Abstract
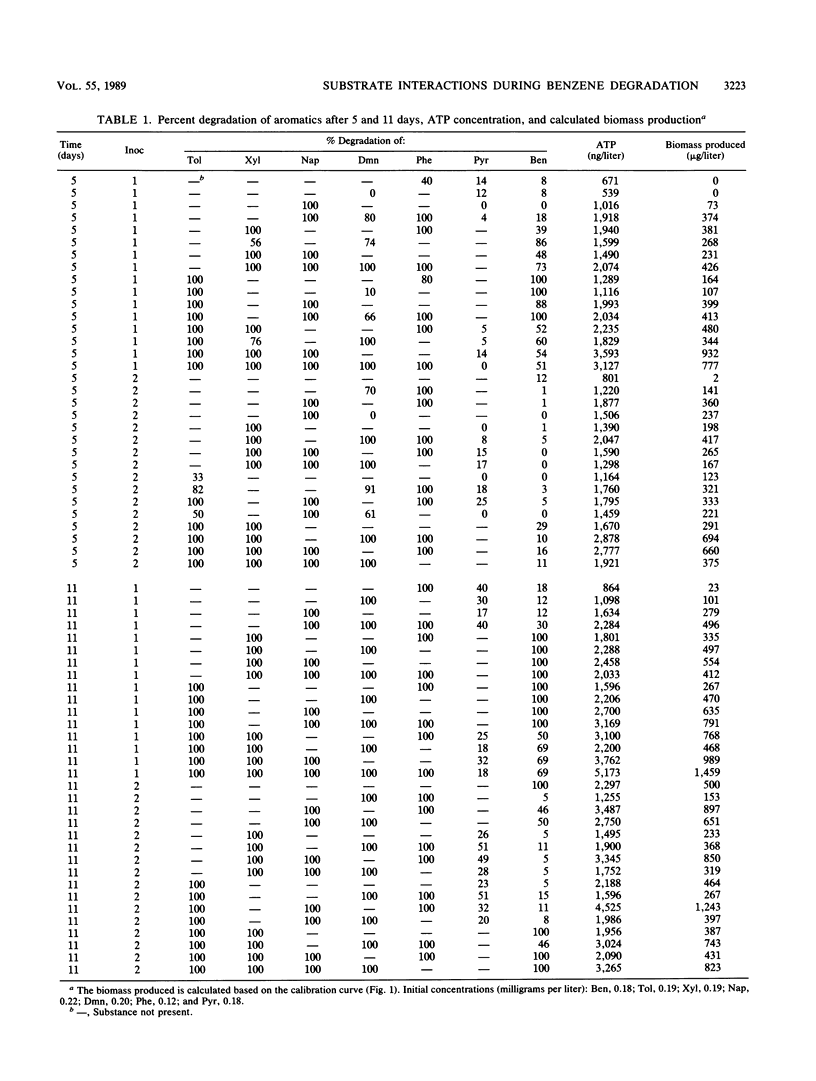
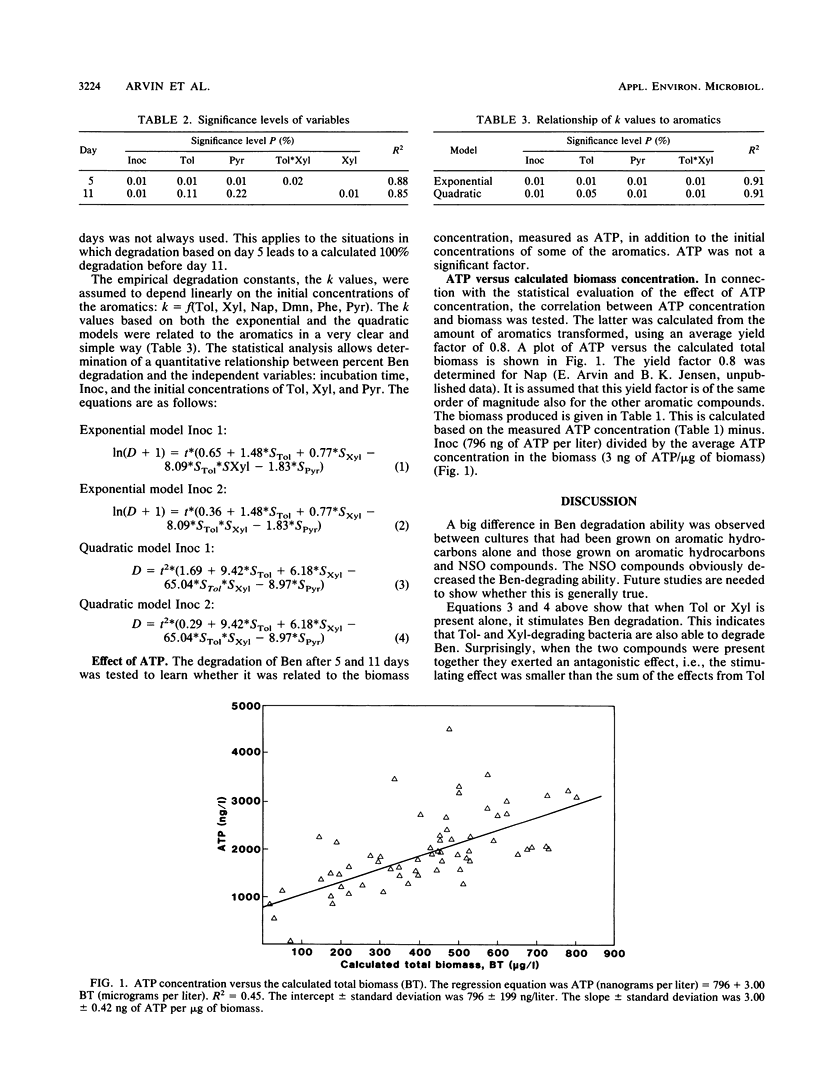
This study dealt with the interactions with benzene degradation of the following aromatic compounds in a mixed substrate: toluene, o-xylene, naphthalene, 1,4-dimethylnaphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrrole. The experiment was performed as a factorial experiment with simple batch cultures. The effect of two different types of inocula was tested. One type of inoculum was grown on a mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons; the other was grown on a mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons and nitrogen-, sulfur-, and oxygen-containing aromatic compounds (NSO compounds), similar to some of the compounds identified in creosote waste. The culture grown on the aromatic hydrocarbons and NSO compounds was much less efficient in degrading benzene than the culture grown on only aromatic hydrocarbons. The experiments indicated that toluene- and o-xylene-degrading bacteria are also able to degrade benzene, whereas naphthalene-, 1,,4-dimethylnaphthalene-, and phenanthrene-degrading bacteria have no or very little benzene-degrading ability. Surprisingly, the stimulating effect of toluene and o-xylene was true only if the two compounds were present alone. In combination an antagonistic effect was observed, i.e., the combined effect was smaller than the sum from each of the compounds. The reason for this behavior has not been identified. Pyrrole strongly inhibited benzene degradation even at concentrations of about 100 to 200 micrograms/liter. Future studies will investigate the generality of these findings.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer J. E., Capone D. G. Effects of co-occurring aromatic hydrocarbons on degradation of individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediment slurries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1649–1655. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1649-1655.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp R. J., Pfaender F. K. Influence of easily degradable naturally occurring carbon substrates on biodegradation of monosubstituted phenols by aquatic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):394–401. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.394-401.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


