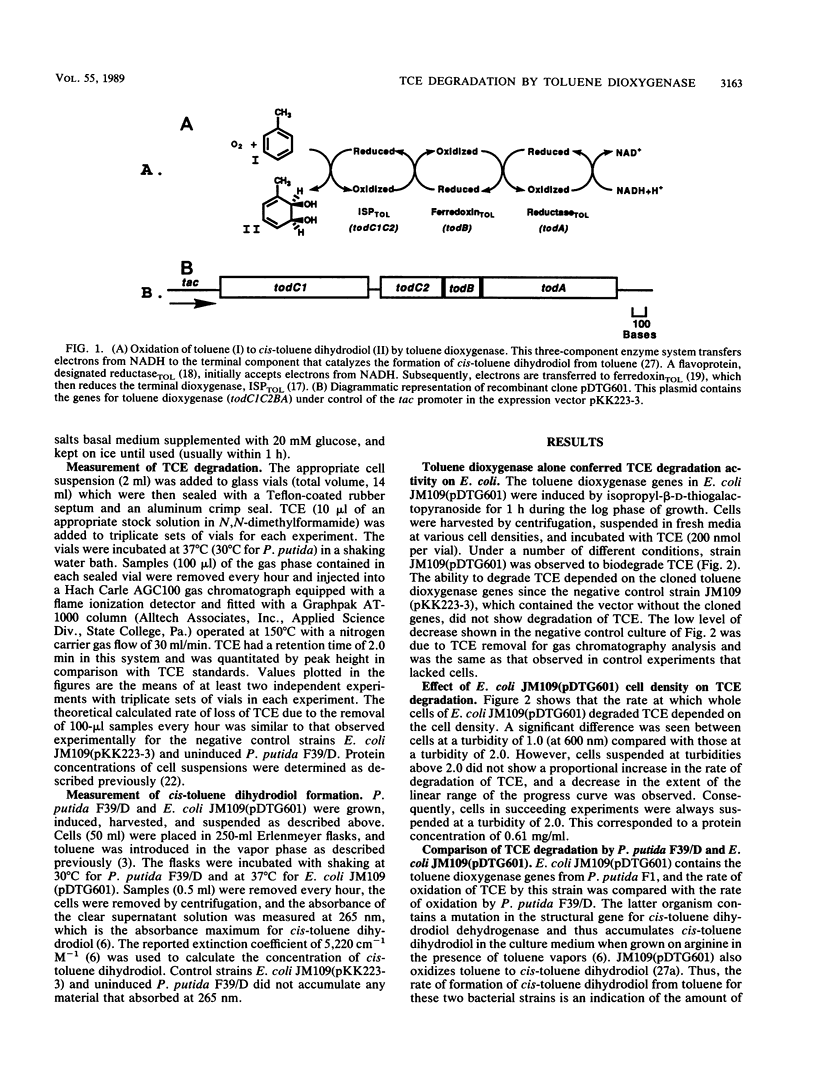
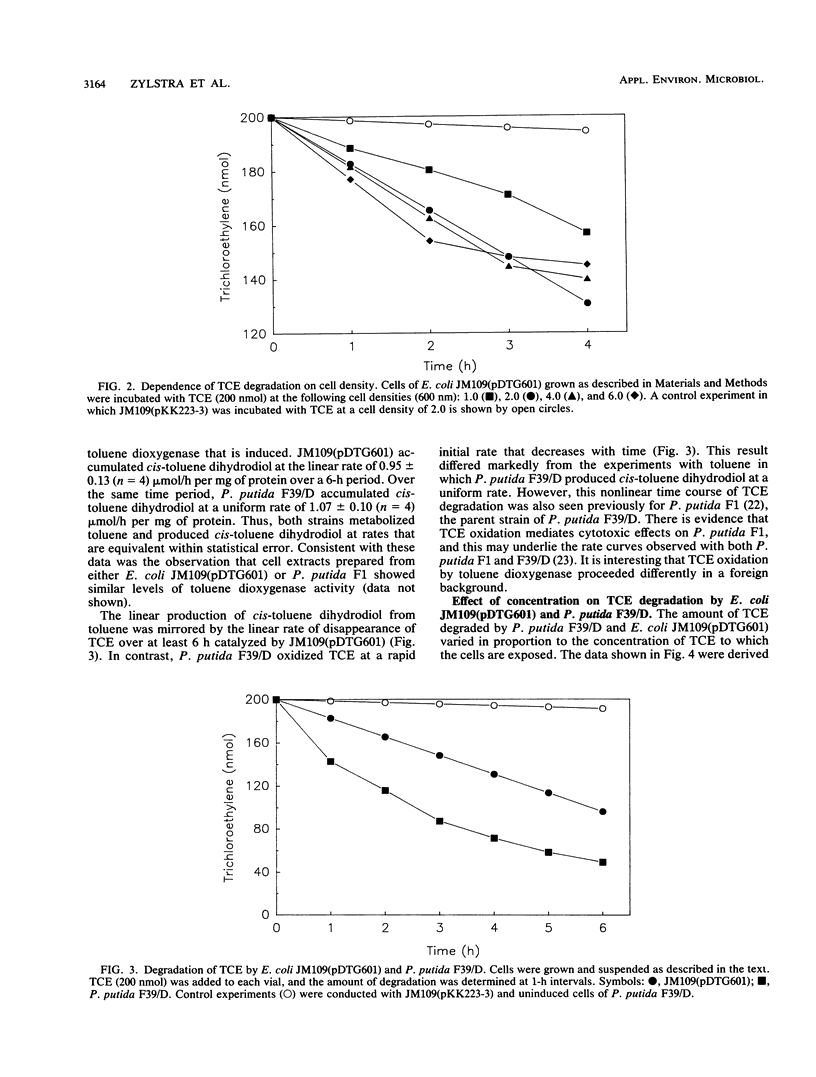
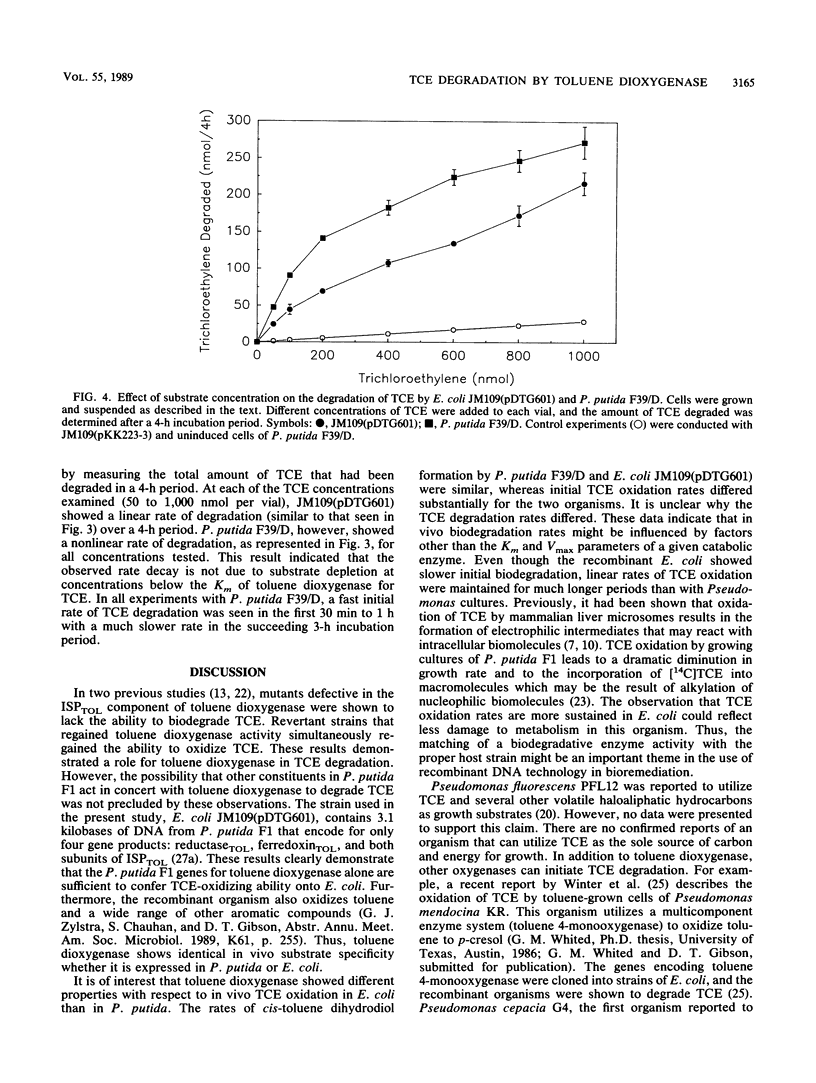
Abstract
Toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida F1 has been implicated as an enzyme capable of degrading trichloroethylene. This has now been confirmed with Escherichia coli JM109(pDTG601) that contains the structural genes (todC1C2BA) of toluene dioxygenase under the control of the tac promoter. The extent of trichloroethylene degradation by the recombinant organism depended on the cell concentration and the concentration of trichloroethylene. A linear rate of trichloroethylene degradation was observed with the E. coli recombinant strain. In contrast, P. putida F39/D, a mutant strain of P. putida F1 that does not contain cis-toluene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase, showed a much faster initial rate of trichloroethylene degradation which decreased over time.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arciero D., Vannelli T., Logan M., Hooper A. B. Degradation of trichloroethylene by the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):640–643. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Holy A. Regulation of ribosomal RNA promoters with a synthetic lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUS D., WALKER N. THE DECOMPOSITION OF TOLUENE BY SOIL BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jul;36:107–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel M. M., Taddeo A. R., Fogel S. Biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes by a methane-utilizing mixed culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):720–724. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.720-724.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Hensley M., Yoshioka H., Mabry T. J. Formation of (+)-cis-2,3-dihydroxy-1-methylcyclohexa-4,6-diene from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1626–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. D., Palumbo A. V., Herbes S. E., Lidstrom M. E., Tyndall R. L., Gilmer P. J. Trichloroethylene biodegradation by a methane-oxidizing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):951–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.951-956.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Guengerich F. P. Oxidation of trichloroethylene by liver microsomal cytochrome P-450: evidence for chlorine migration in a transition state not involving trichloroethylene oxide. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):1090–1097. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Mahaffey W. R., Pritchard P. H. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene and involvement of an aromatic biodegradative pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):949–954. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.949-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., O'neill E. J., Pritchard P. H. Aerobic metabolism of trichloroethylene by a bacterial isolate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):383–384. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.383-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Pritchard P. H. Trichloroethylene metabolism by microorganisms that degrade aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):604–606. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.604-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian V., Liu T. N., Yeh W. K., Gibson D. T. Toluene dioxygenase: purification of an iron-sulfur protein by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1131–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91998-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian V., Liu T. N., Yeh W. K., Narro M., Gibson D. T. Purification and properties of NADH-ferredoxinTOL reductase. A component of toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2723–2730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian V., Liu T. N., Yeh W. K., Serdar C. M., Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Purification and properties of ferredoxinTOL. A component of toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida F1. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2355–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbergh P. A., Kunka B. S. Metabolism of volatile chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2578–2579. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2578-2579.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T. M., McCarty P. L. Biotransformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, vinyl chloride, and carbon dioxide under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1080-1083.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Householder S. R. Toxicity of Trichloroethylene to Pseudomonas putida F1 Is Mediated by Toluene Dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2723–2725. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2723-2725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Gibson D. T., Liu T. N. Toluene dioxygenase: a multicomponent enzyme system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., Gibson D. T. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1. Nucleotide sequence of the todC1C2BADE genes and their expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14940–14946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., McCombie W. R., Gibson D. T., Finette B. A. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1: genetic organization of the tod operon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1498–1503. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1498-1503.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



