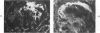Abstract
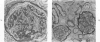
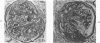
The present studies examined the pathogenesis of focal glomerular sclerosis in aging rats. A marked difference in development of the lesion was noted between males and females, and strain variability was an important factor. Increased glomerular basement membrane permeability with loss of selectivity unrelated to changes in glomerular sialoprotein occurred with aging and was accompanied by increasing proteinuria. Noncomplement-fixing mesangial deposits of rat IgM were present after 1 month of age and were also found in lesser amounts in germfree rats. Fluoresceinated eluates of rat kidneys did not have antibody activity against rat serum or tissue antigens. There was no evidence for a pathogenetic role of IgM deposits. Rat IgG, IgA, IgE, C3, and fibrin were occasionally found in sclerotic areas. Analysis of multiple histologic sections revealed a close correlation between aging and glomerular pathology, with a poor correlation between tubular damage and aging. Glomerular damage appeared to be the initial event leading to tubular damage. Indirect evidence suggests that a relative thymic deficiency may play an important role in the pathogenesis of the lesion.
Full text
PDF





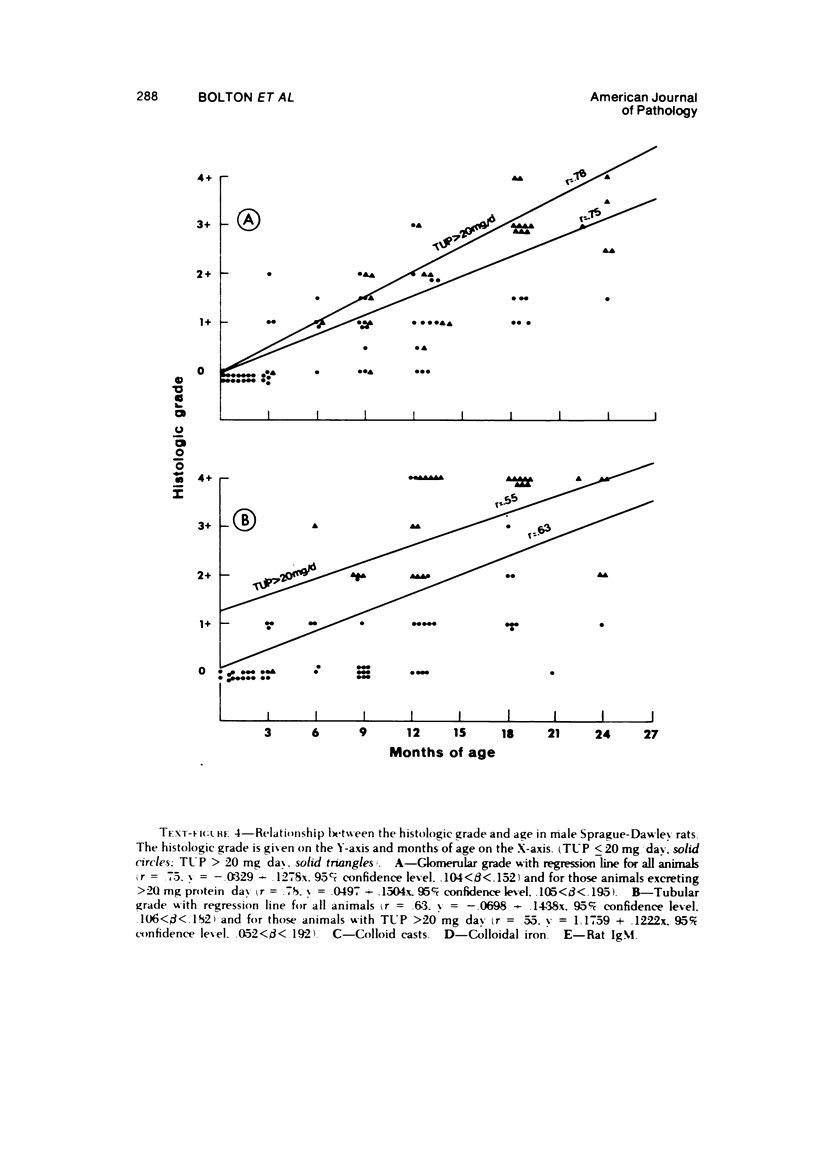
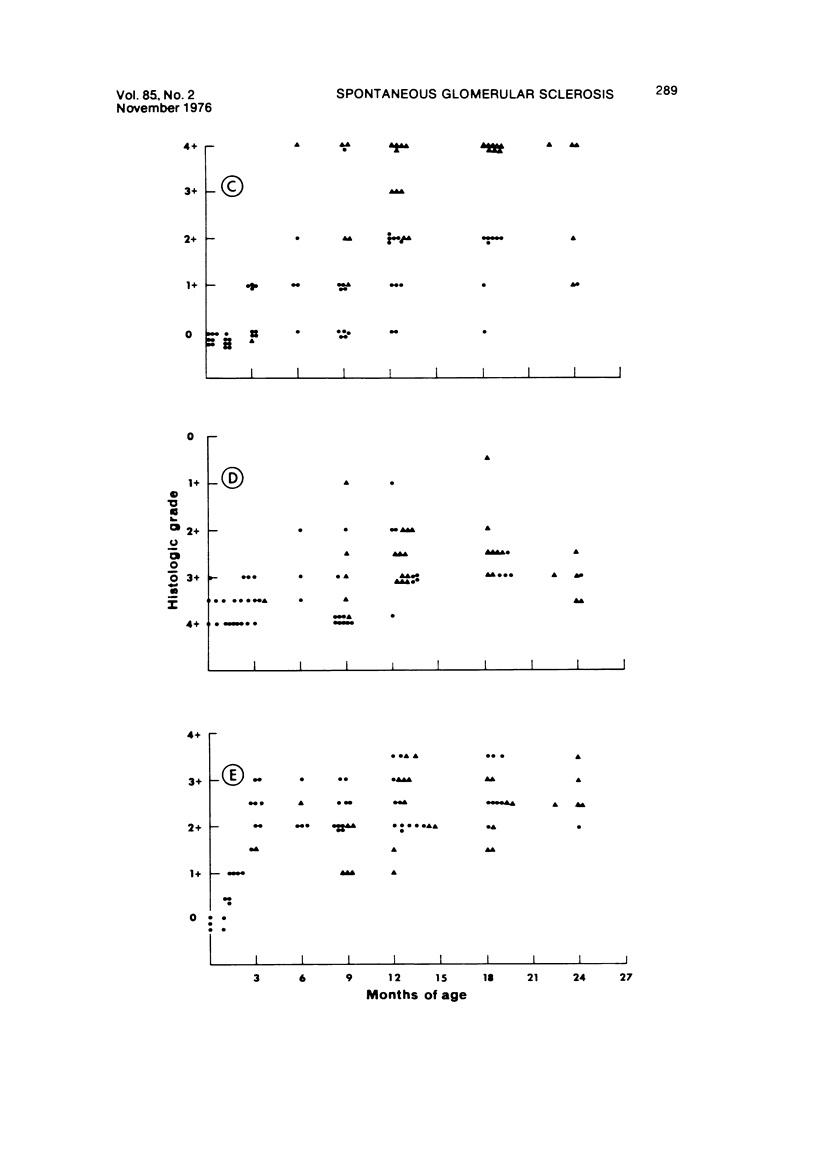











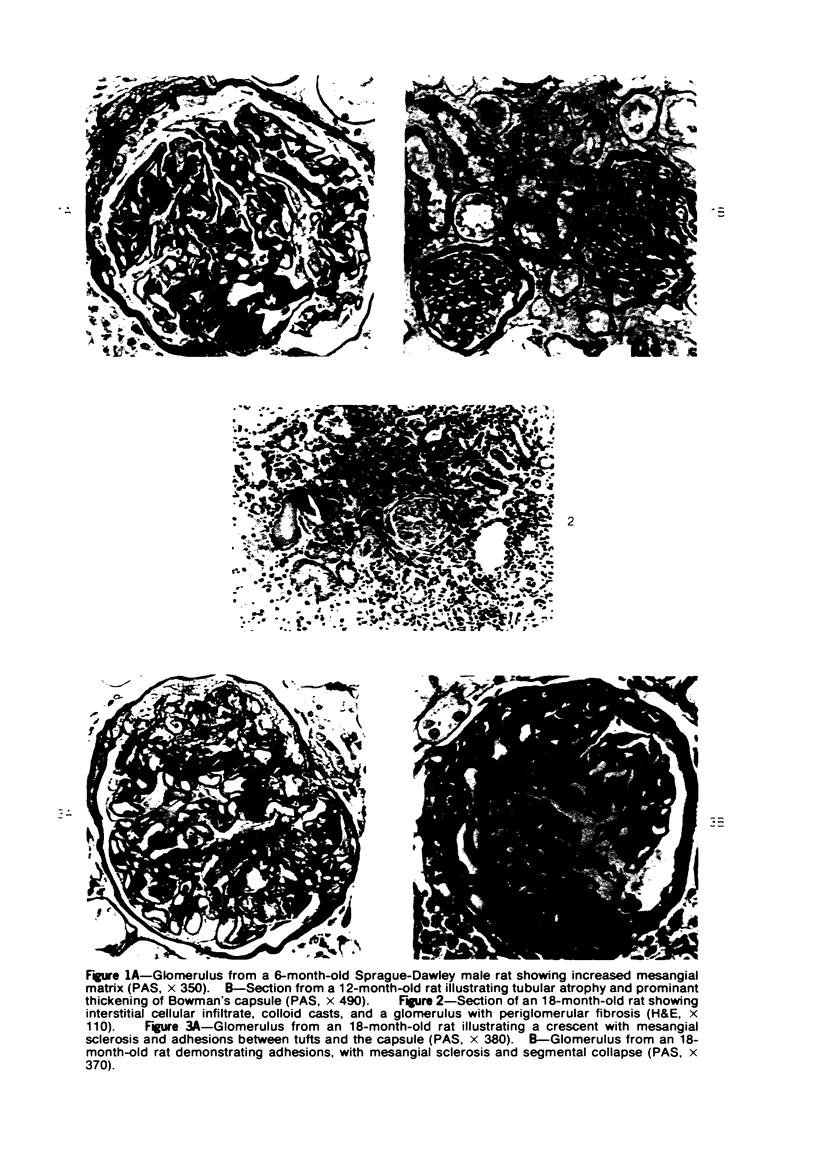
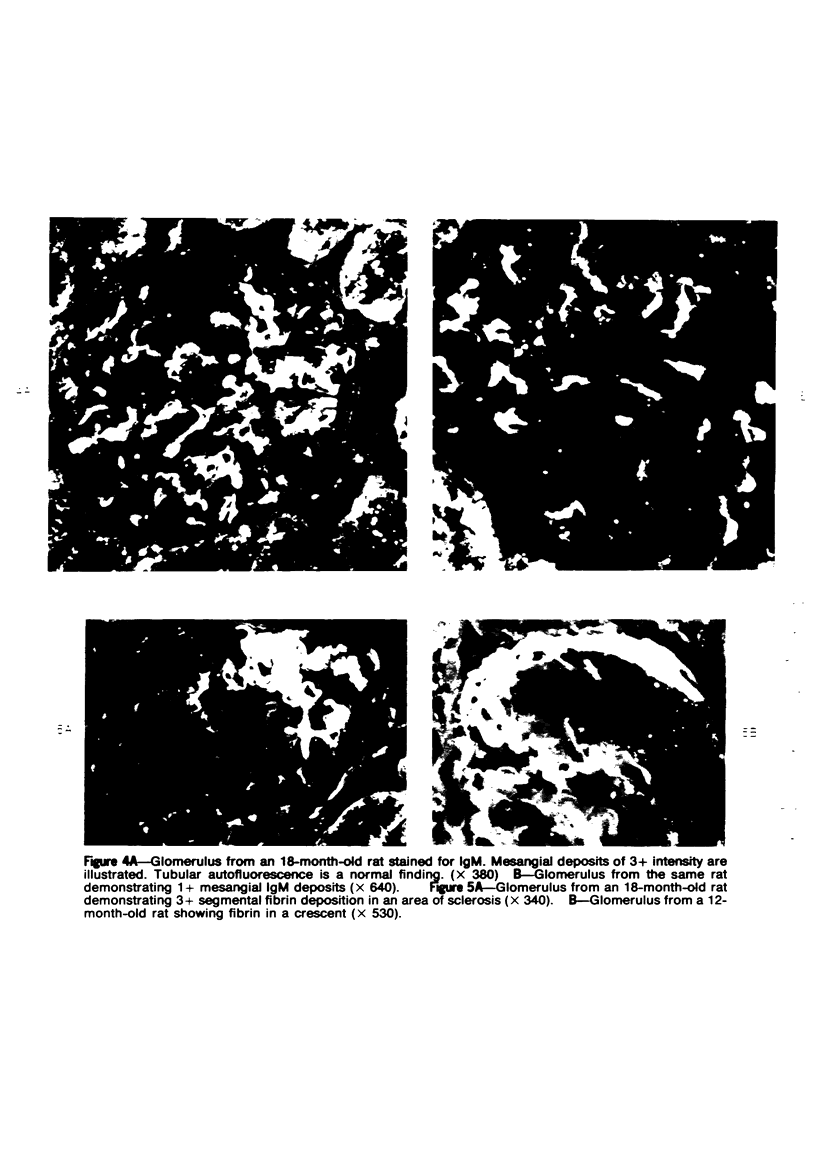
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG B. N., SIMMS H. S. Nutrition and longevity in the rat. II. Longevity and onset of disease with different levels of food intake. J Nutr. 1960 Jul;71:255–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG B. N. SPONTANEOUS NEPHROSIS, WITH PROTEINURIA, HYPERGLOBULINEMIA, AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA IN THE RAT. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jun;119:417–420. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hinglais N. Les ddpôts intercapillaires d'IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1968 Sep;74(9):694–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Spargo B. A., Lewis E. J. Chronic autologous immune complex glomerulopathy: effect of cyproheptadine. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 May;83(5):695–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK H. F., SHEPARD C. C. A DIALYSIS TECHNIQUE FOR PREPARING FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:642–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K. Antibody formation in first and second generation offspring of nutritionally deprived rats. Science. 1975 Oct 17;190(4211):289–290. doi: 10.1126/science.1179211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Stilmant M. M. Mesangial lesions and focal glomerular sclerosis in the aging rat. Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;33(5):491–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY W. A., JONES D. C., OSBORN G. K., KIMELDORF D. J. A RENAL LESION ASSOCIATED WITH DIURESIS IN THE AGING SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RAT. Lab Invest. 1964 May;13:439–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. The splenic suppressor cell. I. Activity of thymus-dependent adherent cells: changes with age and stress. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):127–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay F. W., Maguire M. E., Baskerville A. Etiology of chronic pneumonia in rats and a study of the experimental disease in mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):83–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.83-91.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. E., Weaver R. N., Purmalis A. Ultrastructural observations of chronic progressive nephrosis in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Vet Pathol. 1974;11(2):153–164. doi: 10.1177/030098587401100207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman P. H., Wuepper K. D., Fudenberg H. H. On the presence of gamma G and beta-1 C globulins in renal glomeruli of aging and neonatally x-irradiated mice. Vox Sang. 1967 May;12(5):329–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. R., Burkholder P. M. Focal sclerosing glomerulonephropathy with segmental hyalinosis. A clinicopathologic analysis. Lab Invest. 1973 May;28(5):533–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY G. C. Effects of old age and over-nutrition on the kidney. Br Med Bull. 1957 Jan;13(1):67–70. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konen T. G., Smith G. S., Walford R. L. Decline in mixed lymphocyte reactivity of spleen cells from aged mice of a long-lived strain. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1216–1221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus B., Cain H. Uber eine spontane Nephropathie bei Wistarratten. Die licht- und elektronenmikroskopischen Glomerulumveränderungen. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974;363(4):343–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00447845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINKSWILER H., REYNOLDS M. S., BAUMANN C. A. Factors affecting proteinuria in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1952 Feb;168(2):504–508. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.168.2.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalich J. J., Allen J. R. Protein overload nephropathy in rats with unilateral nephrectomy. II. Ultrastructural study. Arch Pathol. 1971 Apr;91(4):372–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalich J. J., Faith G. C., Harding G. E. Protein overload nephropathy in rats subjected to unilateral nephrectomy. Arch Pathol. 1970 Jun;89(6):548–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R. Ageing and immunological function in man. Gerontologia. 1972;18(5-6):285–304. doi: 10.1159/000211941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. V., Jr, Sutherland J. C., Mardiney M. R., Jr The ubiquitous occurrence of immune complex localization in the renal glomeruli of normal mice. Lab Invest. 1973 Jul;29(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Katz L., Gallo G., Waldo E., Cabaluna C., Eisinger R. P. Glomerular sclerosis in adults with nephrotic syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Apr;80(4):488–495. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-4-488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Michael A. F., Fish A. J., Brown D. M. Spontaneous immunoglobulin and complement deposition in glomeruli of diabetic rats. Lab Invest. 1972 Nov;27(5):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhaul J. J., Jr, Dixon F. J. Characterization of human anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies eluted from glomerulonephritic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):308–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI106240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medlar E. M., Blatherwick N. R. The Pathogenesis of Dietary Nephritis in the Rat. Am J Pathol. 1937 Nov;13(6):881–896.17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A. ENZYMATIC DIGESTION OF RABBIT GAMMA GLOBULIN AND ANTIBODY AND CHROMATOGRAPHY OF DIGESTION PRODUCTS. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:134–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE B. M. ROLE OF ADULT WORMS IN IMMUNITY OF RATS TO NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS. Parasitology. 1965 May;55:325–335. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000068797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie B. M. Reagin-like antibodies in rats infected with the nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):113–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter C. P. Possible immune origin of age-related pathological changes in long-lived mice. J Gerontol. 1973 Jul;28(3):265–275. doi: 10.1093/geronj/28.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Cox N. A. Immune complex glomerulonephritis in one-year-old C57BL-6 mice induced by endogenous murine leukemia virus and erythrocyte antigens. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1626–1633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poskitt T. R., Fortwengler H. P., Jr, Bobrow J. C., Roth G. J. Naturally occurring immune-complex glomerulonephritis in monkeys (Macaca irus). I. Light, immunofluorescence and electron microscopic studies. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jul;76(1):145–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist T. H., Bernick S. Histochemistry of renal basal laminae. Adolescent compared with senescent rats. J Gerontol. 1971 Apr;26(2):176–185. doi: 10.1093/geronj/26.2.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMS H. S., BERG B. N. Longevity and the onset of lesions in male rats. J Gerontol. 1957 Jul;12(3):244–252. doi: 10.1093/geronj/12.3.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Weigle W. O. The production of antisera to human gammaGlobulin subclasses in rabbits using immunological unresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):377–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. Immunoglobulins of rat colostrum. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1052–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Law L. D., Talal N. The role of NZB-NZW F1 thymus in experimental tolerance and auto-immunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Jul-Aug;13(4):369–377. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Nagle R. B., Kohnen P. W., Smuckler E. A. Response to unilateral nephrectomy in old rats. Arch Pathol. 1969 Apr;87(4):439–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sworn M. J., Fox M. Renal age changes in the rat compared with human renal senescence. An autoradiographic study. Invest Urol. 1974 Sep;12(2):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague P. O., Friou G. J. Antinuclear antibodies in mice. II. Transmission with spleen cells; inhibition or prevention with thymus or spleen cells. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):665–675. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urizar R. E., Michael A., Sisson S., Vernier R. L. Anaphylactoid purpura. II. Immunofluorescent and electron microscopic studies of the glomerular lesions. Lab Invest. 1968 Oct;19(4):437–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriesman P. J., Feldman J. D. Rat M immunoglobulin: isolation and some biological characteristics. Immunochemistry. 1972 May;9(5):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel L. W., Cole L. J., Rosen V. J. X-ray-induced glomerulosclerosis in rats: modification of lesion by food restriction, uninephrectomy, and age. J Gerontol. 1966 Jul;21(3):442–448. doi: 10.1093/geronj/21.3.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis E. J., Fernandes G., Stutman O. Susceptibility to involution of the thymus-dependent lymphoid system and autoimmunity. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;56(3):280–292. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]