Abstract
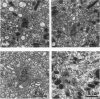
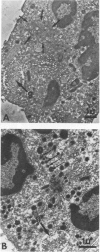
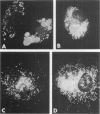
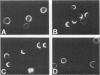
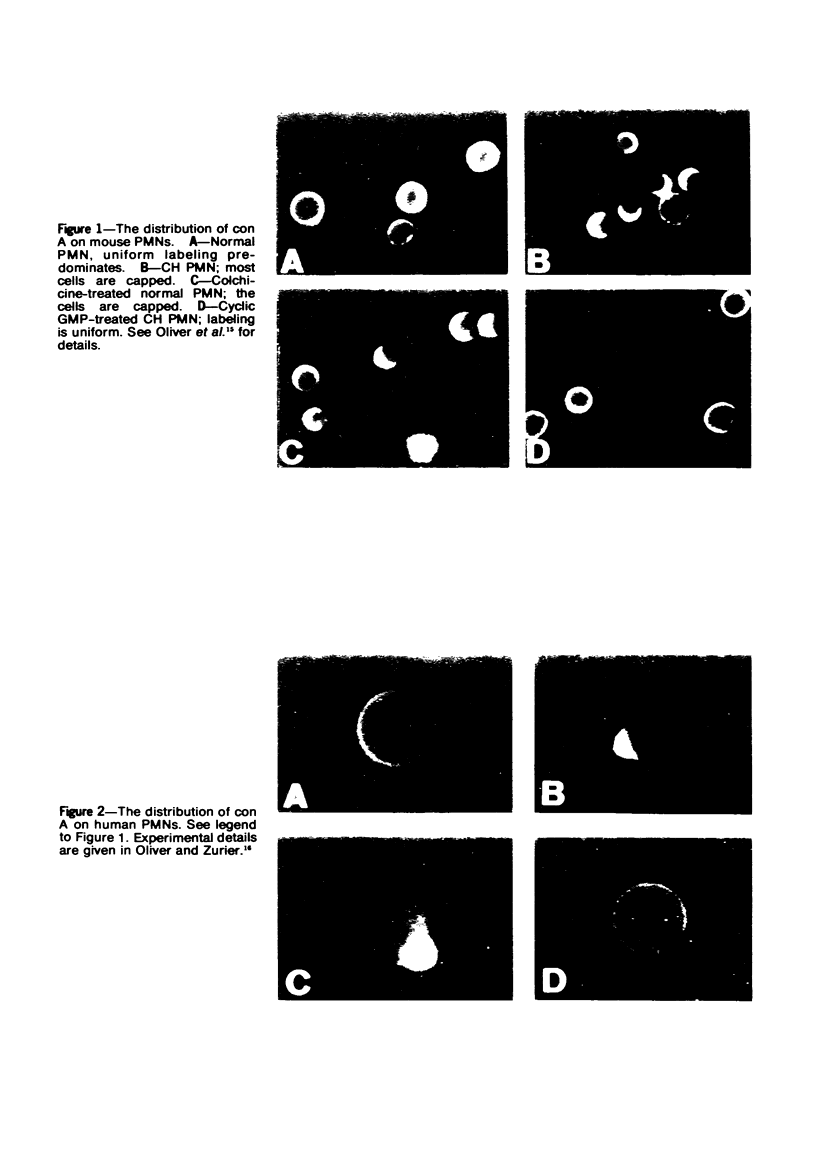
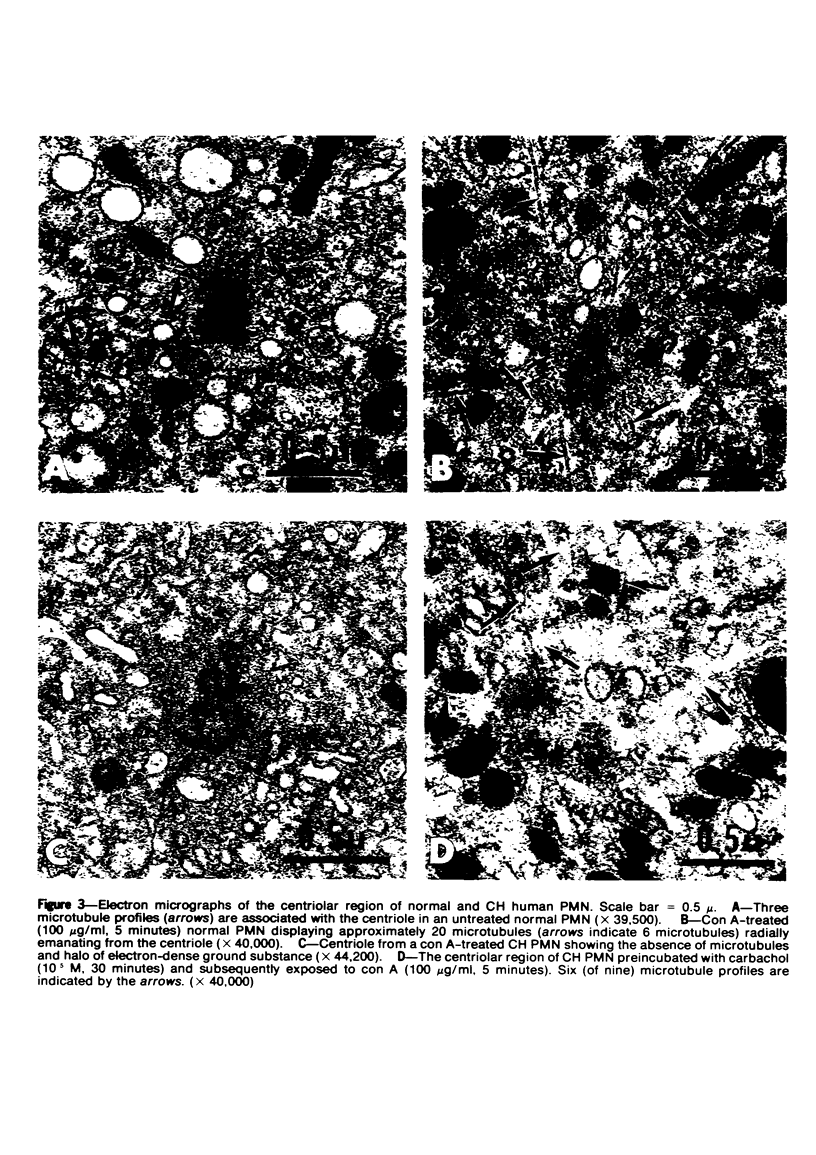
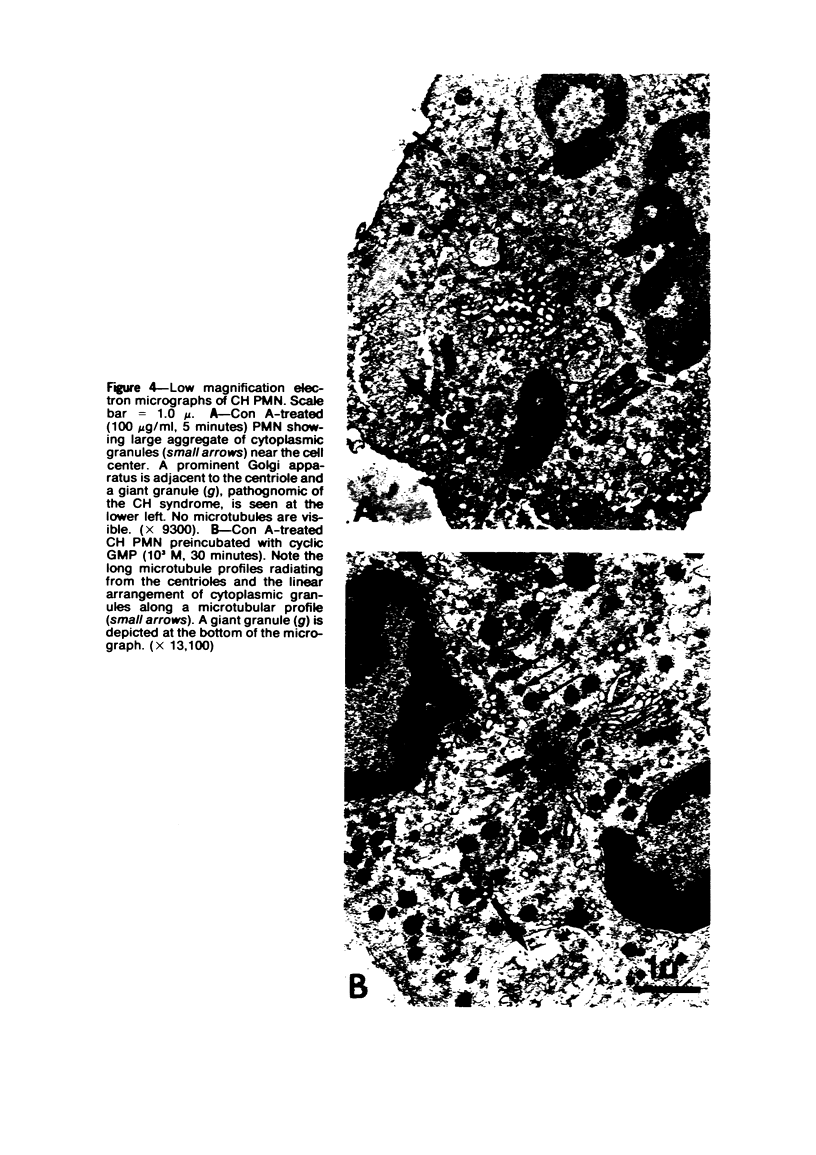
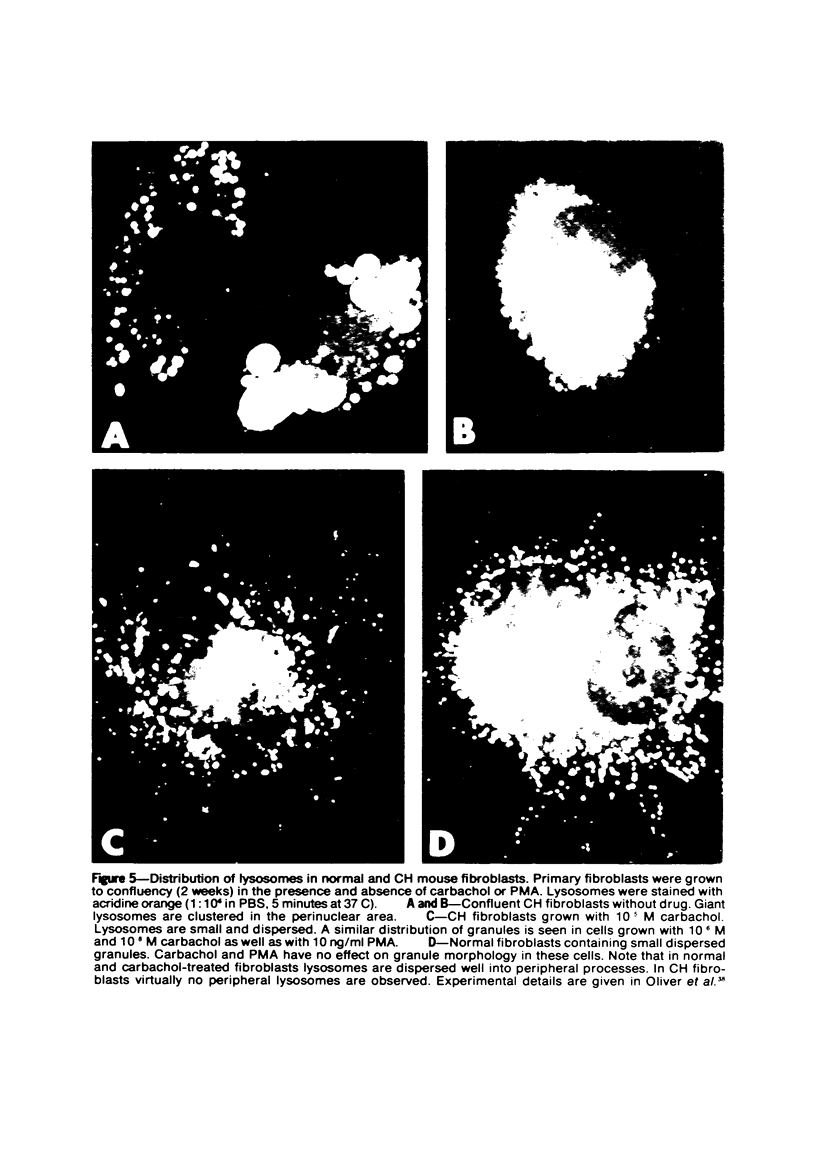
The Chediak-Higashi (CH) syndrome of man and several animal species is characterized by the presence of abnormal giant granules in all granule-containing cells and by defects in chemotaxis and lysosomal degranulation during phagocytosis in polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). Since similar functional abnormalities have been reported in normal PMNs following exposure to colchicine and other agents that disrupt microtubles it was proposed that microtubule function may be impaired in the CH syndrome. The mobility of concanavalin A (con A)-receptor complexes on PMN membranes was used to test microtubule integrity. Normal PMNs showed a uniform distribution of membrane-bound con A. By contrast, con A was aggregated into surface caps on both colchicine-treated normal PMNs and untreated PMNs from mice and a patient with CH syndrome. This result is consistent with impaired microtubule function in the CH cells. The spontaneous capping response of CH PMNs was inhibited by cyclic GMP and by cholinergic agonists that can elevate cyclic GMP levels in neutrophils. This raised the possibility that the microtubule defect in CH cells may be correctable by treatments that increase cyclic GMP generation. Direct evidence for both the absence of microtubule assembly in con A-treated PMNs from the CH patient and for normal microtubule assembly in CH PMNs incubated with cyclic GMP and cholinergic agonists prior to con A treatment was obtained by electron microscopy. In addition, evidence for a direct relationship between the microtubule defect and the development of giant lysosomes in CH cells was obtained. Thus, CH fibroblasts grown in vitro developed abnormal lysosomes in the majority of cells. However, the same cells cultured in the presence of cholinergic agonists developed a majority of lysosomes that were morphologically normal at the level of the light microscope. Similarly, granule morphology appeared normal in peripheral blood leukocytes from mice treated chronically in vivo with cholinergic agonists.
Full text
PDF


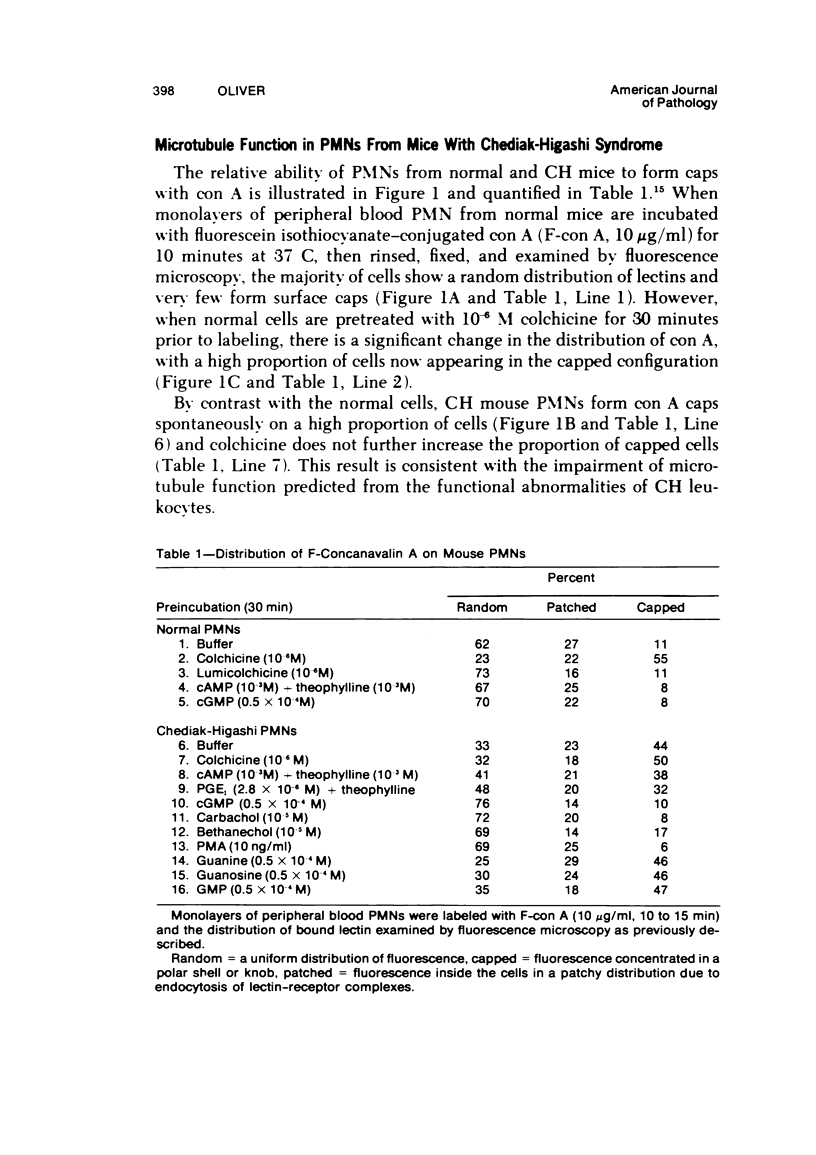
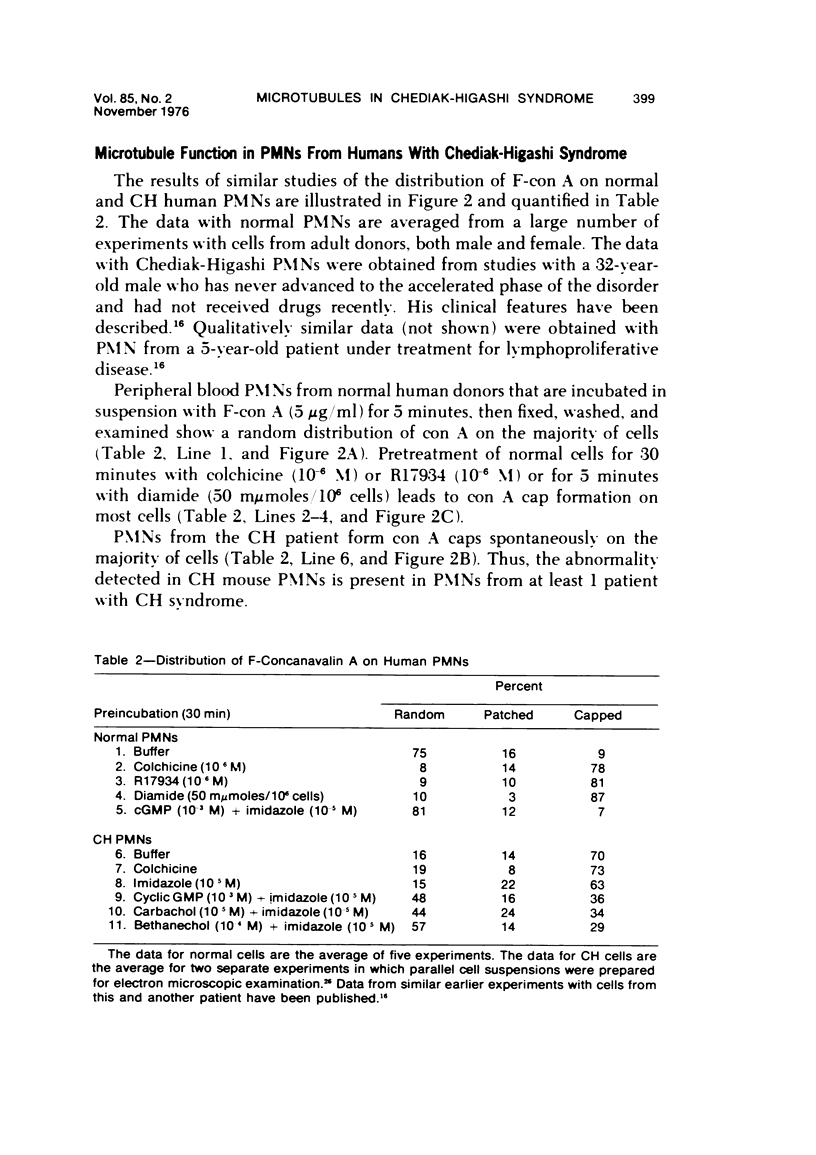



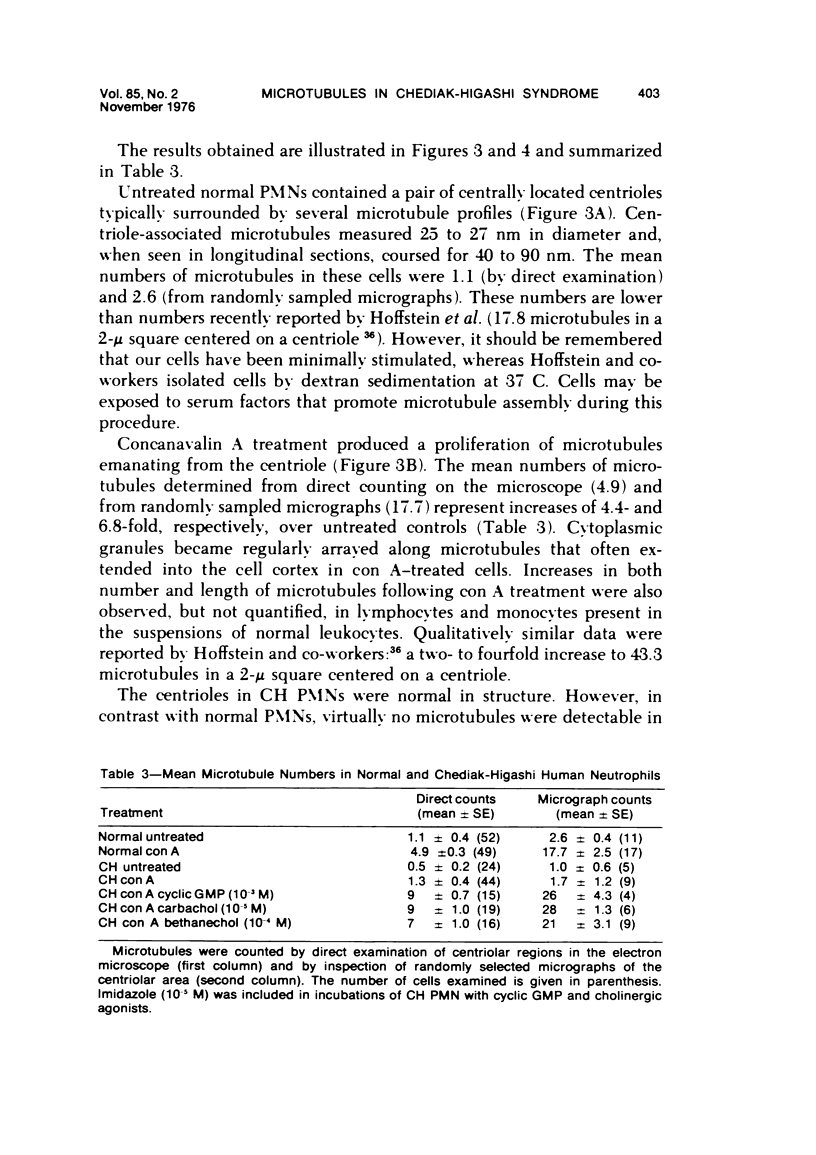









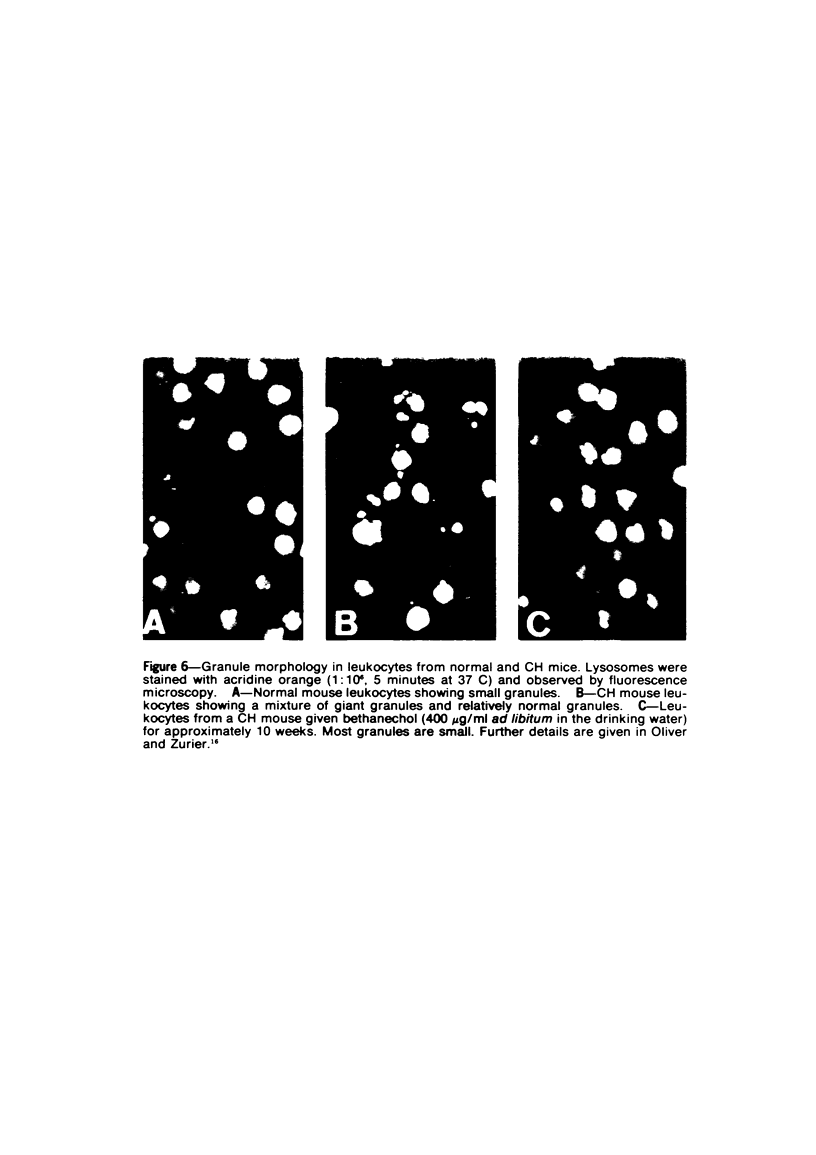
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandmann U., Rydgren L., Norberg B. The difference between random movement and chemotaxis. Effects of antitubulins on neutrophil granulocyte locomotion. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90618-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. S., Oliver J. M., Berlin R. D. Fluorescence techniques for following interactions of microtubule subunits and membranes. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):152–154. doi: 10.1038/254152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. M., Blume R. S., Wolff S. M. Characterization and significance of abnormal leukocyte granules in the beige mouse: a possible homologue for Chediak-Higashi Aleutian trait. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Feb;73(2):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D., Oliver J. M., Ukena T. E., Yin H. H. Control of cell surface topography. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):45–46. doi: 10.1038/247045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D., Oliver J. M., Ukena T. E., Yin H. H. The cell surface. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 6;292(10):515–520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503062921007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D. Temperature dependence of nucleoside membrane transport of rabbit alveolar macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4724–4730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Stossel T. P. Neutrophil action dysfunction and abnormal neutrophil behavior. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 21;291(21):1093–1099. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411212912101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE IN VITRO DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. II. THE INFLUENCE OF SERUM ON GRANULE FORMATION, HYDROLASE PRODUCTION, AND PINOCYTOSIS. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:835–848. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Defective granulocyte chemotaxis in the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2645–2652. doi: 10.1172/JCI106765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Spicer S. S., Greene W. B., Padgett G. A. Ultrastructure of bone marrow granulocytes in normal mink and mink with the homolog of the Chediak-Higashi trait of humans. I. Origin of the abnormal granules present in the neutrophils of mink with the C-HS trait. Lab Invest. 1971 Apr;24(4):303–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M. J., Van de Veire R. M., Aerts F. E., Borgers M., Janssen P. A. The effects of methyl (5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl) carbamate, (R 17934; NSC 238159), a new synthetic antitumoral drug interfering with microtubules, on mammalian cells cultured in vitro. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):905–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Blume R. S., Glade P. R., Chessin L. N., Wolff S. M. Fine structure of continuous long term lymphoid cell cultures from a Chediak-Higashi patient and heterozygote. Lab Invest. 1969 Sep;21(3):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I., Wang J. L. Receptor mobility and receptor-cytoplasmic interactions in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., Hill H. R., Quie P. G., Gogan N., Goldberg N. D. Cyclic GMP and cell movement. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):458–460. doi: 10.1038/245458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Rosenthal A. S. The regulatory role of divalent cations in human granulocyte chemotaxis. Evidence for an association between calcium exchanges and microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):594–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I., Hoffstein S., Gallin J., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: microtubule assembly and membrane fusion induced by a component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Neufeld E. F. A hypothesis for I-cell disease: defective hydrolases that do not enter lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds K., Danes B. S. Letter: Microtubular defect in Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Lancet. 1976 Jul 17;2(7977):146–147. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsimäki Y., Arstila A. U., Trump B. F. Autophagocytosis: in vitro induction by microtuble poisons. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Apr;92(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90630-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S., Soberman R., Goldstein I., Weissmann G. Concanavalin A induces microtubule assembly and specific granule discharge in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):781–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lint T. F., George W. J. Hormonal control of lysosomal enzyme release from human neutrophils. Effects of autonomic agents on enzyme release, phagocytosis, and cylic nucleotide levels. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1395–1414. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer J. N., Blume R. S., Yankee R. A., Wolff S. M. Alteration of sphingolipid metabolism in leukocytes from patients with the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 22;279(8):410–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808222790806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E. Microtubules and the mobilization of lysosomes in phagocytizing human leukocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:738–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M. Concanavalin A cap formation on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by R17934, a new antitumor drug that interferes with microtubule assembly. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Jun;19(6):389–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Krawiec J. A., Berlin R. D. Carbamycholine prevents giant granule-formation in cultured fibroblasts from beige (Chediak-Higashi) mice. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):205–210. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Ukena T. E., Berlin R. D. Effects of phagocytosis and colchicine on the distribution of lectin-binding sites on cell surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):394–398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Zurier R. B. Correction of characteristic abnormalities of microtubule function and granule morphology in Chediak-Higashi syndrome with cholinergic agonists. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1239–1247. doi: 10.1172/JCI108392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell H. C., Wolf P. L. Neutrophilic leukocyte inclusions in colchicine intoxication. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Mar;100(3):136–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Axline S. G. Subplasmalemmal microfilaments and microtubules in resting and phagocytizing cultivated macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):12–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Rosenthal A. S., Balestra D. J. Abnormal bactericidal, metabolic, and lysosomal functions of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):649–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI106854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblith J. Z., Ukena T. E., Yin H. H., Berlin R. D., Karnovsky M. J. A comparative evaluation of the distribution of concanavalin A-binding sites on the surfaces of normal, virally-transformed, and protease-treated fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1625–1629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler J. A., Gallin J. I., Vaughan M. Effects of serotonin, carbamylcholine, and ascorbic acid on leukocyte cyclic GMP and chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 1975 Nov;67(2PT1):480–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Silver J. M., Cohn Z. A. Pinocytosis in fibroblasts. Quantitative studies in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):949–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Root R. K., Vaughan M. Phagocytosis in chronic granulomatous disease and the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 20;286(3):120–123. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201202860302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., Berlin R. D. Effect of phagocytosis on membrane transport of nonelectrolytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):1016–1035. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Goldstein I., Hoffstein S., Tsung P. K. Reciprocal effects of cAMP and cGMP on microtubule-dependent release of lysosomal enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:750–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. M. The Chediak-Higashi syndrome: studies of host defenses. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Feb;76(2):293–306. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Weissmann G., Hoffstein S., Kammerman S., Tai H. H. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. II. Effects of cAMP and cGMP, autonomic agonists, and agents which affect microtubule function. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]