Abstract
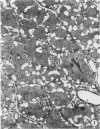
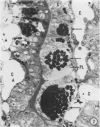
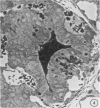
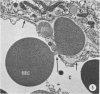
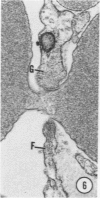
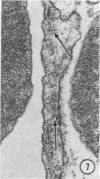
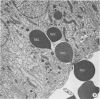
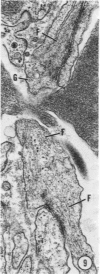
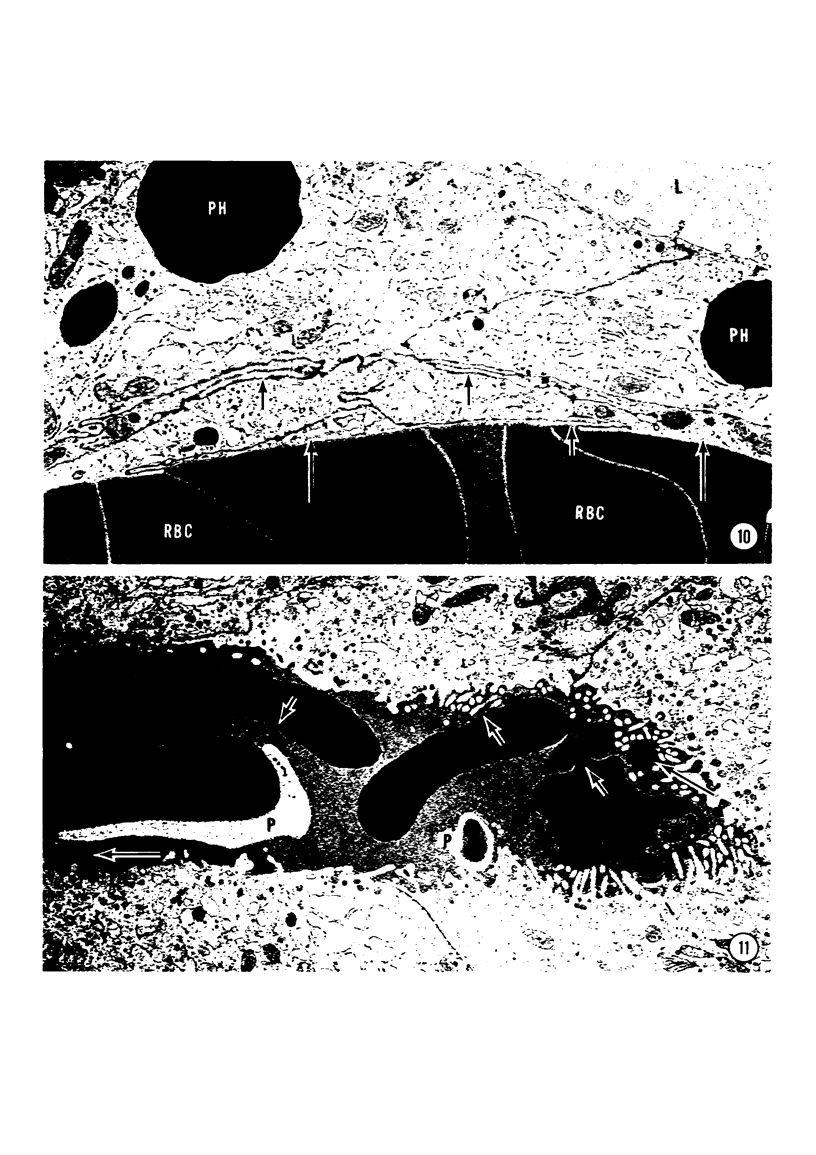
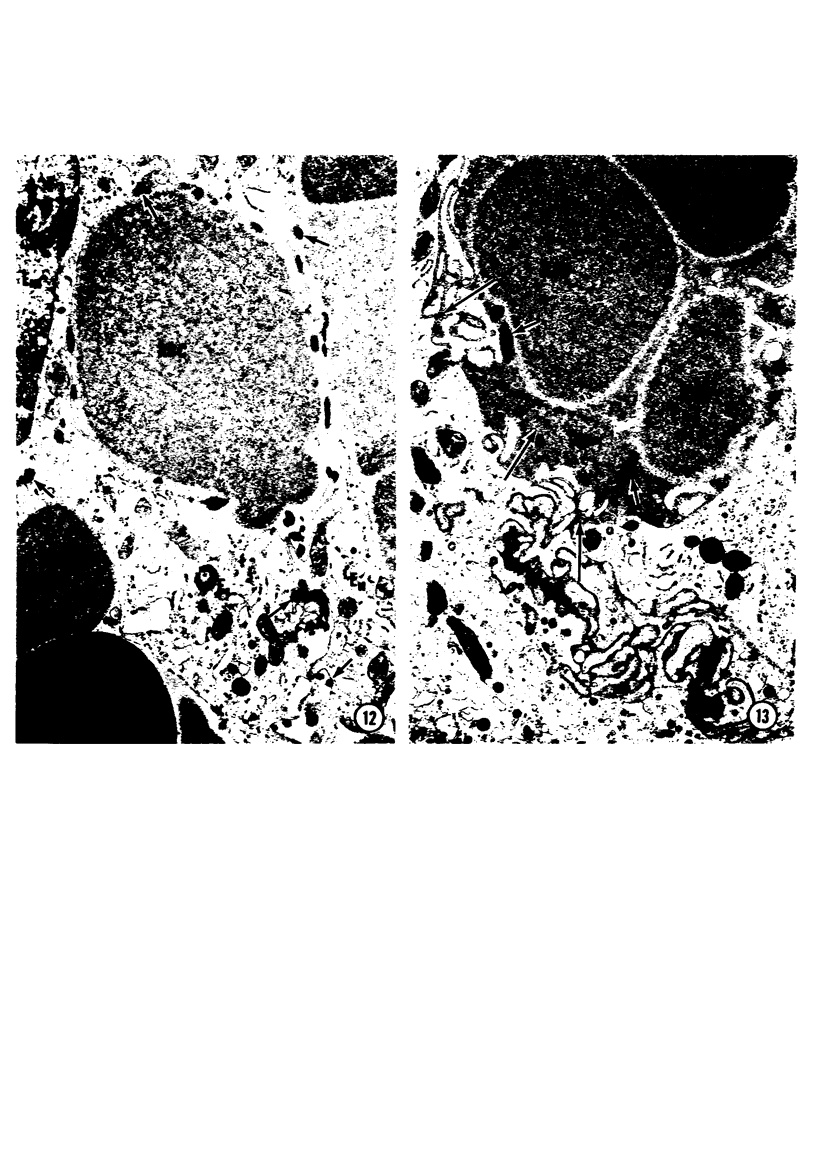
A microhemorrhagic process was consistently observed in association with the induction of thyroid hyperplasia by dietary thiouracil in the rat. This process appeared to involve the extravasation of erythrocytes (RBCs) through hyperplastic capillary walls. Those sites of extravasation which were directly visualized involved endothelial openings of less than 1 mu. These openings were surrounded by endothelial cytoplasm containing a dense fibrous material and were associated with RBC constriction during passage. Extravasated RBCs were most often noted singly or in small groups, either in columns between follicular epithelial cells or embedded amongst the basal epithelial infoldings. Occasionally, extravasated RBCs were also observed within follicular lumens. Extravasated RBCs were usually intact ultrastructurally, but occasionally an apparent hemolytic process was observed, both for RBCs embedded amongst epithelial cells and for those within follicular lumens. The nature and etiology of this microhemorrhagic process are considered in relation to the hypervascularity of the gland, the possibility of capillary wall alterations, the presence of endothelial cell mitoses, and the localization of the process.
Full text
PDF











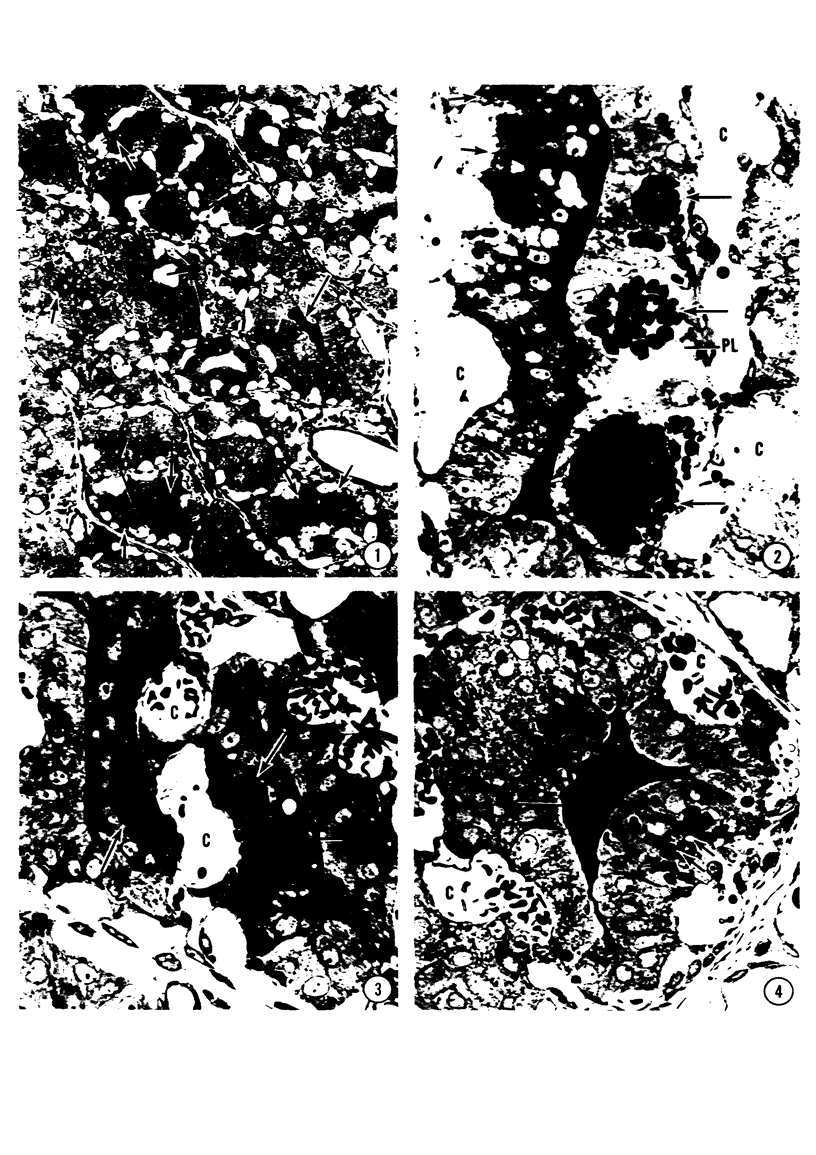
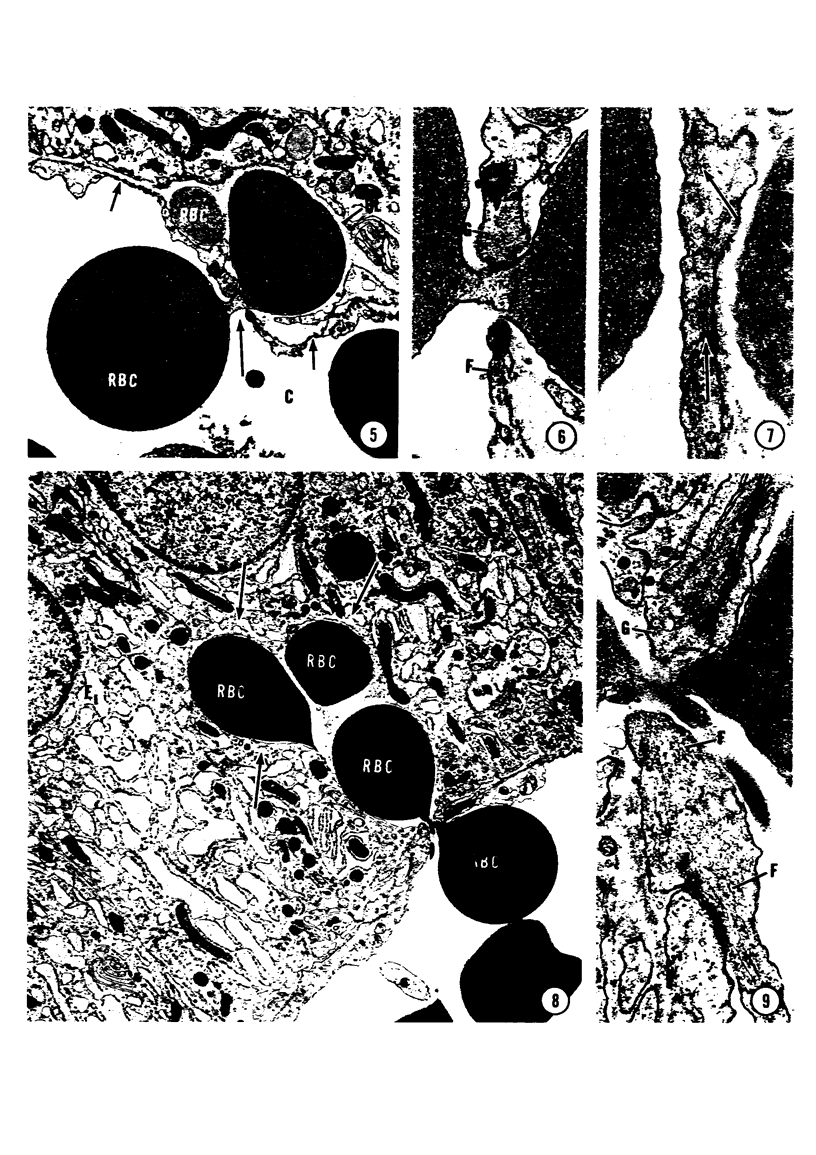
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bluemink J. G. Cortical wound healing in the amphibian egg: an electron microscopical study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Oct;41(1):95–114. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohman S. O., Maunsbach A. B. Effects on tissue fine structure of variations in colloid osmotic pressure of glutaraldehyde fixatives. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Jan;30(1):195–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald K. J. An electron-microscope study of defibrination during carbon clearance in rabbits stimulated by a tubercle bacillary lipid. J Pathol. 1972 Dec;108(4):329–333. doi: 10.1002/path.1711080408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeon K. W., Jeon M. S. Cytoplasmic filaments and cellular wound healing in Amoeba proteus. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):243–249. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckenbill L. M. Dense material associated with wound closure in the axolotl egg (A. mexicanum). Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osaka A., Suzuki K., Oashi M. The spurting of erythrocytes through junctions of the vascular endothelium treated with snake venom. Microvasc Res. 1975 Sep;10(2):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(75)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Ultrastructure of membrane lesions in immune lysis, osmotic lysis and drug-induced lysis. Fed Proc. 1974 Oct;33(10):2116–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tice L. W., Wollman S. H., Carter R. C. Changes in tight junctions of thyroid epithelium with changes in thyroid activity. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):657–663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]