Abstract
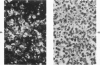
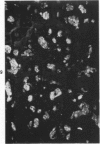
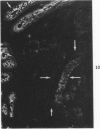
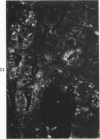
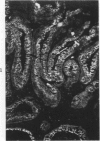
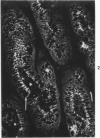
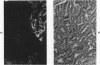
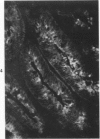
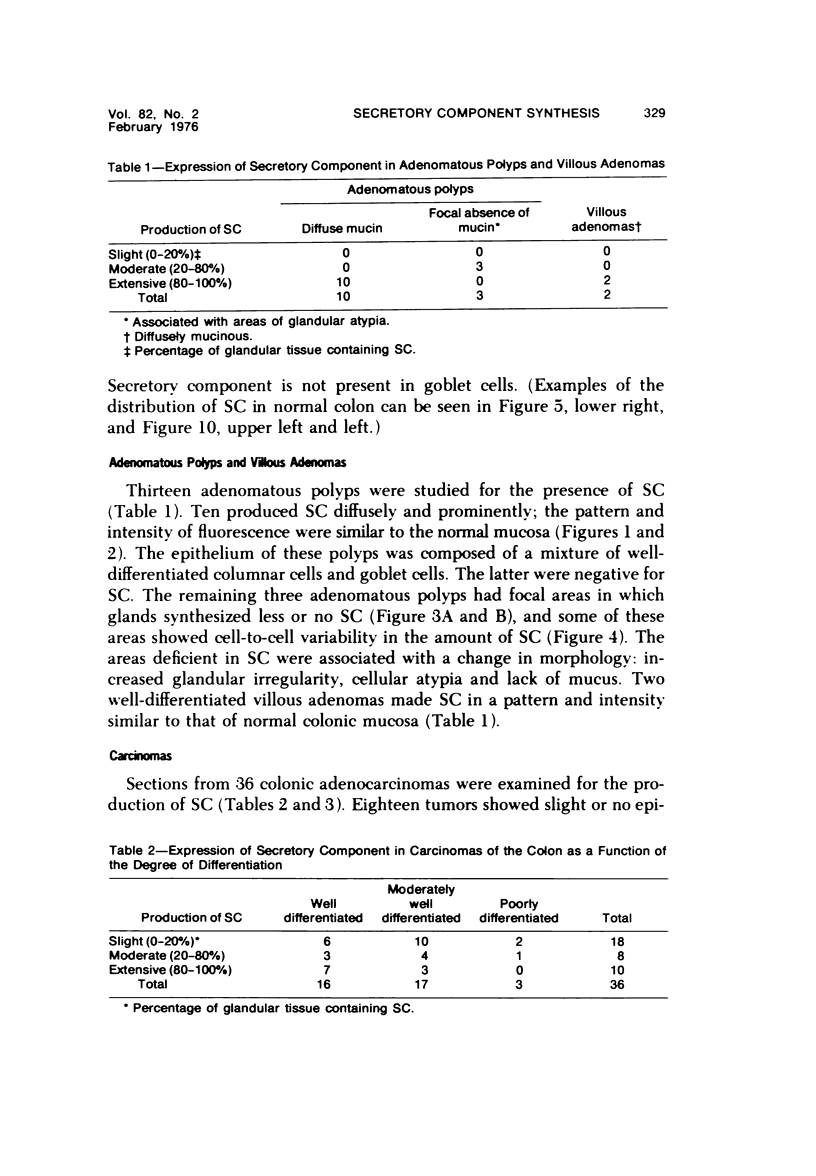
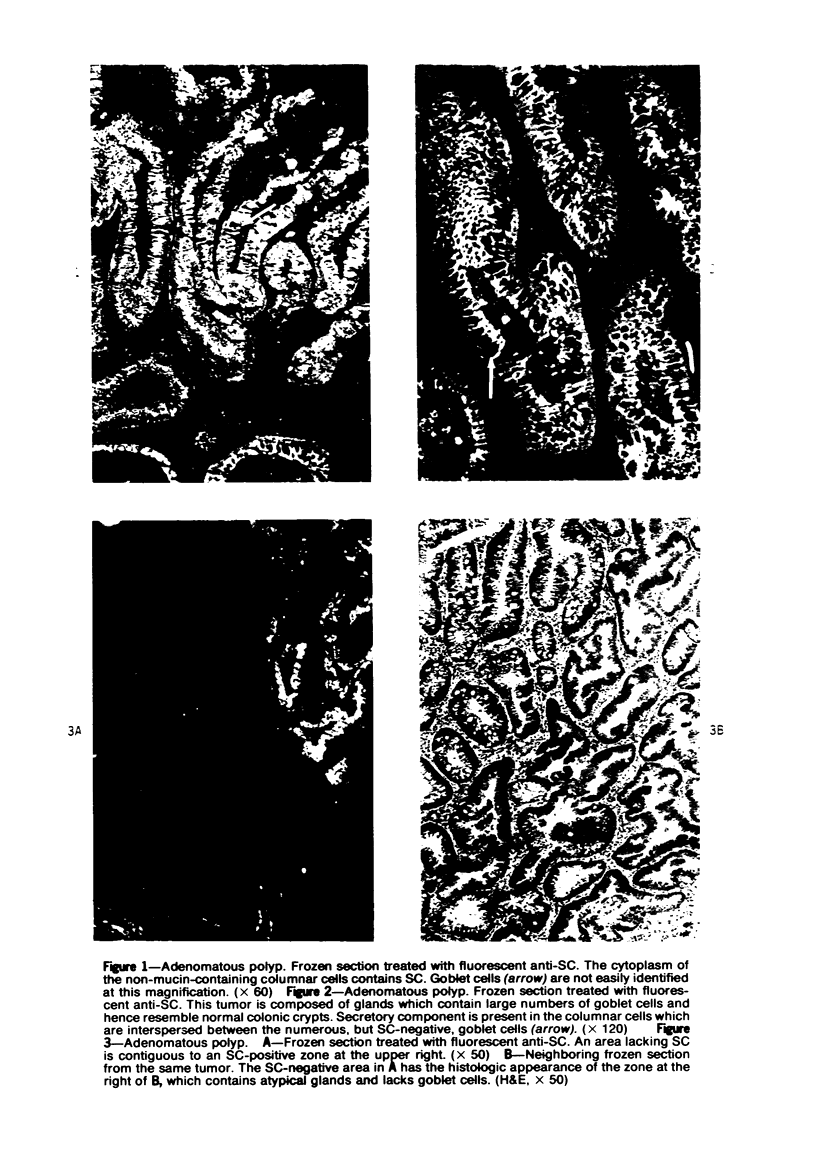
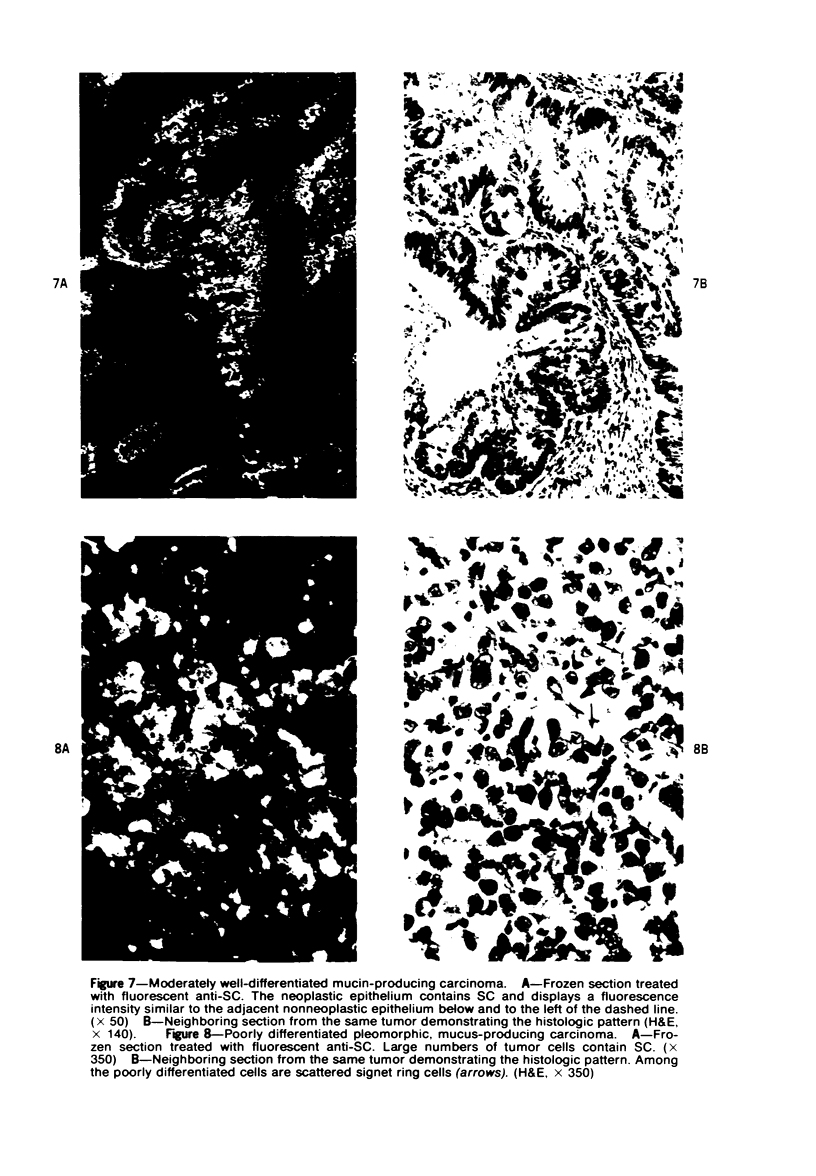
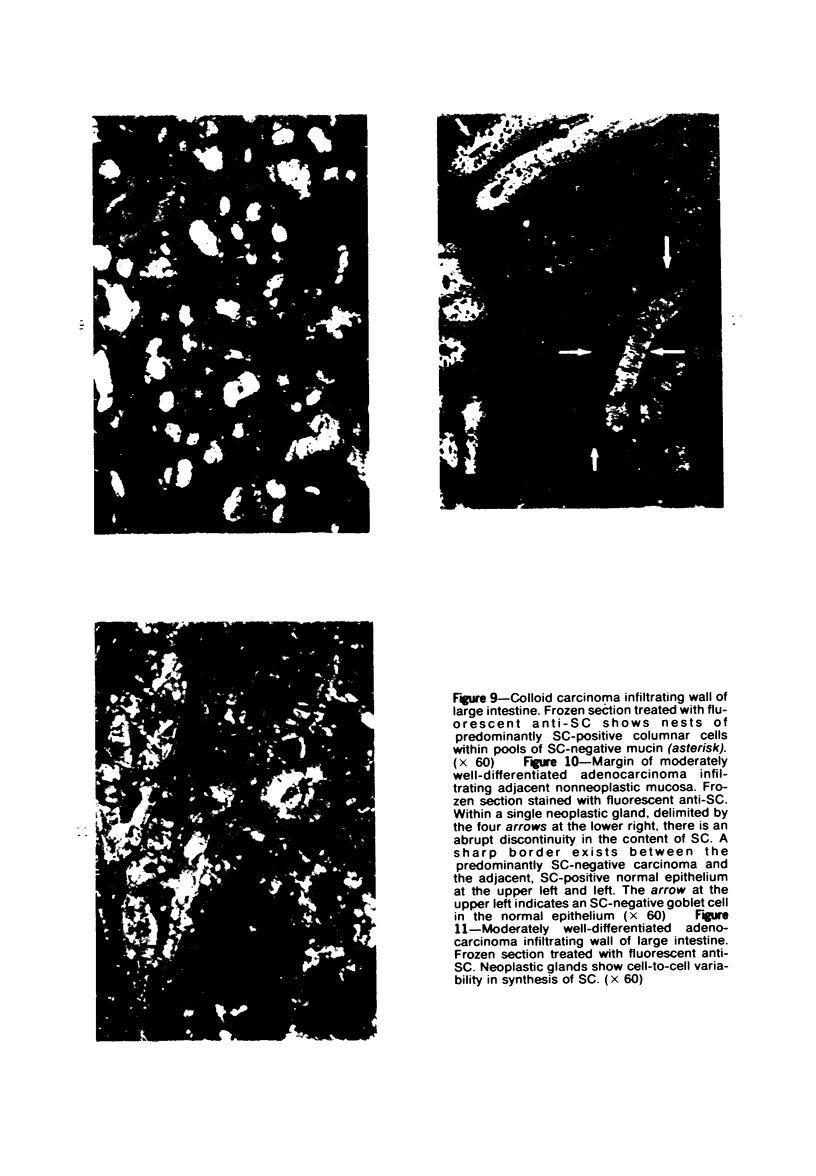
The secretory component (SC) polypeptide chain of secretory immunoglobulin A can be considered as a differentiation marker in that it is normally synthesized in the non-mucus-containing columnar epithelial cells, but not goblet cells, of the large intestine. With this in mind, we have studied the expression of SC in 36 colonic adenocarcinomas and 15 polyps (adenomatous and villous) by the fluorescent antibody technique. As in the normal mucosa, the synthesis of SC in tumors found in non-mucus-containing columnar cells and was absent from goblet cells. However, in several well-differentiated carcinomas it appeared that columnar cells contained both SC and mucin; these cells could be analogous to the normal mucosal precursor of both cell types. SC was synthesized throughout all adenomatous polyps and villous adenomas with the exception of some atypical nonmucinous areas of adenomatous polyps. Secretory component synthesis by carcinomas was associated with mucus production, although goblet cells did not contain SC. The presence of SC also correlated with the degree of differentiation. Secretory component was absent from half of the carcinomas as well as from atypical nonmucinous areas of polyps, and this could represent one of the earliest changes associated with the development of malignancy.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P. Mucosal and glandular distribution of immunoglobulin components: differential localization of free and bound SC in secretory epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1553–1559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtin P., Von Kleist S., Sabine M. C. Loss of a normal colonic membrane antigen in human cancers of the colon. Cancer Res. 1971 Jul;31(7):1038–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C., Lamm M. E., Franklin E. C. Human secretory component. NH2-terminal amino acid sequences and peptide maps of the form occurring in exocrine immunoglobulin A and the free form. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5654–5657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C., Lamm M. E. Reactive half-cystine peptides of the secretory component of human exocrine immunoglobulin A. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):1987–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernobilsky B., Tsou K. C. Adenocarcinoma, adenomas and polyps of the colon. Histochemical study. Cancer. 1968 Feb;21(2):165–177. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196802)21:2<165::aid-cncr2820210202>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidsohn I., Kovarik S., Lee C. L. A, B, and O substances in gastrointestinal carcinoma. Arch Pathol. 1966 May;81(5):381–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D., Miller F. Chemical and immunological differences between normal and tumoral colonic mucoprotein antigen. Nature. 1975 May 1;255(5503):85–87. doi: 10.1038/255085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P., Freedman S. O. Specific carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):467–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. M., Pegram C. A., Vazquez J. J. Identification of a colon-specific antigen (CSA) in normal and neoplastic tissues. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1008–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm M. E., Greenberg J. Human secretory component. Comparison of the form occurring in exocrine immunoglobulin A to the free form. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2744–2750. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIRN R. C., FOTHERGILL J. E., McENTEGART M. G., PORTEOUS I. B. Gastro-intestinal-specific antigen: an immunohistological and serological study. Br Med J. 1962 Jun 30;1(5295):1788–1790. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5295.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn R. C., Fothergill J. E., McEntegart M. G., Richmond H. G. Loss of Gastro-intestinal-specific Antigen in Neoplasia. Br Med J. 1962 Jun 30;1(5295):1791–1793. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5295.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poger M. E., Lamm M. E. Localization of free and bound secretory component in human intestinal epithelial cells. A model for the assembly of secretory IgA. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):629–642. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappeiner G., Denk H., Eckerstorfer R., Holzner J. H. Vergleichende Untersuchungen über Auftreten und Lokalisation des carcinoembryonalen Antigens (CEA) und eines normalen perchlorsäureextrahierbaren Dickdarmschleimhaut-Antigens (NC) in Carcinomen und Polypen des Dickdarmes. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1973 Aug 9;360(2):129–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]