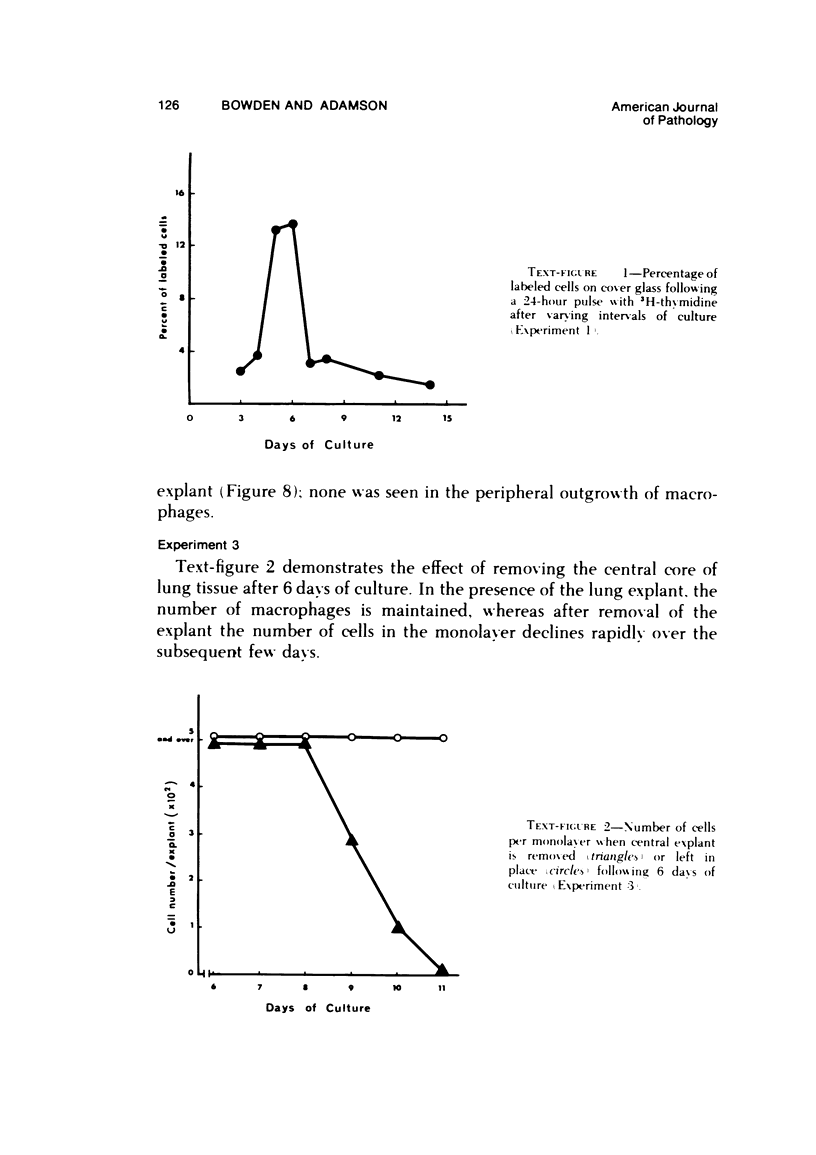
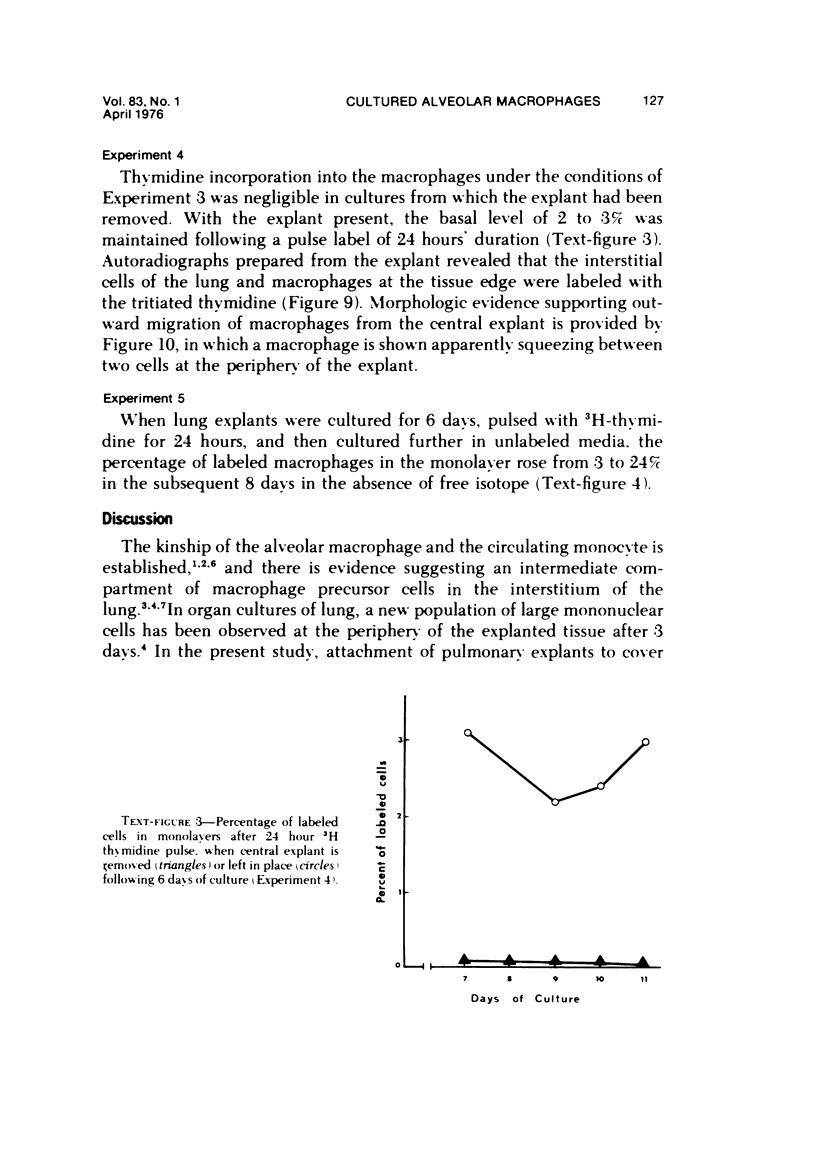
Abstract
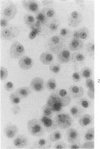
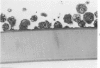
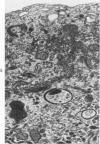
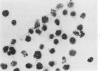
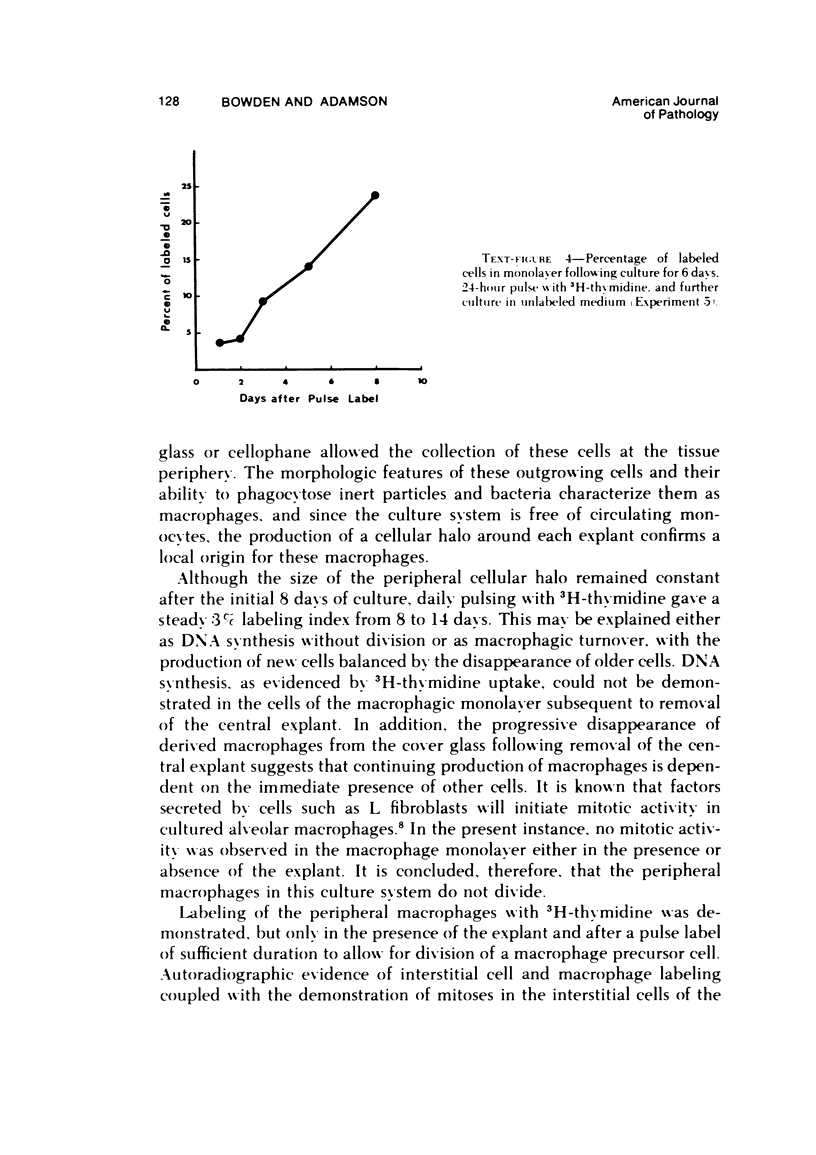
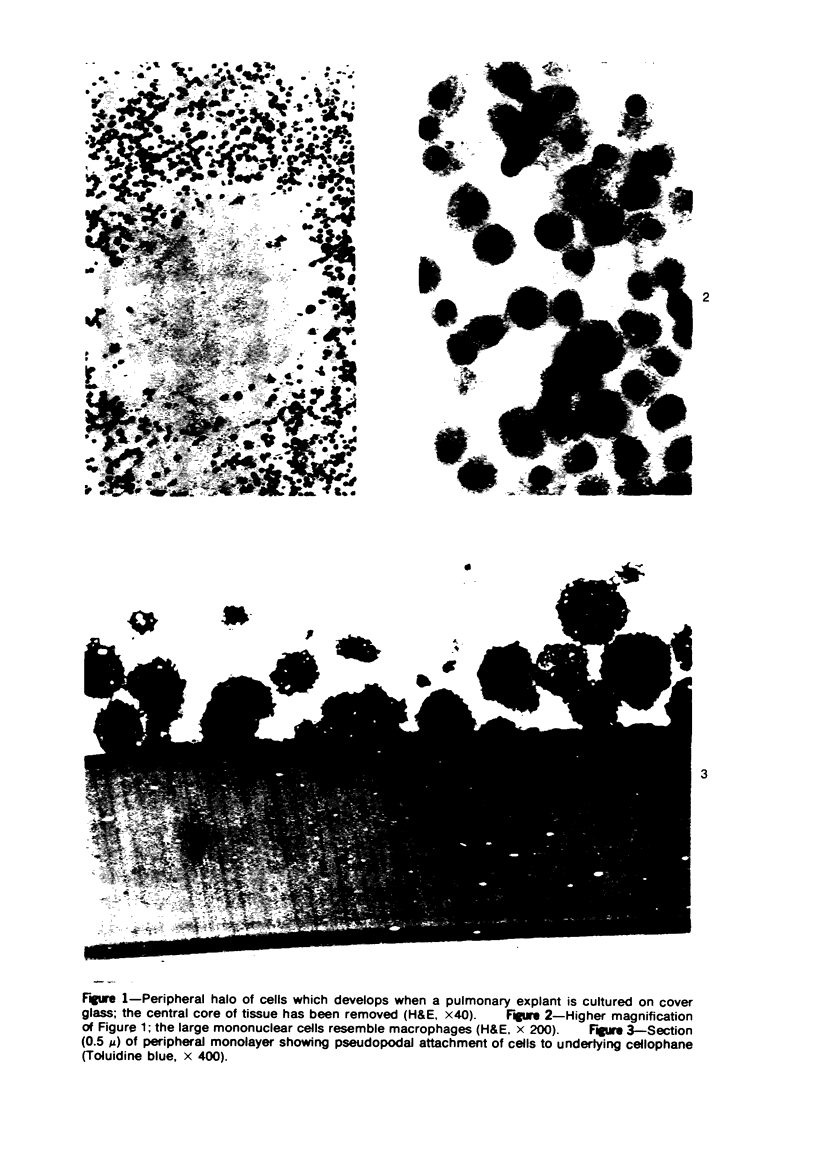
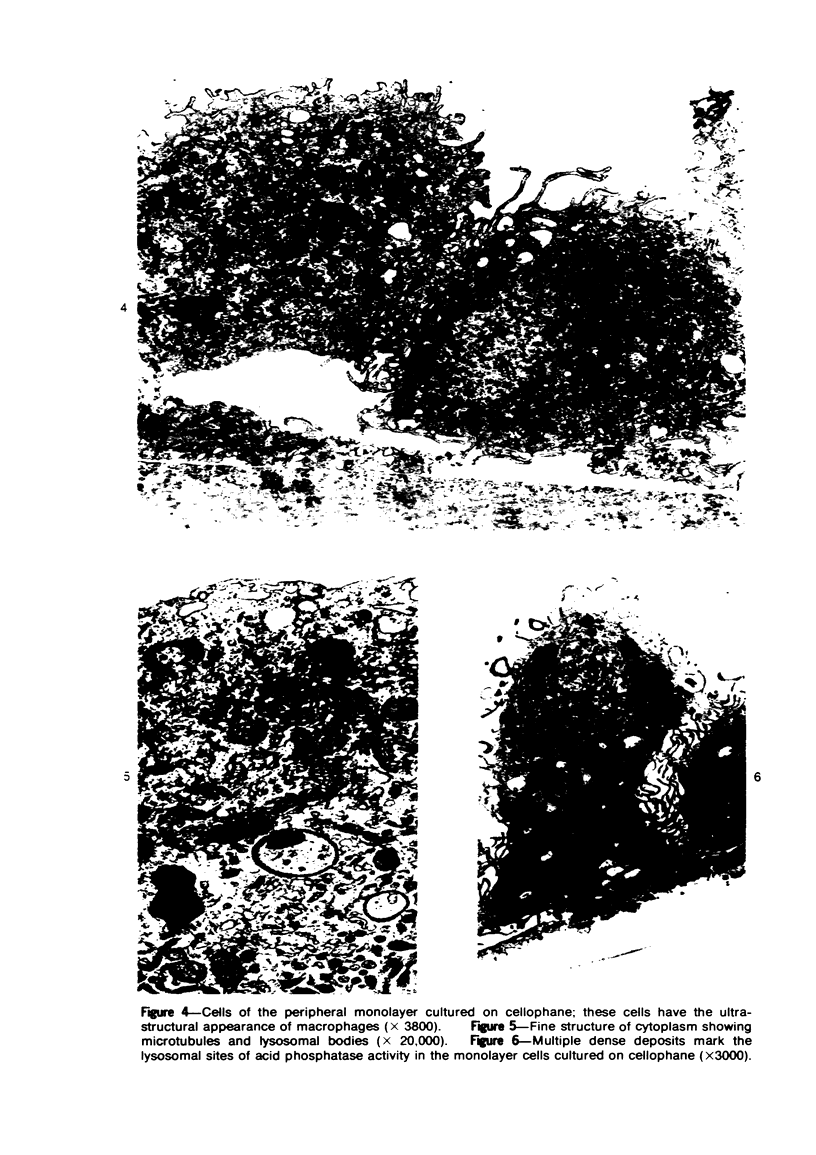
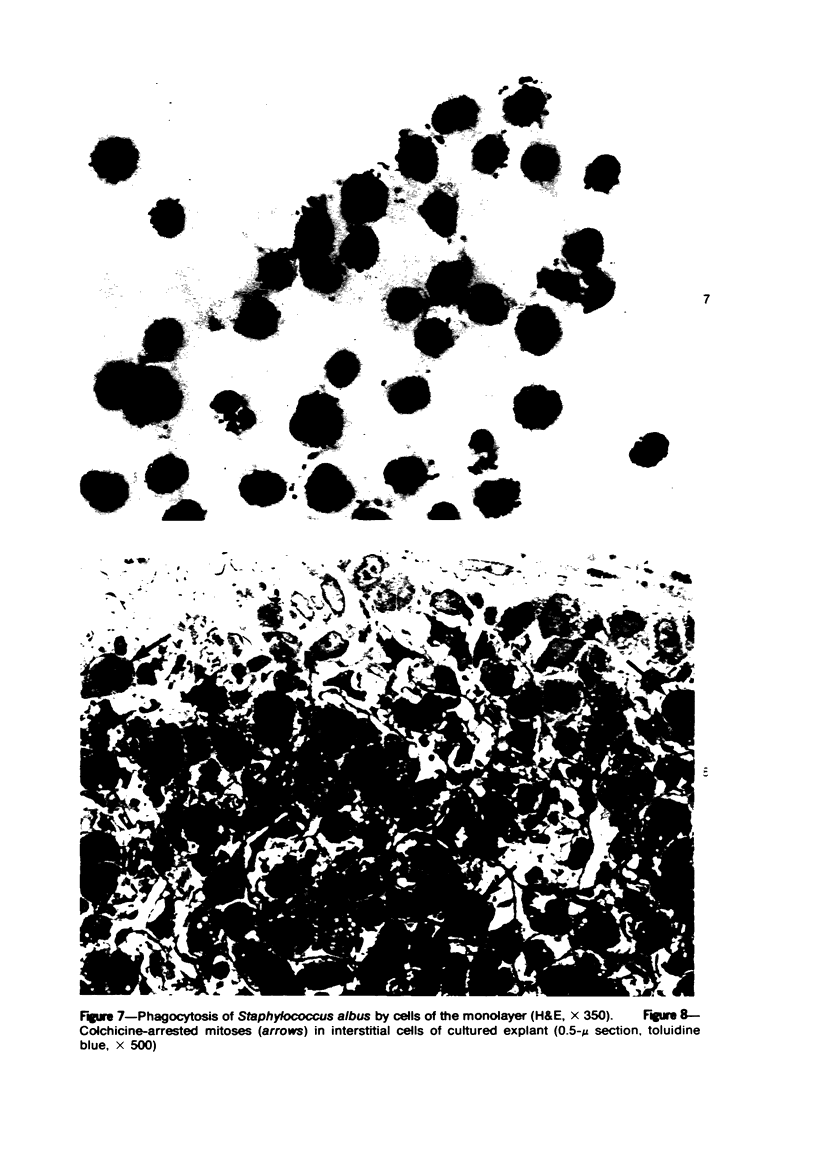
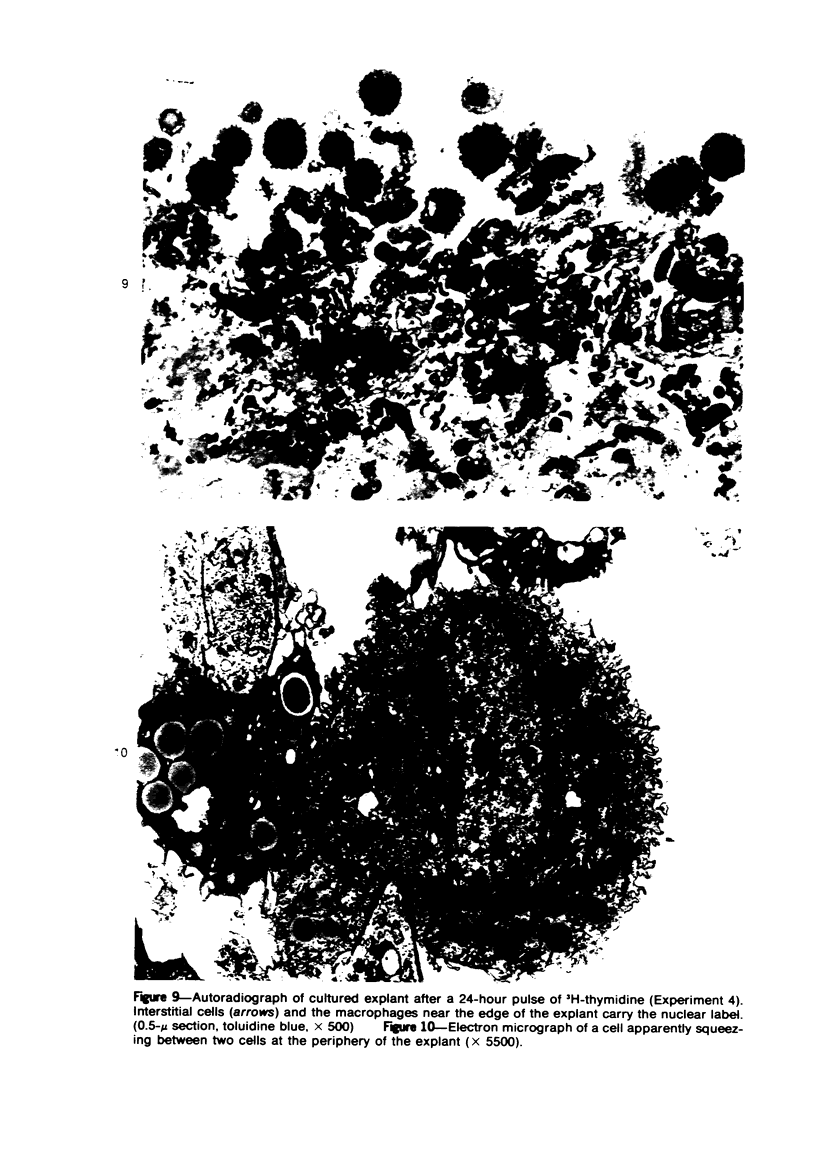
The production of alveolar macrophages in a blood-free organ culture system has been studied to determine whether free macrophages undergo mitosis or whether their ongoing production is dependent upon continuing division of interstitial cells. Explants of murine long were attached to cellophane or glass; after 6 days of culture, a population of cells identified morphologically and functionally as macrophages appeared around the central tissue. These cells did not divide, and they disappeared 4 days after removal of the central lung explant. 3H-thymidine labeling of these peripheral macrophages was observed only when the central tissue was present and when the thymidine pulse was 24 hours in duration. Actual cell division was observed only in the interstitial cells of the explant. It is concluded that the interstitial cell population provides a continuing pool of precursor cells that divide and migrate outwards, creating a "steady state" system in which macrophage loss at the periphery is balanced by cell production at the center.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolphe M., Fontagne J., Pelletier M., Giroud J. P. Induction of DNA synthesis in rat macrophages in vitro by inflammatory exudate. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):637–637. doi: 10.1038/253637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton J. E., Botham C. M. Factors affecting lead capture methods for the fine localization of rat lung acid phosphatase. Histochem J. 1970 Nov;2(6):507–519. doi: 10.1007/BF01003128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo B., Imaeda T. Cellular response to Freund's adjuvant in the rabbit lung. An electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1966 Nov;15(11):1659–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Monocyte migration across pulmonary membranes in mice infected with cytomegalovirus. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Feb;22(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velo G. P., Spector W. G. The origin and turnover of alveolar macrophages in experimental pneumonia. J Pathol. 1973 Jan;109(1):7–19. doi: 10.1002/path.1711090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Origin of the pulmonary alveolar macrophage studied in the iprindole-treated rat. J Pathol. 1972 Oct;108(2):115–118. doi: 10.1002/path.1711080204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne K. M., Spector W. G., Willoughby D. A. Macrophage proliferation in vitro induced by exudates. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):636–637. doi: 10.1038/253636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]