Abstract
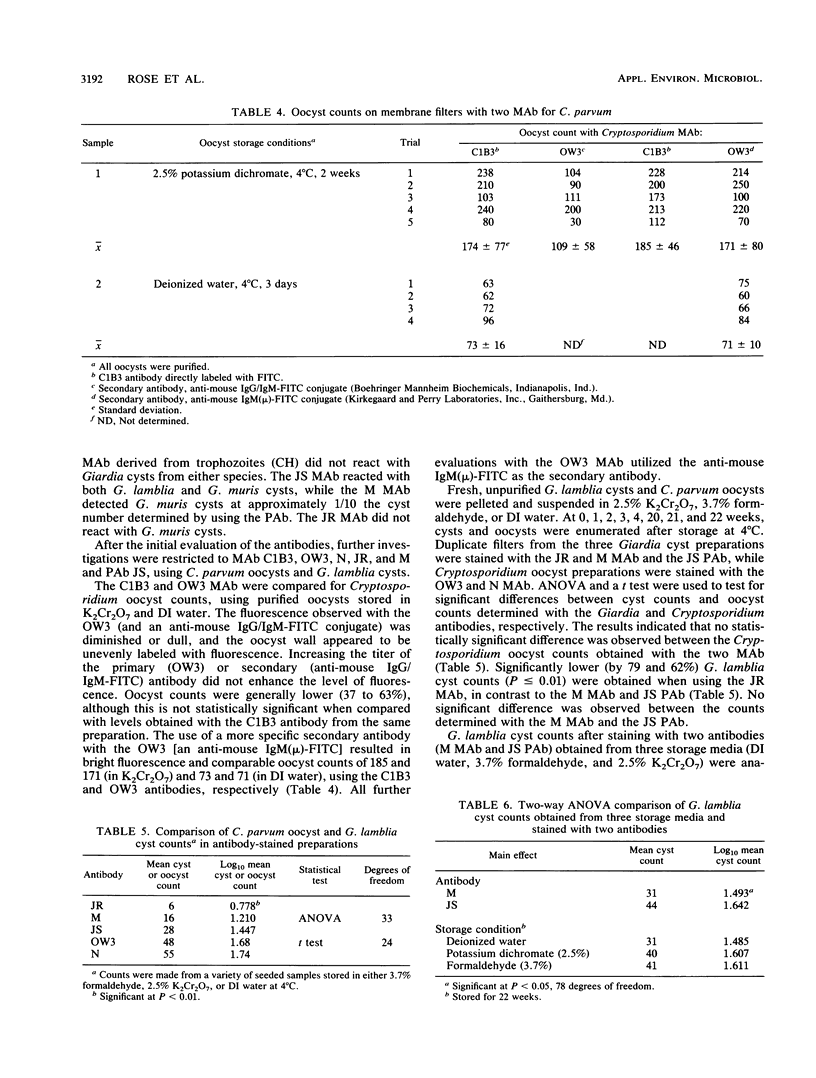
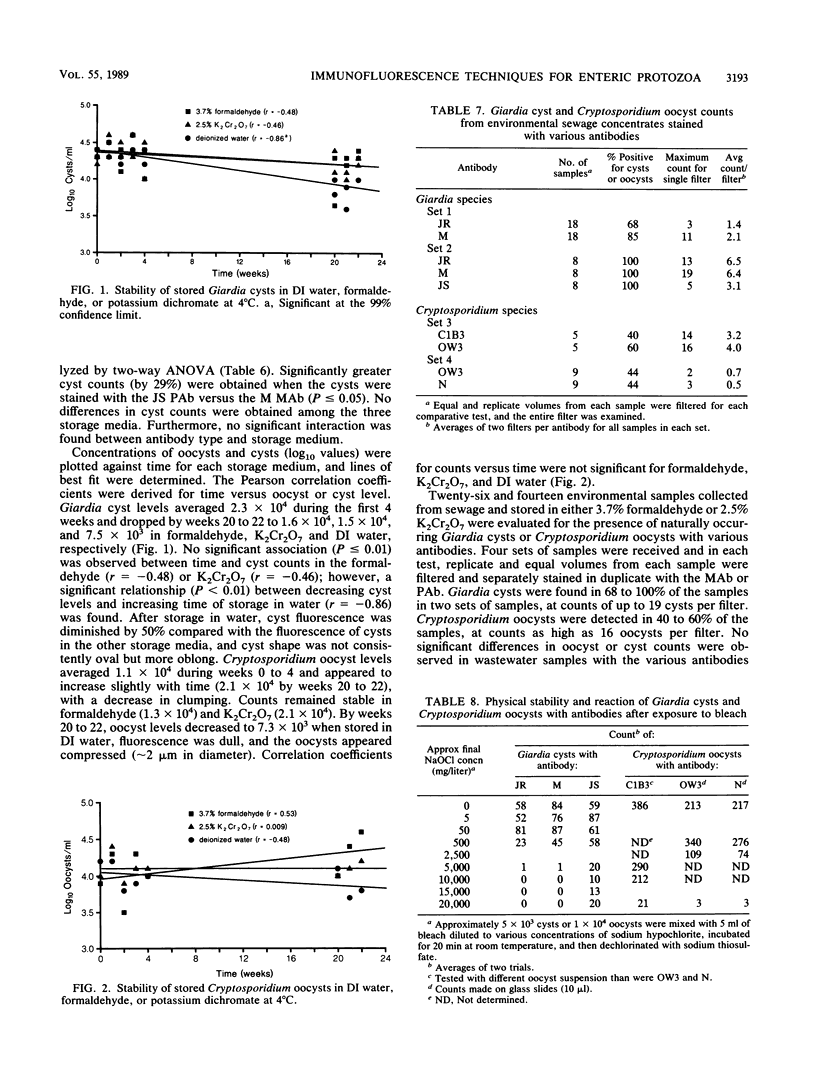
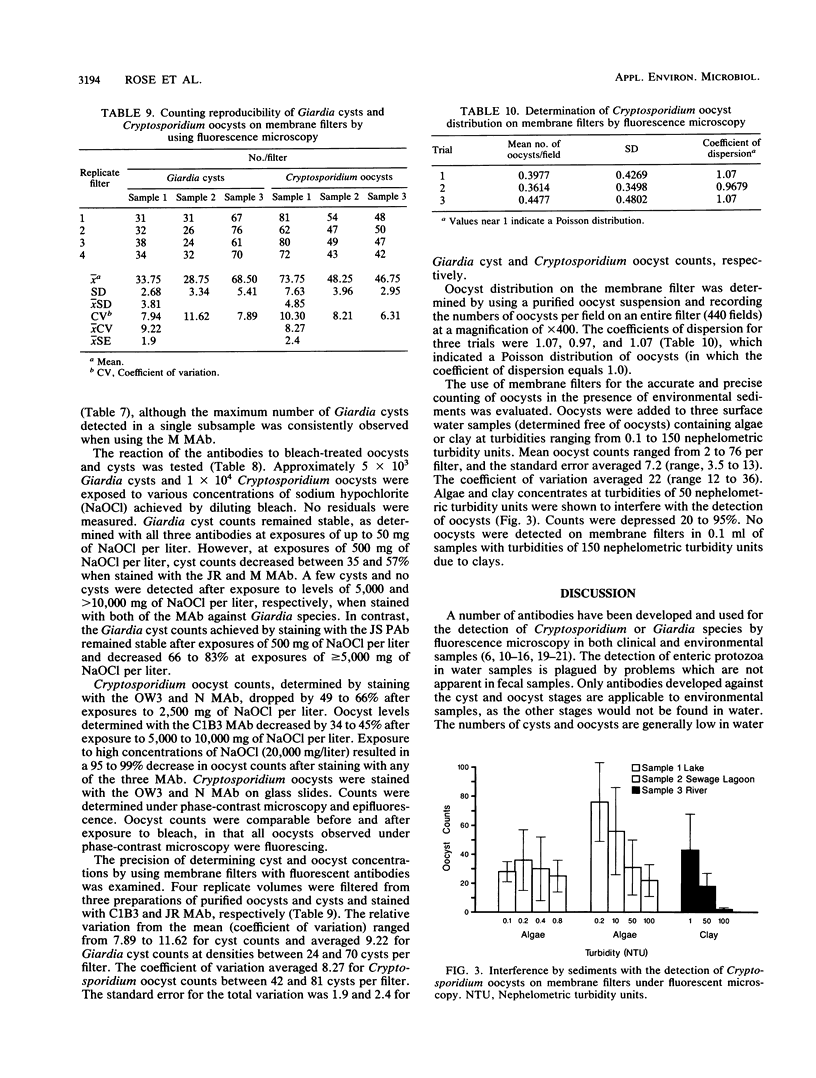
Cryptosporidium and Giardia species are enteric protozoa which cause waterborne disease. The detection of these organisms in water relies on the detection of the oocyst and cyst forms or stages. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies were compared for their abilities to react with Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts after storage in water, 3.7% formaldehyde, and 2.5% potassium dichromate, upon exposure to bleach, and in environmental samples. Three monoclonal antibodies to Cryptosporidium parvum were evaluated. Each test resulted in an equivalent detection of the oocysts after storage, after exposure to bleach, and in environmental samples. Oocyst levels declined slightly after 20 to 22 weeks of storage in water, and oocyst fluorescence and morphology were dull and atypical. Oocyst counts decreased after exposure to 2,500 mg of sodium hypochlorite per liter, and fluorescence and phase-contrast counts were similar. Sediment due to algae and clays found in environmental samples interfered with the detection of oocysts on membrane filters. Two monoclonal antibodies and a polyclonal antibody directed against Giardia lamblia cysts were evaluated. From the same seeded preparations, significantly greater counts were obtained with the polyclonal antibody. Of the two monoclonal antibodies, one resulted in significantly lower cyst counts. In preliminary studies, the differences between antibodies were not apparent when used on the environmental wastewater samples. After 20 to 22 weeks in water, cyst levels declined significantly by 67%. Cysts were not detected with monoclonal antibodies after exposure to approximately 5,000 mg of sodium hypochlorite per liter.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. C. Abomasal cryptosporidiosis in cattle. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):235–238. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Antonio R. G., Winn R. E., Taylor J. P., Gustafson T. L., Current W. L., Rhodes M. M., Gary G. W., Jr, Zajac R. A. A waterborne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis in normal hosts. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):886–888. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia L. S., Brewer T. C., Bruckner D. A. Fluorescence detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in human fecal specimens by using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):119–121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.119-121.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia L. S., Bruckner D. A., Brewer T. C., Shimizu R. Y. Techniques for the recovery and identification of Cryptosporidium oocysts from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):185–190. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.185-190.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. B., Matte T. D., O'Brien T. R., McKinley T. W., Logsdon G. S., Rose J. B., Ungar B. L., Word D. M., Pinsky P. F., Cummings M. L. Large community outbreak of cryptosporidiosis due to contamination of a filtered public water supply. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 25;320(21):1372–1376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905253202103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore M. S., Rose J. B., Gerba C. P., Arrowood M. J., Sterling C. R. Occurrence of Cryptosporidium oocysts in sewage effluents and selected surface waters. J Parasitol. 1987 Aug;73(4):702–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musial C. E., Arrowood M. J., Sterling C. R., Gerba C. P. Detection of Cryptosporidium in water by using polypropylene cartridge filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):687–692. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.687-692.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauch J. F. Use of immunofluorescence and phase-contrast microscopy for detection and identification of Giardia cysts in water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1434–1438. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1434-1438.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. V., Girdwood R. W., Patterson W. J., Hardie R., Green L. A., Benton C., Tulloch W., Sharp J. C., Forbes G. I. Waterborne outbreak of cryptosporidiosis. Lancet. 1988 Dec 24;2(8626-8627):1484–1484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90951-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding J. J., Pacha R. E., Clark G. W. Quantitation of Giardia cysts by membrane filtration. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):713–715. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.713-715.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



